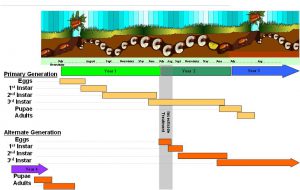
Figure 1. Carolina redroot infestation in cranberry bog
Carolina redroot (Lachnanthes caroliniana), a native plant of New Jersey Pine Barrens, has becoming an increasingly troublesome weed for cranberry production across the state (Figure 1). Carolina redroot is a perennial herbaceous weed species belonging to the Haemodoraceae family. It competes for nutritional resources during the cranberry growing season, and its rhizome serve as a feeding resource for wintering waterfowl that can cause severe uprooting damages of cranberry vines when bogs are flooded. Carolina redroot blooms after cranberry and its flower is very attractive to pollinators (Figure 2) at a time when insecticides may be applied to cranberry bogs. Additionally, the desiccated seed head of Carolina redroot can be picked up by harvesting equipment and broken in small pieces that will be difficult to eliminate during fruit processing.

Figure 2. Carolina redroot is very attractive for pollinators… at a time when insecticides may be applied!
Studies have been conducted at Rutgers since 2017 to screen various herbicides that can properly control or suppress Carolina redroot without injuring cranberry. In greenhouse screenings, Callisto® 4SC (mesotrione) has provided good control of Carolina redroot while maintaining excellent crop safety. Callisto is a systemic herbicide that will cause bleaching of weed leaves by indirectly inhibiting the biosynthesis of carotenoid that protect chlorophyll from photodegradation. Cranberry is highly tolerant because it is capable of rapidly metabolizing the mesotrione. Callisto will not kill Carolina redroot outright, but will weaken it and stunt it, preventing the formation of the floral stem (Figure 3). We are still evaluating if continued annual use of Callisto for two or three years will completely eliminate Carolina redroot.

Figure 3. Bleaching and stunting of Carolina redroot floral stem following Callisto applied at 4 fl oz/A
Spot application: ideally, Carolina redroot should be controlled before it starts colonizing large areas of a cranberry bogs. Therefore, scouting and mapping is a crucial and necessary step to detect early infestation that be treated with spot application of Callisto. We obtained in 2019 a 24(c) Special Local Need label for spot application of Callisto at rates that will help controlling perennial weeds such as Carolina redroot. We recommend mixing 3.2 teaspoons of Callisto per gallon of water and add crop oil concentrate (COC) at 1% v:v or 2.5 tablespoon per gallon of water. This rate will allow to spray up to 15 gallons of solution per acre while not exceeding the maximum labeled rate of 8 fl oz per acre and per application.
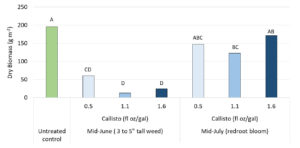
Figure 4. Reduction of Carolina redroot biomass with spot application of Callisto at three different rates and two different timings of application
At this rate and if Callisto is applied when Carolina redroot emerge above cranberry canopy in early to mid-June, we observed a reduction of Carolina redroot biomass by 70% at the end of the season. Higher rate will not significantly increase Carolina redroot suppression and later application in mid-July will not be effective (Figure 4). Spot applications will be sprayed with a backpack or hand-held sprayer that needs to be properly calibrated. Calibration of hand sprayers is determined by the walking speed of the applicator and the discharge rate from the nozzle along with the concentration of the material in the tank. Use great care in spot-treating. The difference between an 8-oz application and an 80-oz application is only seconds on the trigger. Spot treatments made to runoff will exceed the maximum application rate.

Figure 5. Annual sedge control with Callisto applied at 4 fl oz/A
Broadcast application: in bogs where Carolina redroot has colonized large areas, chemigation using irrigation sprinklers or boom application should be considered for broadcasting Callisto. Callisto can be applied at up to 8 fl oz per acre per application, but we observed bleaching and stunting of Carolina redroot floral stem with Callisto at a 4 fl oz/A rate applied with a regular boom. If chemigating, we recommend Callisto to be applied at 8 fl oz/A. Always use a COC adjuvant at 1% v:v. All application should be made when Carolina redoot leaves emerge from cranberry canopy but before the on-start of bloom because COC adjuvant may injure cranberry flowers and reduce pollination. A second application at 8 fl oz/A can eventually be applied after cranberry bloom to help suppressing Carolina redroot. Callisto will also help controlling sedges or rushes (Figure 5). Callisto applications cannot exceed 2 per acre per year and a maximum of 16 fl oz per acre per year.