Observation Overview: The IPM observations for 2024 come from the North and South Jersey Tree Fruit IPM Programs. There are 29 farms that participate in the North Jersey program and 13 farms in the South Jersey Program. The program includes approximately 600 acres of apples and 1,650 acres of peaches. Each farm has traps for the pests included in the trap data and are scouted once a week. The data for the charts below comes from the NEWA model, using Snyder Farm in Pittstown as the weather station. The trap data comes from each of the farms in the program and excludes farms using mating disruption. This is because the mating disruption proved to be very effective this year and I had no or very low trap catches in orchards utilizing this method of control.
2024 Weather: Using the weather data from our Snyder research farm in Pittstown, New Jersey (Hunterdon County), the weather (highs, lows and precipitation), was average for the 2024 growing season. There were no notable statewide frost events in the spring however, in our most northern counties we experienced temperatures of 27°F on 4/8/2024 (during tight cluster) and again on 4/22/2024 (during bloom) which affected some of the blossoms but overall, did not affect crop load. However, the high temperatures were sustained above 80 °F for much of June through August. Precipitation was above the 20-year normal until May and then dropped to about half of normal from June-July, then seemingly increased in August but that was largely due to a very large squall that occurred at the Pittstown research station at the beginning of August. There was a hailstorm that occurred in Sussex and Warren counties on 7/16 which resulted in significant crop loss for some growers.
| March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | |
| Hunterdon, NJ: 30 year normal precipitation | 4.05 | 3.92 | 4.18 | 4.55 | 5.04 | 4.61 | 4.53 | 4.36 |
| Hunterdon NJ: 2024 precipitation | 6.89 | 4.97 | 4.16 | 2.21 | 3.28 | 6.83 | .99 | .02 |

Datasources:
| https://climate.rutgers.edu/stateclim_v1/nclimdiv/# |
| https://www.njweather.org/data/daily |
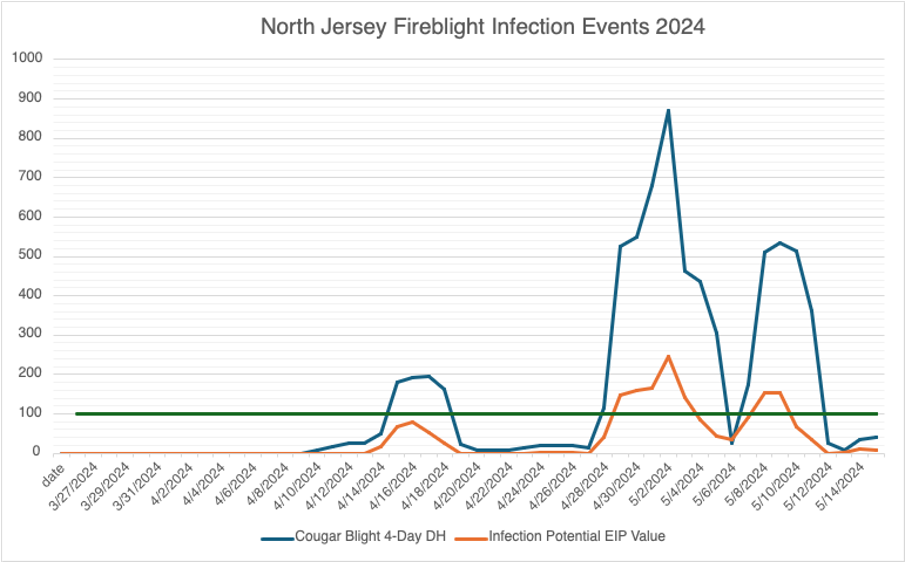
Fireblight: Fireblight presented an issue during the blossom blight phase for growers in both North and South Jersey. As you can see from the chart below, which pulls data from the NEWA fireblight model using the weather station in Pittstown, New Jersey, there were at least two infection periods during bloom where the EIP value was over 100. One of these periods persisted over the course of 5 days which required two applications of an antibiotic, 3 days apart from each other for optimal control.
Apple Scab: Compared to last year, we experienced more scab infection periods during the primary scab phase. Most of these infection periods spanned over a couple days with the longest period lasting 5 days. Most growers were able to avoid primary scab by applying effective fungicides prior to NEWA predicted infection periods. There were a few orchards with heavy scab pressure that experienced major scab outbreaks with over 20% infected fruit found in post-harvest assessments. If growers experienced heavy scab pressure this year, it is recommended to apply urea and mow the leaves once they have fallen from trees to reduce the inoculum moving into the next season.

