The July 1, 2022, beef cow inventory compiled by USDA NASS indicates the national beef replacement heifer inventory is below 5 million head. Unprecedented cow culling is occurring in the southwest due to the ongoing drought conditions. To put that in perspective, the United States has not seen numbers this low since 1972 and 1973 when the national beef replacement heifer inventory hovered around 7 million head. Even in 1965, beef cattle replacement heifer inventories were above 5 million head nationally.
The July 1, 2022, beef cow inventory compiled by USDA NASS indicates the national beef replacement heifer inventory is below 5 million head. Unprecedented cow culling is occurring in the southwest due to the ongoing drought conditions. To put that in perspective, the United States has not seen numbers this low since 1972 and 1973 when the national beef replacement heifer inventory hovered around 7 million head. Even in 1965, beef cattle replacement heifer inventories were above 5 million head nationally.
New Jersey reported 5,000 head of beef cattle replacements in 1973 and only 2,500 head in 2019. With all cattle and calve numbers in 2020 reported at 28,000 head down 2,000 head from 2019, it is probable that state raised beef heifer replacement numbers are below 5,000 head going into the fall of 2022.
What is more contrasting compared to 1973 is the difference in calf crops. In 1973, the national calf crop was estimated at 50 million head. Going into summer of 2022 the calf crop is estimated at 25 million head. With an estimated 5,000 of these 500 lb calves or less in weight coming from New Jersey and only half assumed to be heifers, these heifers have considerable value beyond the feedlot, if they have brood cow qualities. Maintaining those selected for replacement herd purposes requires considerable attention to body conditioning to grow a weaned heifer to be bred at 15 months to meet industry replacement standards.
To learn more about raising replacement heifers contact Melissa Bravo for a copy of ‘A Checklist For Calving Success. A first-time heifer is a long-term investment.’
What are replacement heifers worth? The USDA AMS Show-Me-Select Special – Carthage, MO Livestock, Poultry, & Grain May 2022 report is a good example of the criteria that brings $1450.00 to $3,100 bred replacement heifer sale prices. Remember, these heifers were born, weaned, and fed through 15 months of age on 2019 (conception), 2020 (birth year), 2021 (breeding year) feed prices.
- All met minimum standards for reproductive soundness, pelvic size, body condition and weight.
- All immunized including Brucellosis calf-hood vaccination and tested negative for PI BVD.
- Heifers bred to bulls meeting strict calving ease or birth weight EPD’s.
- Many were synchronized and artificially bred.
- Projected calving dates were given.
- All heifers pregnancy checked within 30 days of sale.
- Sale animals screened for blemishes, muscle, frame and body condition score, and disposition.
- Heifers sorted and sold according to calving dates and similar body types.
- The average price per head was $1913.00. The highest selling lot brought $3100.00 per head.
- The A.I. bred heifers brought $141.00 more than natural bred heifers.
- About 40% of the heifers were black, 30% black, white-face, and 30% red.
Salem County Producers: If you would like to host a calf crop evaluation pasture walk for replacement heifer qualities, contact Melissa Bravo at the Salem County Extension Office.
 But the following week of low humidity was less than conducive for disease proliferation until the 22nd through the 25th when humidity levels briefly rose and remained in the high 80’s and 90’s for three days, before dropping nicely to the mid 60’s the last two days of June. However, wind speeds of 15 to 25 mph from June 13th to June 19th wicked moisture out of corn and soybeans leaving the crops in a moisture deficit.
But the following week of low humidity was less than conducive for disease proliferation until the 22nd through the 25th when humidity levels briefly rose and remained in the high 80’s and 90’s for three days, before dropping nicely to the mid 60’s the last two days of June. However, wind speeds of 15 to 25 mph from June 13th to June 19th wicked moisture out of corn and soybeans leaving the crops in a moisture deficit.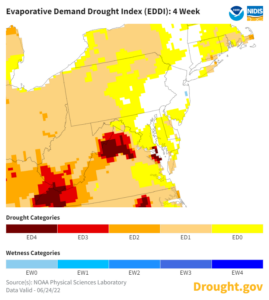 -Jersey. This tool created by the NOAA Physical Science Laboratory is an indicator of both rapidly evolving “flash” droughts and sustained droughts. “EDDI can offer early warning of agricultural drought, hydrologic drought, and fire-weather risk.”
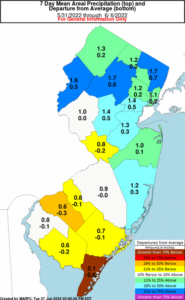
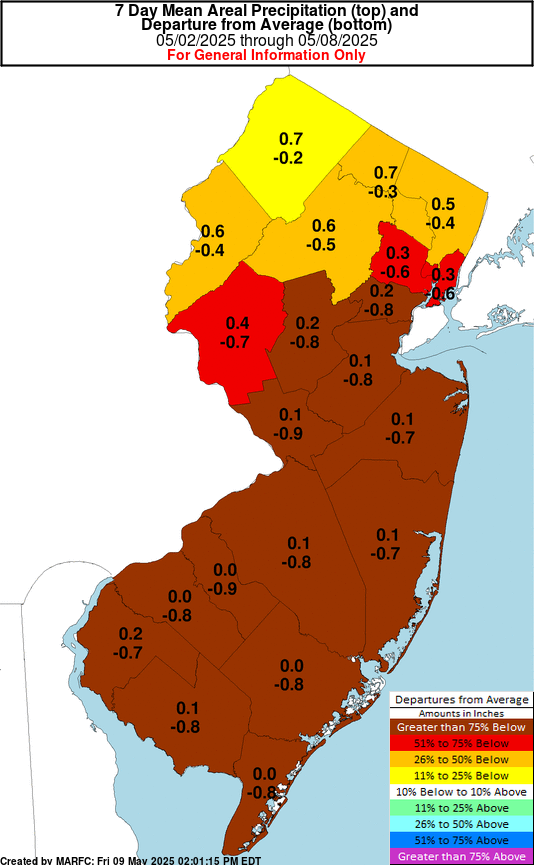
-Jersey. This tool created by the NOAA Physical Science Laboratory is an indicator of both rapidly evolving “flash” droughts and sustained droughts. “EDDI can offer early warning of agricultural drought, hydrologic drought, and fire-weather risk.”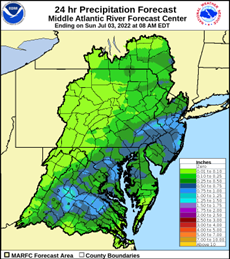 New Jersey anticipates a tenth of an inch to half inch of rainfall for most of Salem County through July 3 and much-needed swath probable for the northern counties where drought conditions the last seven days are 51% to 75% below normal.
New Jersey anticipates a tenth of an inch to half inch of rainfall for most of Salem County through July 3 and much-needed swath probable for the northern counties where drought conditions the last seven days are 51% to 75% below normal.