Greetings from the Veg IPM team!
Sweet Corn
With the hot weather, we’re starting to see sweet corn really coming along. Some plantings of sweet corn are silking (especially in the south), so it’s time to think about corn earworm management. Moth captures in the Southern part of the state (see map) are indicating that 4 and even 3 day intervals are necessary in some areas. Rotation is important for avoiding resistance, and there are four IRAC groups that are registered in silking sweet corn: 1 (carbamates), 3 (pyrethroids), 5 (spinosyns), and 28 (diamides). Corn earworm is at least partly resistant to several pyrethroids, so a spray program should not rely solely on pyrethroids, although they can be useful in tank-mixes or as pre-mixed products, such as Besiege or Elevest (Group 28 + Group 3). For detailed information about resistance and potential spray programs, the University of Delaware has an excellent resource on corn earworm management.
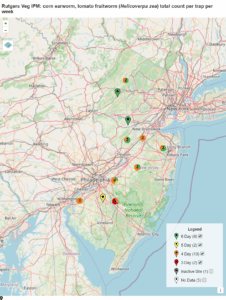
Spray intervals based on nightly pheromone moth captures for the southern part of New Jersey. Note that not all locations in the IPM program are currently trapping. This map is based on the following thresholds: 0 moths = 6-7 day schedule, 1 moth = 5 day spray schedule, 2-20 moths = 4 day spray schedule, 20+ moths = 3 day spray schedule.
Cole Crops

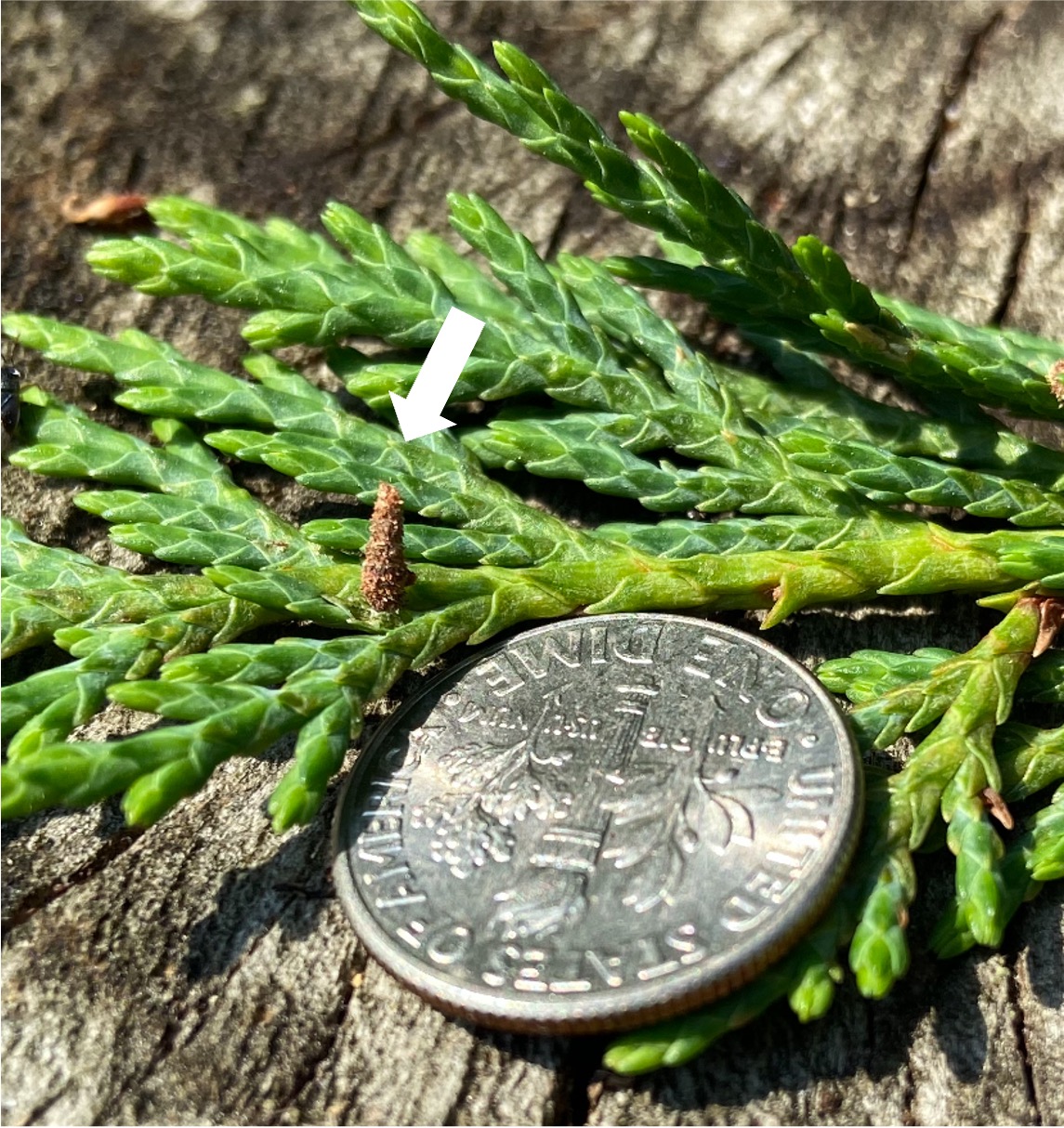
Flea beetle surrounded by feeding damage. Picture by Maria Cramer.
Flea beetle activity seems to be slowing down some, but they are still active in various cole crops. This year, they have been especially prevalent in lacinato kale, Napa cabbage and bok choy. Young plants are especially vulnerable to attack from flea beetles. The treatment threshold for flea beetles in heading cole crops is 50% infestation.

