Cornell Agricultural Workforce Development will be offering two Ag Supervisory Leadership courses for all agricultural operations starting in June for farms in the Northeastern Region including: Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Vermont. Registration is currently open and closes on June 25. There are separate registration fees for New York residents and out of state residents. See below.
The courses available are:
ASL101-SP: Transición a Supervisor (in Spanish)
Transition to Supervisor helps to develop leaders and focuses on skills to improve communication and manage conflict. Learn how to recognize our inherent biases and how to build better working relationships. Gain insight into your leadership style and learn how to effectively lead diverse and multicultural teams.
Course topics include:
How to make the mental transition to supervisor
How to develop effective working relationships
Essential communication skills
How to be the leader of a multicultural group
How to build better working relationships
Course begins: Friday, June 20, 2025
Live Zoom discussions: Thursdays, June 26 – July 31, 4:00–5:00 PM ET
Register for ASL101-SP Transición a Supervisor
ASL106: Ethics and Employment Regulations (in English)
In ASL106: Ethics and Employment Regulations, you’ll explore how to implement fair and ethical labor practices in agriculture and why they matter. You’ll learn to recognize and prevent sexual harassment, understand wage and hour laws, and apply Equal Employment Opportunity regulations to foster a respectful, inclusive workplace. The course also covers best practices for handling employee discipline and termination.
Course topics include:
Ethics and sustainability
Equal Employment Opportunity, laws and implications
Hiring regulations and practices
Safety issues in agriculture
Farm employee housing
Compensation regulations
Being an ethical supervisor
Course begins: Friday, June 20, 2025
Live Zoom discussions: Thursdays, June 26 – July 31, 3:00–4:00 PM ET
Register for ASL106: Ethics and Employment Regulations
Course costs:
$275 for NYS residents/$325 for out-of-state residents
Scholarship Opportunity for Dairy Producers:
Thanks to the Northeast Dairy Business Innovation Center (NEDBIC), eligible dairy producers can apply for a $100 scholarship to help cover registration fees. Scholarships are available to participants from qualifying states in the Northeast, including Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Vermont.
Questions? Email cu-agworkforce@cornell.edu
Follow us on Facebook: www.facebook.com/cornellagworkforcedevelopment
Fruit Crops Edition - Cranberry Section
Seasonal updates on diseases, insects, weeds impacting small fruit (blueberry, cranberry, and wine grape). Fruit Pest Alerts are also available via this category feed.
Subscription is through the general Fruit feed available via EMAIL and RSS.
Registration Open for 2 Agricultural Supervisor Training Courses: In English and Spanish
Blunt-nosed Leafhopper in Cranberries – May 2025
New Jersey cranberry growers are increasingly concerned about the rising populations of blunt-nosed leafhoppers (BNLH). This increase is likely linked to shifts in pest management strategies, including the adoption of reduced-risk insecticides and reduced use of broad-spectrum products, as well as the expansion of high-yielding cranberry varieties. BNLH is particularly troubling because it transmits a phytoplasma—a type of bacterium—that causes false blossom disease (Figure 1). Symptoms of this disease include stunted growth, deformed and sterile flowers that point upward, and a characteristic branching of upright shoots known as witches’ broom.
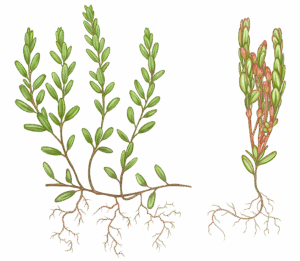
Figure 1. Healthy cranberry (left) and phytoplasma-infected cranberry (right). Drawing by Lindsay Lindhult.
Life Cycle
The blunt-nosed leafhopper (BNLH) has one generation per year (Figure 2). Its eggs overwinter embedded in cranberry stems and begin hatching in early May. Nymphs pass through five instars over the course of about 2 months. Adults emerge in early July, peak in mid to late July, and decline by the first week of August. These adults are characterized by their distinctive blunt heads and vary in color from light yellowish-gray to dark brown. Egg-laying occurs between July and August.
Damage
Nymphs and adults feed on cranberry plant juices using their piercing-sucking mouthparts. While this direct feeding causes little visible damage, BNLH is an important pest because it serves as a vector for the phytoplasma that causes false blossom disease.
