Sweet Corn
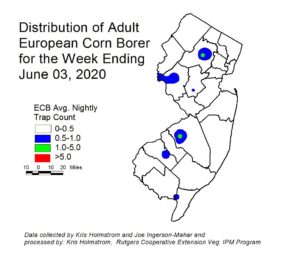 Increasing numbers of European corn borer (ECB) moths have been captured over the past week, although overall numbers remain low. At this time, activity is highest in central Morris County and western Burlington County (see ECB map at left). The number of traps registering moderate catches is fairly low, and catches are widely dispersed. Overall, this year’s population is late, and whether numbers increase much or not remains an open question. Early corn is now in whorl or pre-tassel stage and able to support ECB larvae. It is time to begin scouting corn in these advanced growth stages.
Increasing numbers of European corn borer (ECB) moths have been captured over the past week, although overall numbers remain low. At this time, activity is highest in central Morris County and western Burlington County (see ECB map at left). The number of traps registering moderate catches is fairly low, and catches are widely dispersed. Overall, this year’s population is late, and whether numbers increase much or not remains an open question. Early corn is now in whorl or pre-tassel stage and able to support ECB larvae. It is time to begin scouting corn in these advanced growth stages.
 Look for the characteristic “shot-hole” type of feeding (photo below at right) and consider treating when infested plants exceed 12% in a 50 plant sample. As plantings proceed to the pre-tassel stage, ECB larvae may be found in emerging tassels (see photo at left). It is a good idea to treat individual plantings as they move into the full tassel/first silk stage one time. This eliminates any ECB larvae that have emerged with the tassels as they begin to move down the stalk to re-enter near developing ears.
Look for the characteristic “shot-hole” type of feeding (photo below at right) and consider treating when infested plants exceed 12% in a 50 plant sample. As plantings proceed to the pre-tassel stage, ECB larvae may be found in emerging tassels (see photo at left). It is a good idea to treat individual plantings as they move into the full tassel/first silk stage one time. This eliminates any ECB larvae that have emerged with the tassels as they begin to move down the stalk to re-enter near developing ears.
Useful insecticides for this particular application include synthetic  pyrethroids (IRAC Grp 3), spinosyns (including OMRI approved Entrust) IRAC Grp 5), and diamides such as Coragen (IRAC Grp 28) or materials such as Besiege which include the active ingredient in Coragen. Synthetic pyrethroids alone should NOT be used for corn earworm (CEW) protection on silking corn. Control with these materials is very inconsistent.
pyrethroids (IRAC Grp 3), spinosyns (including OMRI approved Entrust) IRAC Grp 5), and diamides such as Coragen (IRAC Grp 28) or materials such as Besiege which include the active ingredient in Coragen. Synthetic pyrethroids alone should NOT be used for corn earworm (CEW) protection on silking corn. Control with these materials is very inconsistent.
The highest nightly trap catches of ECB for the week ending 6/03/20 are as follows:
| Denville 2 | Clinton 1 | Milford 1 |
| Asbury 1 | Downer 1 | Oldwick 1 |
| Bellemeade 1 | Eldora 1 | South Branch 1 |
| Califon 1 | Medford 1 | Springdale 1 |
Widely scattered, and low catches of corn earworm (CEW) occurred this past week. While there was an increase in activity over the previous week, this pest does not pose a threat to sweet corn that has not yet reached the silk stage.
The highest nightly trap catches of CEW in black light traps for the week ending 6/03/20 are as follows:
| Chester 1 | Eldora 1 | Milltown 1 | Oldwick 1 |
| Crosswicks 1 | Elm 1 | Morristown 1 |