Left: Diamondback moth caterpillar, showing characteristic tapering at each end. Right: Imported cabbageworm caterpillar showing characteristic fuzziness. Pictures by Maria Cramer.
We’re still seeing caterpillar activity in cabbage and other cole crops. Treatment thresholds vary between crops and growth stage, but for heading cole crops between early vegetative and cupping, the treatment threshold is 30%. At this stage, sprayable Bt products (IRAC 11A) such as Dipel, Xentari, or Javelin can be effective on young imported cabbage worm caterpillars. Other materials approved for caterpillar control include Entrust/Radiant (IRAC 5), Proclaim (IRAC 6), Torac (IRAC 21A), and Exirel (IRAC 28). Diamondback moth has resistance to many insecticide groups, and pyrethroids (IRAC 3A) are not effective for their management. For Bt products and contact insecticides, coverage on the undersides the leaves is essential.
Tomatoes
In high tunnels and field plantings of tomatoes, we’re seeing limited aphid, thrips, and spider mite activity. If dealing with primarily aphids, products such as Beleaf (IRAC 29) are recommended, especially if plants have reached the flowering stage. We have seen aphid populations decline over the last couple of weeks without spray, probably due to natural enemies predation. For thrips, Entrust, Radiant (IRAC 5) and Torac (IRAC 21A) can be used. For spider mites, Nealta (IRAC 25) is an effective material that is more friendly to beneficial insects, but Portal (IRAC 21A) and other materials can be used to manage populations. We’ve seen very few Colorado potato beetles (CPB) in tomatoes, so while no controls are needed yet, we’ll keep an eye out for increasing populations.
Eggplants
In eggplants we have seen some damaging populations of CPB. For plants under 6 inches, 2 small/1 large larvae per plant is the threshold, while for plants taller than 6 inches, the threshold is 4 small/2 large larvae per plant. Adults are hard to kill, so sprays should target the larvae, with younger/smaller larvae being more vulnerable than older larvae. CPB has resistance to many classes of insecticides and is notorious for quickly developing resistance to new ones, so plan to rotate IRAC groups if you’ve already treated or need to treat more than once. If you haven’t used a neonic (IRAC 4) at planting or in the drip, you can use a foliar neonic like Assail or a spinosyn like Entrust or Radiant (IRAC 5). Avoid IRAC 5 groups if you’ve already used a neonic, because there is risk of cross resistance. Diamide products like Coragen and Exirel (IRAC 28), Rimon (IRAC 15), and Torac (IRAC 21A) should all give good control.

Left: Colorado potato beetle larvae and feeding damage on an eggplant leaf. Right: Adult Colorado potato beetle. Photos by Maria Cramer.
Diseases
We’ve detected bacterial diseases of tomatoes and peppers on a few farms in the central and northern parts of the state (see photos below). Copper may help mitigate symptoms, but some strains have developed resistance due to continued copper use. Other products that may help include Actigard and Quintec. Otherwise, properly managing nutrients and growing conditions for the plant will be crucial for reducing the severity of this disease.

Bacterial leaf spot on tomato. Photo by Amanda Quadrel

Bacterial leaf spot on pepper. Photo by Amanda Quadrel.
Please consult the Mid-Atlantic Commercial Vegetable Production Guide for a more comprehensive list of materials that are labeled for specific crops and pests. As always, be sure to follow label rates and application instructions.
Authors: Amanda Quadrel (Northern NJ Veg IPM coordinator) and Maria Cramer (Southern NJ Veg IPM coordinator)