Fruit Crops Edition
Seasonal updates on diseases, insects, weeds impacting tree fruit and small fruit (blueberry, cranberry, and wine grape). Fruit Pest Alerts are also available via this category feed.
Subscriptions are available via EMAIL and RSS.
Private Applicators: NJDEP August Mailing of 2023 Invoices & Recertification Credit Status
Managing Cranberry Toad Bugs
Populations of the cranberry toad bug, Phylloscelis rubra (Figure 1), have increased in the last week in some beds. In a recent study, we showed that even relatively low densities of this insect can cause significant injury to cranberries (Rodriguez-Saona et al. 2020. Characterizing the Feeding Injury Caused by Phylloscelis rubra (Hemiptera: Dictyopharidae) to Cranberries, Journal of Insect Science, 20 (6), 37, https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/ieaa143). Thus, monitoring for this insect from the end of July through mid-August is critical.

Figure 1. Cranberry toad bug
Life cycle. Cranberry toad bugs feed only on cranberries. This insect has a single generation per year (Figure 2). It overwinters as eggs. The nymphs appear by the end of June through early September, and the adults from end of July through October (harvest). Eggs are laid from end of August through October.
Damage. Feeding damage can be noticed in two stages. 1st-stage feeding damage on vines causes closing in (towards the branch) of the leaves on the new growth. 2nd-stage feeding causes changed in color (reddish to brown) of new growth. The damage can be seen from July until harvest. This damage will cause dying of the branch and the berries to shrivel up (Figure 3). Heavy infestation will result in dwarfed berries.
Management. To determine infestation, lightly sweep problematic beds (bugs should be easy to catch in sweep nets as they are very active). Currently there is no threshold established for this pest. Thus, insecticide applications should be based on the relative number of bugs per sweep compared with other sites and previous history of infestation. If needed, growers can use the following control options: Sevin 4F (broad-spectrum carbamate), Diazinon, Imidan 70W (broad-spectrum organophosphates), and Actara or Assail 30SG (neonicotinoid insecticides, effective against piercing-sucking insects). If infestation is high, treatments should be applied now (mid-August) for best control.

Figure 3. Cranberry toad bug injury
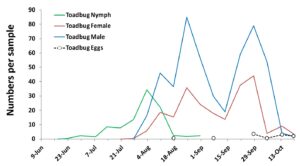
Figure 2. Cranberry toad bug phenology
Tree Fruit IPM Report for August 8, 2022
Peach:
Oriental Fruit Moth: A biofix point for OFM was set on 4/11 in southern counties, and on 4/14 in northern counties. The third generation timings are are over in all regions. Additional treatments should be made if trap captures are over 6 moths per trap.
| Insecticide Type | |||
| County/Region | Degree Days by 7/28 base 45 | Conventional
2000-2100 2350-2450 |
Diamide
2025–2150 2375-2450 |
| Gloucester – Southern | 2437 | 1st –past
2nd –7/26-7/28 |
1st –past
2nd –7/26-7/28 |
| Middlesex – Northern | 2394 | 1st –past
2nd –past |
1st –past
2nd –past |
Scale Insects: Second generation crawler emergence has started for both San Jose and White Peach scale and will last well into August. White Peach scale has a third generation in September and San Jose scale may have a third generation in October. Esteem and Centaur are both good scale materials. Esteem and Centaur should be applied at the start of crawler emergence. These materials should only need one application. Other options include: Assail, Belay, Actara (Group 4A): Closer (Group 4C); Sivanto (Group 4D) and the bioinsecticide Venerate. These products may need more than one application, typically 2 applications bracketing peak crawler emergence which should occur between the first and third week of August. Only Venerate has a 0 day PHI, making it useful for blocks near or at harvest. Diazinon is also still labelled for peach and apple: for San Jose Scale, it is labeled at a rate of 1#/100 with a 21 day PHI for both peach and apple; for White Peach Scale it is labeled at a rate of 1.5-2#/100 for post-harvest application only. The label requires 14 days between applications. These products may need more than one application, typically 2 applications bracketing peak crawler emergence which should occur between the first and third week of August.
Apples and Pears:
Diseases: Summer scab, rots and sooty blotch and fly speck are the main targets at this stage. Where scab is present rely primarily on protectant fungicides. Last year Captan plus a phosphorous acid like Prophyt was observed to slow scab development as well as provide good summer disease control.
Brown Marmorated Stink Bugs: Brown Marmorated Stink bugs are present at low to moderate levels in orchards statewide. See the NJ Tree Fruit Production guide for effective materials.