Rots: Bitter Rot remains the most challenging to control throughout all New Jersey orchards. Incidence of this disease occurred in almost all farms in our Tree Fruit IPM Program and appeared most devastating in the Honeycrisp, Empire, Ambrosia and Evercrisp varieties. It may be beneficial to remove infected apples from the trees at the end of this season to reduce inoculum moving into the next season. Some of the most effective fungicides to include in cover sprays are Captan, Aprovia, Omega, Merivon, Luna Sensation and Topsin. These all work best when applied before a wetting event. In South Jersey, White Rot was also prevalent this season, we did not experience this in our North Jersey counties.
Cedar Apple Rust and Quince Rust: In Southern New Jersey these diseases, particularly Quince Rust, are becoming more prevalent, especially in Asian Pear. In North Jersey, we also saw a higher incidence of these diseases compared to last season. It is important to begin applying effective materials from pink through first cover.
Nectria Canker: This disease has not presented a major issue in New Jersey in previous years and when it has shown up, it has typically been on varieties that are known to be susceptible. This year one grower experienced this disease on the MAIA variety, Ludacrisp. Almost every tree in the row was infected with multiple cankers per tree.
Bacterial Spot: In South Jersey control of this disease was very good. In North Jersey there was more incidence of this disease than last year with 4 farms having minor outbreaks. Growers should begin including effective materials for this disease as soon as green leaf tissue is present. For resistance management growers should rotate between copper and oxytetracycline (Fireline or Mycoshield). It is important to remember that combining copper and captan will can cause phytotoxicity to the leaves which may be exacerbated in slow drying conditions.
Peach Scab: Control of this disease remains very good in commercial orchards across both North and South Jersey.
Brown Rot: This disease did not present a major issue in North or South Jersey this season. In North Jersey, most growers had less than 2% crop loss caused by brown rot.
Codling Moth: In South Jersey, a biofix was set for this pest on 4/22 which is 3 days later than last year. A biofix was set for this pest on 5/1 for five North Jersey counties (Middlesex, Mercer, Hunterdon, Warren, and Sussex counties) and on 5/6 for one North Jersey county (Morris County) which is 3-4 days earlier than last year. Across the state, trap captures were lower than average, but this pest was more damaging than last year. This season, all 3 generations of this pest caused damage in orchards which are known to have high pest pressure. Mating disruption remained effective in most blocks, but small amounts of damage were found at one farm which had irregularly shaped blocks. In Southern New Jersey, over the last 3 seasons there has been incidence of another internal feeder which is believed to be lesser apple worm. In North Jersey damage of this pest was noted in one orchard on 10/15.
Brown Marmorated Stinkbug: In both North and South Jersey, trap counts for this pest were higher than the past few seasons. There was also a higher incidence of damage found in post-harvest assessments of Pome fruit. In North Jersey, there was also a higher incidence of damage to Stone fruit compared to last season.
Ambrosia Beetle: In North Jersey, we began a monitoring program for this pest this year utilizing clear sticky traps baited with Trece’s ethanol lures and wood dowel traps. We had significant trap captures, and this pest attacked the wood dowel traps at all 29 farms in our program. This pest only attacked apples at 4 of the 29 farms, 3 of which were previously known infestation sites. The one farm which had not previously experienced crop loss to this pest experienced 43.3% loss of the trees they had topworked at the beginning of the season. In South Jersey, tree loss continued at normal levels in known infestation sites. The best management practice for control of this pest is reducing tree stress through cultural techniques.
Scale: In South Jersey, incidence of San Jose Scale infestation increased over the last season. Early season controls suppressed crawler populations, however, damage in August was notable in many orchards. In North Jersey, this pest did not cause notable damage except in known problem areas. White Peach Scale was observed at slightly increased levels in orchards across the state. The late generation of this pest continues to cause damage to later ripening peach varieties in North Jersey. Dormant oil sprays at the beginning of next season will help manage this pest. Ensuring proper coverage of these sprays is essential for control.
Oriental Fruit Moth: A biofix for this pest was set on 4/10 in South Jersey and 4/12 in North Jersey. This pest did not present a major issue to growers across the state this season. Only a few growers had a small incidence of damage to their peaches found in post-harvest assessments.
Plum Curculio: Plum curculio damage was above average in stone fruit. This pest also caused significant damage to pome fruit due to the long bloom period which made control difficult.