Management
At this time of year eggs should be hatching and early-instar nymphs should be active (Figure 2).
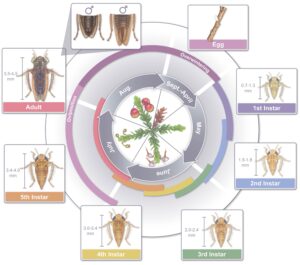
Figure 2. Life cycle of blunt-nosed leafhopper. Drawing by Lindsay Lindhult.
Here are some guidelines to consider when managing BNLH in cranberries:
Identify Infestation Sites: The key to effective BNLH control is identifying infestation sites. The most reliable method for monitoring this insect is by using a sweep net. Before bloom, use sweep nets to collect nymphs. Because nymphs are small and difficult to see, bag and freeze the samples to kill them, then count the nymphs using a microscope or magnifying lens.
Sweep net Monitoring: Perform sweep sets of 25 sweeps each. The recommended number of sweep sets is:
- 1 per 1–10 acres
- At least 10 sweep sets per 10–20 acres
- 1 sweep set per 2 acres for areas larger than 20 acres
Lack of Economic Thresholds: Establishing an economic threshold for BNLH is difficult, as the proportion of false blossom infected individuals within BNLH populations is unknown and may vary by cranberry variety and location. Notably, higher infection rates have been observed in newer varieties, even when BNLH populations are low.
Control Measures: Control measures should be based on BNLH population trends relative to previous years, the history of insecticide applications, and the cranberry variety grown. If BNLH populations are increasing compared to prior seasons and the beds have not been treated for BNLH in the past 2–3 years, treatment should be considered.
Treatment Options: If treatment is necessary, consider the following options to manage BNLH:
- Timing: The best time for insecticide treatment is before bloom to target young nymphs.
- Insecticide Options:
Organophosphates: Diazinon (diazinon), Orthene (acephate)
Carbamates: Sevin (carbaryl)
Pyrethroids: Fanfare or Brigade (bifenthrin), Danitol (fenpropathrin)
Neonicotinoids: Assail (acetamiprid), Actara (thiamethoxam). Note: Use neonicotinoids with caution before bloom due to their potential negative effects on pollinators. These systemic insecticides can accumulate in pollen and nectar, posing a risk to bees.
Sulfoximine: Closer (sulfoxaflor). Although effective in small plot trials at the P.E. Marucci Center, more data are needed to confirm efficacy on larger commercial scales.
- Be aware that, while not scientifically proven, there are claims that Orthene and Sevin may reduce pollinator activity by repelling bees.
- Rotate insecticides with different modes of action to prevent the development of resistance in BNLH populations.
Survey: Novel Weed Management Strategies for Perennial Crop Systems
Take a Quick Survey Regarding your Needs for Novel Weed Management in Perennial Crops!
Dr. Thierry E. Besançon, Associate Extension Weed Science Specialist, Rutgers University
Our interdisciplinary team of weed scientists and sociologists is conducting research under a Specialty Crop Research Initiative (SCRI) grant to understand perennial crop growers’ priorities regarding novel weed control technologies. This survey aims to identify drivers and barriers to implementing robotic weeding systems in your operations.
We seek to understand your:
- Perspectives on robotic technologies for weed management
- Specific needs and challenges in weed control
- Preferences and limitations when considering new technology adoption
This anonymous, voluntary survey takes approximately 10 minutes to complete. All information collected will be used solely to inform future research questions and outreach activities, and will not be published or distributed. This Friday, May 9th, will be the final day of the survey!
Your participation is invaluable to future developments in the industry regarding new technologies for weed management. We need more inputs from New Jersey perennial crops growers so that they have a say on the direction that weed science research will take in the future!
To contribute, scan the QR code or visit: https://iastate.qualtrics.com/jfe/form/SV_eqzMrFKtlcDjjgO

If you have questions, comments or concerns contact Dr. Thierry Besançon at thierry.besancon@rutgers.edu.