Codling Moth (CM): Timings for the second generation are updated below. A biofix was set for CM on April 25th in southern counties, and May 6 in Northern counties (Middlesex County). Second generation treatments according to the degree day model are now over. Additional treatments should be made if trap captures are over 5 moths/trap. Some orchards have had continuing trap captures above threshold.
| Codling Moth Degree Day Timing | ||||||
| Application and Insecticide Type | ||||||
| County Area | Biofix | Intrepid; Diamides – Altacor, Voliam mixes:
1150-1200 + 1450-1500 DD
|
Cyd-X, Madex
1250 DD + every 7-9 days during brood hatch (later if first spray is an IGR) |
Standard Insecticides – Delegate, Avaunt, OP’s, carbamates, pyrethroids
1250 DD + 1550-1600 DD
|
||
| DD | 1150-1200 | 1450-1500 | 1250 | 1250 | 1550-1600 | |
| Southern | April 25 | Past | Past | Past | Past | Past |
| Northern | May 6 | Past | past | Past | Past | Past |
Scale Insects: For San Jose scale see the peach section above.
Grape
Bunch Rots: Grapes are beginning veraison in southern counties. Disease management continues to focus on downy and powdery mildew and and now also turns to bunch rot management. Refer to the NJ Commercial Grape Production Guide as well as the linked presentation from Dr. Nita in Virginia. Additional information can be found in this linked presentation from Dr. Bryan Hed at Penn Sate.
Grape Berry Moth: The timing for the third generation is past. In some hot summers a fourth generation may occur, however no further treatments should be needed, especially where insecticides are being applied for SLF.
Spotted Lantern Fly: Spotted lantern fly adults are now appearing in vineyards. At this stage it is border treatments with effective materials should be adequate since most adults will be found on vineyard edges and populations will be low. As we move into September adult migration will increase and at that point growers should apply materials with long residual efficacy (refer to the table from Penn Sate below.) More information on biology and control can be found from Penn State.
Tree Fruit Trap Counts – Southern Counties
| Weekending | STLM | TABM-A | CM | BMSB | OFM-A | DWB | OFM-P | TABM-P | LPTB | PTB |
| 4/9/2022 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| 4/16/2022 | 0 | 2 | 3 | |||||||
| 4/23/2022 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 28 | 5 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 4/30/2022 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 31 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 5/7/2022 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 50 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 5/14/2022 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 19 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 5/21/2022 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 20 | 2 | 7 | 3 | |||
| 5/28/2022 | 0 | 19 | 3 | 13 | 0 | 11 | 36 | |||
| 6/4/2022 | 0 | 10 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 13 | 49 | 0 | ||
| 6/11/2022 | 0 | 9 | 2 | 6 | 36 | 0 | 8 | 47 | 3 | |
| 6/18/2022 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 62 | 0 | 3 | 13 | 1 | |
| 6/25/2022 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 3 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 4 |
| 7/2/2022 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 3 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 4 |
| 7/9/2022 | 10 | 4 | 2 | 15 | 6 | 31 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 3 |
| 7/16/2022 | 2 | 0 | 7 | 1 | 5 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 7 |
| 7/23/2022 | 15 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 2 |
| 7/31/2022 | 16 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 12 | 1 | 1 | 11 | 3 |
| 8/6/2022 | 10 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 3 | 31 | 2 | 0 | 21 | 4 |
Tree Fruit Trap Counts – Northern Counties
| Weekending | STLM | TABM-A | CM | BMSB | OFM-A | DWB | OFM-P | TABM-P | LPTB | PTB |
| 4/9/2022 | ||||||||||
| 4/16/2022 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |||||||
| 4/23/2022 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | ||||||
| 4/30/2022 | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | 0 | ||||||
| 5/7/2022 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | ||||||
| 5/14/2022 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 5/21/2022 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 27 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 0 | |
| 5/28/2022 | 34 | 19 | 3 | 6 | 13 | 1 | 23 | 15 | 0 | |
| 6/4/2022 | 17 | 21 | 4 | 4 | 11 | 1 | 27 | 17 | 0 | |
| 6/11/2022 | 22 | 25 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 30 | 9 | 0 | |
| 6/18/2022 | 66 | 20 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 27 | 7 | 0 |
| 6/25/2022 | 58 | 21 | 1 | 8 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 22 | 4 | 0 |
