With the increased temperatures we saw this month, being aware of potential heat stress signs and how to prevent them from happening is very important with livestock production. Luckily, in the North East, our summers are not brutally hot compared to our neighbors in the South and in the Mid-West. It is worth noting that our area can have high humidity that can cause problems for livestock. Depending on the species, and the stage of production, points on the heat index will vary for causes of heat stress. Identify animals that may be more susceptible to heat stress, i.e. overweight animals, younger and older ones, as well as animals that are pregnant. Establishing a plan of action prior to extreme weather days will also help out.
1) Make sure there is plenty of clean water for drinking. If it is possible, add another trough so there is more access to water. This will allow all animals in your herd to have the ability to obtain water.
2) Do not work your animals on hot days.
3) Provide shade if possible and have access to air movement (wind and breezes).
4) Cool the ground- pigs love to wallow in the mud to keep cool, or you could wet some straw in a shady spot in the pasture for a herd of cattle.
5) Control flies as much as possible because this will add more stress to the animals.
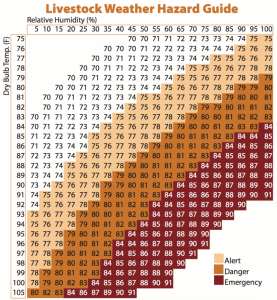
6) Pay attention to the weather forecast and check the livestock weather hazard guide.
7) Know when to intervene (the heat index is 75 or greater for a 72-hour period or the daytime heat index reaches 84 or higher for two consecutive days).
Things are going to happen that are uncontrollable (the weather), but if you plan ahead, you can minimize the effects of heat stress to your livestock.
It’s Hot Out There and Shade is Key to Cattle Performance | Panhandle Agriculture (ufl.edu)