South Jersey Tree Fruit Twilight Meeting – I
When: May 7th (Wed) @ 6:00 pm
Where: Gloucester County Govt. Services Building, 1200 N. Delsea Drive, Clayton, NJ 08312
Pesticide credits – 4 each PP2, 1A, and 10
6:00 pm Light Fare (Pizza, Donuts, and Coffee)
6:15 pm Welcome and updates.
Hemant Gohil, Gloucester County Agricultural Agent, Rutgers NJAES
Peach Quality and Quality Standards
Daniel Ward, Extension Specialist, Pomology, Rutgers NJAES
Field Observations from the IPM Program
Janine Spies, Statewide Fruit IPM Agent, Rutgers NJAES.
Tree Fruit Disease Update
Kaitlin Quinn, Fruit IPM Program Associate, Rutgers NJAES.
Insect-Pest Management in the Orchard.
Anne Nielsen, Extension Specialist, Fruit Entomology, Rutgers NJAES
Managing the Nitrogen Cycle, N Sources, Timing, Rates, and Placement
Joseph Heckman, Extension Specialist, Soil Fertility, Rutgers NJAES
Farm Fresh Marketing: Harnessing Customer Photos, Posts, and Praise
Claudia Gill Arroyo, Cape May County Extension Agent, Rutgers NJAES
8:50 pm Pesticide recertification credits application.
Meeting Adjourn
Light fare will be provided. If you plan to attend, please call Joan Medany at jmedany@co.gloucester.nj.us or 856-224-8030. If you have any questions, please contact Hemant Gohil at 856-224-8029 before the meeting.
High Risk of Frost Damage in Peach Orchards
The below-freezing temperatures on Tuesday (4/8) and Wednesday (8/9) will likely invite frost damage to peach orchards in New Jersey. In several parts of New Jersey, peach flower buds are in the bud swell to the petal fall stage.

Figure 1. Peach bud development stages and corresponding critical temperatures. Adapted from MSU Fruit Extension. Photos by H. Gohil
Bloom progression in southern New Jersey indicates that except for very few delayed blooming varieties such as ‘Gloria’ and “Scarlet Rose’ most varieties will be in the bloom or post-bloom, next week. These are the most vulnerable stages to frost damage (Figure 1). Often, the cause is a few hours below the injury threshold temperature for the developing buds. Monitoring the growth stage and weather conditions will help in determining the actual threat of frost damage and whether to start a frost protection system.
Monitor the orchard temperature. Frost can occur when the ambient temperature dips below freezing (32°F). The hourly falling rate and the lowest forecasted temperature should also be monitored. Because the threshold temperature for each bud development stage is different, and a slight temperature difference can make a difference between frost damage and no damage, it is essential to know the precise temperature. In most cases, the orchard temperature will not be the same as forecasted or reported by the weather channels because the weather station could be farther away than the orchard location. Remember that the nighttime temperatures often dip below the predicted temperatures. It is crucial to have a thermometer in the orchard. Even the data from the nearby weather station could be unreliable. Also, frost alarm systems can give precise temperatures in the orchard and send warning messages to your mobile phone at a set temperature. Some systems can also report wet-bulb temperature, essential when using overhead irrigation for frost protection (Figure 2).
Monitor the bud development stage for each variety block, starting from bud swell. Critical temperatures have been researched and calculated for each bud development stage. For example, at 25°F, a peach orchard in full bloom can expect up to 90% crop loss, but at the first pink stage, it will suffer only marginal loss (Figure 1).
The critical temperature for damage at a particular bud stage may vary by 4-5°F depending on temperatures during the previous few days before the cold event.
Therefore, growers should use caution when using these published critical temperatures for active frost protection methods. Also, knowing the bud development stage for all varieties in the orchard will allow you to prioritize varieties or blocks that need frost protection.
Cloud coverage: Clear skies enhance radiative heat loss into the sky, which results in lower temperatures than when there is cloud cover, which can trap radiant energy from the ground.
Wind Speed: Wind increases the rate of heat loss from the ground and plant tissues. Low speed allows the formation of the inversion layer. Most frost protection methods will have reduced efficiency at wind speeds above 10 mph. Fire or heat application-based methods are less effective at wind speeds below five mph.