| 7/2/2022 | 55 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 14 | 15 | 2 | 9 | 4 | 1 |
| 7/9/2022 | 60 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 20 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 1 |
| 7/16/2022 | 64 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 19 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 3 |
| 7/23/2022 | 97 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 18 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 7/31/2022 | 46 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 13 | 22 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 8/6/2022 | 26 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 20 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 3 |
| Pest Event or Growth Stage | Approximate Date | 2022 Observed Date |
| Bud Swell (Redhaven) | March 23 +/- 15 Days | March 20 |
| 1/4″ Green Tip Red Delicious | March 31 +/- 13 Days | March 21 |
| Pink Peach (Redhaven) | April 4 +/- 15 Days | March 31 |
| Tight Cluster Red Delicious | April 9 +/- 13 Days | March 31 |
| Full Bloom Peach (Redhaven) | April 9 +/- 14 Days | April 10 |
| Pink Apple (Red Delicious) | April 14 +/- 12 Days | April 14 |
| Full Bloom Apple (Red Delicious) | April 22 +/- 11 Days | April 21 |
| Petal Fall (Redhaven) | April 22 +/- 10 Days | April 14 |
| Petal Fall (Red Delicious) | April 27 +/- 13 Days | May 3 |
| Shuck Split (Redhaven) | April 30 +/- 11 Days | April 26 |
| Pit Hardening | June 15 +/- 9 Days | June 10 |
Non-Herbicide Nutsedge Management Resources for Specialty Crop Growers
Learn more about the weed nutsedge and appropriate management strategies based on the plants growth preferences and dislikes. These resources can be used to develop a short and long term management plan for nutsedge control. Visit the NJAES Weed Management YouTube playlist for a video presentation or download our nutsedge decision tool fact sheet. These resources are one of a five-part weed management series funded by USDA Specialty Crop Block Grant AM190100.
Tree Fruit IPM Report for July 28, 2022
Peach:
Oriental Fruit Moth: A biofix point for OFM was set on 4/11 in southern counties, and on 4/14 in northern counties. The third generation timings are updated below.
| Insecticide Type | |||
| County/Region | Degree Days by 7/28 base 45 | Conventional
2000-2100 2350-2450 |
Diamide
2025–2150 2375-2450 |
| Gloucester – Southern | 2437 | 1st –past
2nd –7/26-7/28 |
1st –past
2nd –7/26-7/28 |
| Middlesex – Northern | 2394 | 1st –past
2nd –7/27-7/30 |
1st –past
2nd –7/27-7/30 |
Japanese Beetles: Japanese beetles have emerged and have been observed in some orchards. Products containing imidacloprid (Admire Pro, Leverage, etc.) are effective and have a short preharvest interval. Danitol is also very effective. and See the Tree Fruit Production guide for more information.
Tarnished Plant Bugs; and Other Catfacing Insects: Catfacing insect activity is increasing with the arrival of hot weather and is present at moderate to high levels in some orchards.
Scale Insects: Second generation crawler emergence has started for both San Jose and White Peach scale and will last well into August. White Peach scale has a third generation in September and San Jose scale may have a third generation in October. Esteem and Centaur are both good scale materials. Esteem and Centaur should be applied at the start of crawler emergence. These materials should only need one application. Other options include: Assail, Belay, Actara (Group 4A): Closer (Group 4C); Sivanto (Group 4D) and the bioinsecticide Venerate. These products may need more than one application, typically 2 applications bracketing peak crawler emergence which should occur between the first and third week of August. Only Venerate has a 0 day PHI, making it useful for blocks near or at harvest. Diazinon is also still labelled for peach and apple: for San Jose Scale, it is labeled at a rate of 1#/100 with a 21 day PHI for both peach and apple; for White Peach Scale it is labeled at a rate of 1.5-2#/100 for post-harvest application only. The label requires 14 days between applications. These products may need more than one application, typically 2 applications bracketing peak crawler emergence which should occur between the first and third week of August.
Apples and Pears:
Diseases: Summer scab, rots and sooty blotch and fly speck are the main targets at this stage. Where scab is present rely primarily on protectant fungicides. Last year Captan plus a phosphorous acid like Prophyt was observed to slow scab development as well as provide good summer disease control. Bitter Rot symptoms are now appearing in susceptible varieties.
Brown Marmorated Stink Bugs: Brown Marmorated Stink bugs are present at low to moderate levels in orchards statewide. See the NJ Tree Fruit Production guide for effective materials.