The frost protection method should only be employed after determining the actual risk of frost and considering the cost-benefit analysis. The articles below have information on passive and active frost protection methods.
- Active Frost Protection Methods in the Orchard. https://njaes.rutgers.edu/e363/
- Preparing Orchard against Frost – Low Tech Strategies. https://plant-pest-advisory.rutgers.edu/preparing-orchards-against-the-frost-low-tech-strategies-2/
NJ DEP issues Open Burn Permit from April 6 through April 12, 2025
To Agriculture and Agribusiness Representatives:
The New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection (DEP) is issuing this notice concerning open burning due to colder spring overnight temperatures presently forecasted for areas of New Jersey from April 6 (Sun), through April 12 (Sat), 2025, which could adversely affect fruit, vegetable, and floriculture crops in bloom or near bloom around the state. The DEP intends to exercise its authority and discretion under the Air Pollution Control Code, N.J.A.C. 7:27, et seq., and other applicable authorities to permit the following procedure for open burning or the use of smudge pots to assist farmers in protecting their crops in low temperatures. These cold events could adversely affect some of the fruit, vegetable, and floriculture crops.
Note: The NJDEP and New Jersey Forest Fire Service caution all farmers and agriculture businesses with respect to the use of open burning in high wind velocity conditions. Please take note that farmers are encouraged to utilize smudge pots is warming as necessary during higher wind conditions. Use of open burning when wind velocity is greater than 5mph is strictly prohibited, may contribute to wildfire risk, and can carry significant penalties.
For the Burn Permit Application form, please see: https://www.state.nj.us/dep/parksandforests/fire/docs/ag-permit.pdf
The DEP intends to exercise its authority and discretion under the Air Pollution Control Code, N.J.A.C. 7:27, et seq., and other applicable authorities to permit the following procedure for open burning or the use of smudge pots to assist farmers in protecting their crops in low temperatures. Procedures for Open Burning and the Use of Smudge Pots Pertaining to New Jersey Fruit, Vegetables, and Floriculture
- Facilities that believe they will conduct open burning or use smudge pots must provide notice to the DEP 24-hour Communications Center at 1-877- WARN DEP (1-877-927-6337) prior to the use of either technique. • Facilities should notify DEP if they believe they may need to use either technique. • Where DEP cannot be notified in advance, a facility must notify DEP the following morning no later than 9:00 a.m. • The following information must be provided to DEP upon each notification:
- Name of the individual deciding to conduct the open burning or use of smudge pots.
- Name of the farm or facility
- Actual street address of the facility on which either technique will be used.
- Contact person and telephone number at the facility.
- Predicted temperature (in F) at facility anticipated when the technique will be used.
- Predicted wind speed at facility anticipated when the technique will be used.
- Predicted hours of open burning or use of smudge pots
- Predicted material to be used for open burning or use of smudge pots.
- Upon completion of the open burning or the use of smudge pots, the facility must provide the following information within 2 business days to the DEP 24-hour Communication Center at 1877-WARN DEP (1-877-927-6337):
- The DEP Communications Center incident number
- Ambient orchard(s) temperature (in F) at the time the technique was used.
- Actual wind speed at the orchard(s) location at the time the technique was used.
- A statement that all restrictions in the open burning or use of smudge pots were followed. The restrictions are noted below.
RESTRICTIONS
- NO OPEN BURNING WILL BE PERMITTED UNLESS: 1. The temperature within the orchard area is at or below the critical temperature for the bud stage. The attached report lists the critical temperatures for New Jersey crops. -AND 2. The wind velocity is less than 5 miles per hour.
- Authorized open burning material may consist only of either the following materials: clean scrap lumber (untreated), felled trees, prunings, hedgerows or firewood.
- ABSOLUTELY NO refuse, trade waste, tires, garbage, or other solid waste may be added to the authorized open burning material. Introduction of any unauthorized material into an authorized open burn is a violation of environmental laws and may carry significant penalties.
- Smudge pots are only permitted when the temperature within the orchard area is at or below the critical temperature for the bud stage (wind velocity restriction does not apply).
- Smudge pots must be fueled only with either kerosene or No. 2 fuel oil.
- Failure to abide by these provisions and restrictions may result in enforcement action.