Codling Moth (CM): Timings for the second generation are updated below. A biofix was set for CM on April 25th in southern counties, and May 6 in Northern counties (Middlesex County). Estimated timings for the second generation are updated below.
| Codling Moth Degree Day Timing | ||||||
| Application and Insecticide Type | ||||||
| County Area | Biofix | Intrepid; Diamides – Altacor, Voliam mixes:
1150-1200 + 1450-1500 DD
|
Cyd-X, Madex
1250 DD + every 7-9 days during brood hatch (later if first spray is an IGR) |
Standard Insecticides – Delegate, Avaunt, OP’s, carbamates, pyrethroids
1250 DD + 1550-1600 DD
|
||
| DD | 1150-1200 | 1450-1500 | 1250 | 1250 | 1550-1600 | |
| Southern | April 25 | Past | Past | Past | Past | Past |
| Northern | May 6 | Past | past | Past | Past | Past |
Scale Insects: For San Jose scale see the peach section above.
Grape
Bunch Rots: Grapes are beginning veraison in southern counties. Disease management continues to focus on downy and powdery mildew and and now also turns to bunch rot management. Refer to the NJ Commercial Grape Production Guide as well as the linked presentation from Dr. Nita in Virginia.
Grape Berry Moth: The next timing for Grape Berry Moth will be on or about 7/24 for Intrpeid or Diamides, or a few days later for other insecticides.
Japanese Beetles: Japanese beetle pressure is high compared to other years. Many insecticides are effective for JB. See the NJ Commercial Grape Production Guide for more information.
Tree Fruit Trap Counts – Southern Counties
| Weekending | STLM | TABM-A | CM | BMSB | OFM-A | DWB | OFM-P | TABM-P | LPTB | PTB |
| 4/9/2022 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| 4/16/2022 | 0 | 2 | 3 | |||||||
| 4/23/2022 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 28 | 5 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 4/30/2022 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 31 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 5/7/2022 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 50 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 5/14/2022 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 19 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 5/21/2022 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 20 | 2 | 7 | 3 | |||
| 5/28/2022 | 0 | 19 | 3 | 13 | 0 | 11 | 36 | |||
| 6/4/2022 | 0 | 10 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 13 | 49 | 0 | ||
| 6/11/2022 | 0 | 9 | 2 | 6 | 36 | 0 | 8 | 47 | 3 | |
| 6/18/2022 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 62 | 0 | 3 | 13 | 1 | |
| 6/25/2022 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 3 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 4 |
| 7/2/2022 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 3 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 4 |
| 7/9/2022 | 10 | 4 | 2 | 15 | 6 | 31 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 3 |
| 7/16/2022 | 2 | 0 | 7 | 1 | 5 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 7 |
| 7/23/2022 | 15 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 2 |
Tree Fruit Trap Counts – Northern Counties
| Weekending | STLM | TABM-A | CM | BMSB | OFM-A | DWB | OFM-P | TABM-P | LPTB | PTB |
| 4/9/2022 | ||||||||||
| 4/16/2022 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |||||||
| 4/23/2022 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | ||||||
| 4/30/2022 | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | 0 | ||||||
| 5/7/2022 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | ||||||
| 5/14/2022 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 5/21/2022 | 6 | 8 | 4 | 27 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 0 | |
| 5/28/2022 | 34 | 19 | 3 | 6 | 13 | 1 | 23 | 15 | 0 | |
| 6/4/2022 | 17 | 21 | 4 | 4 | 11 | 1 | 27 | 17 | 0 | |
| 6/11/2022 | 22 | 25 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 30 | 9 | 0 | |
| 6/18/2022 | 66 | 20 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 27 | 7 | 0 |
| 6/25/2022 | 58 | 21 | 1 | 8 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 22 | 4 | 0 |
| 7/2/2022 | 55 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 14 | 15 | 2 | 9 | 4 | 1 |
| 7/9/2022 | 60 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 20 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 1 |
| 7/16/2022 | 64 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 19 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 3 |
| 7/23/2022 | 97 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 18 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Pest Event or Growth Stage | Approximate Date | 2022 Observed Date |
| Bud Swell (Redhaven) | March 23 +/- 15 Days | March 20 |
| 1/4″ Green Tip Red Delicious | March 31 +/- 13 Days | March 21 |
| Pink Peach (Redhaven) | April 4 +/- 15 Days | March 31 |
| Tight Cluster Red Delicious | April 9 +/- 13 Days | March 31 |
| Full Bloom Peach (Redhaven) | April 9 +/- 14 Days | April 10 |
| Pink Apple (Red Delicious) | April 14 +/- 12 Days | April 14 |
| Full Bloom Apple (Red Delicious) | April 22 +/- 11 Days | April 21 |
| Petal Fall (Redhaven) | April 22 +/- 10 Days | April 14 |
| Petal Fall (Red Delicious) | April 27 +/- 13 Days | May 3 |
| Shuck Split (Redhaven) | April 30 +/- 11 Days | April 26 |
| Pit Hardening | June 15 +/- 9 Days | June 10 |