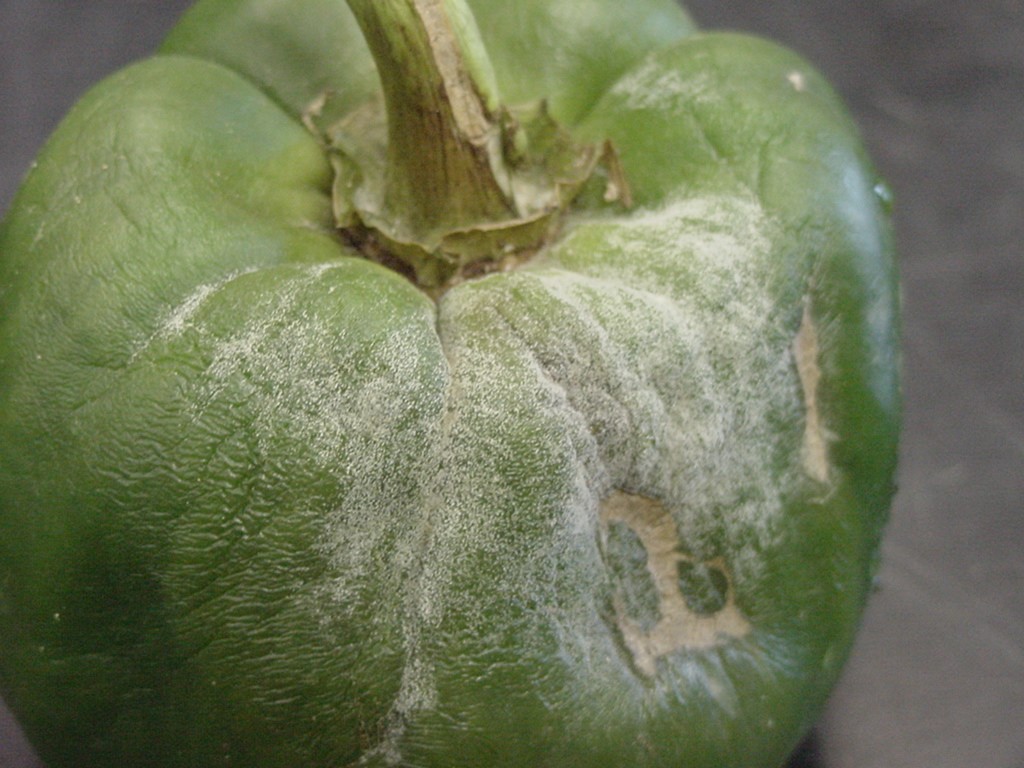
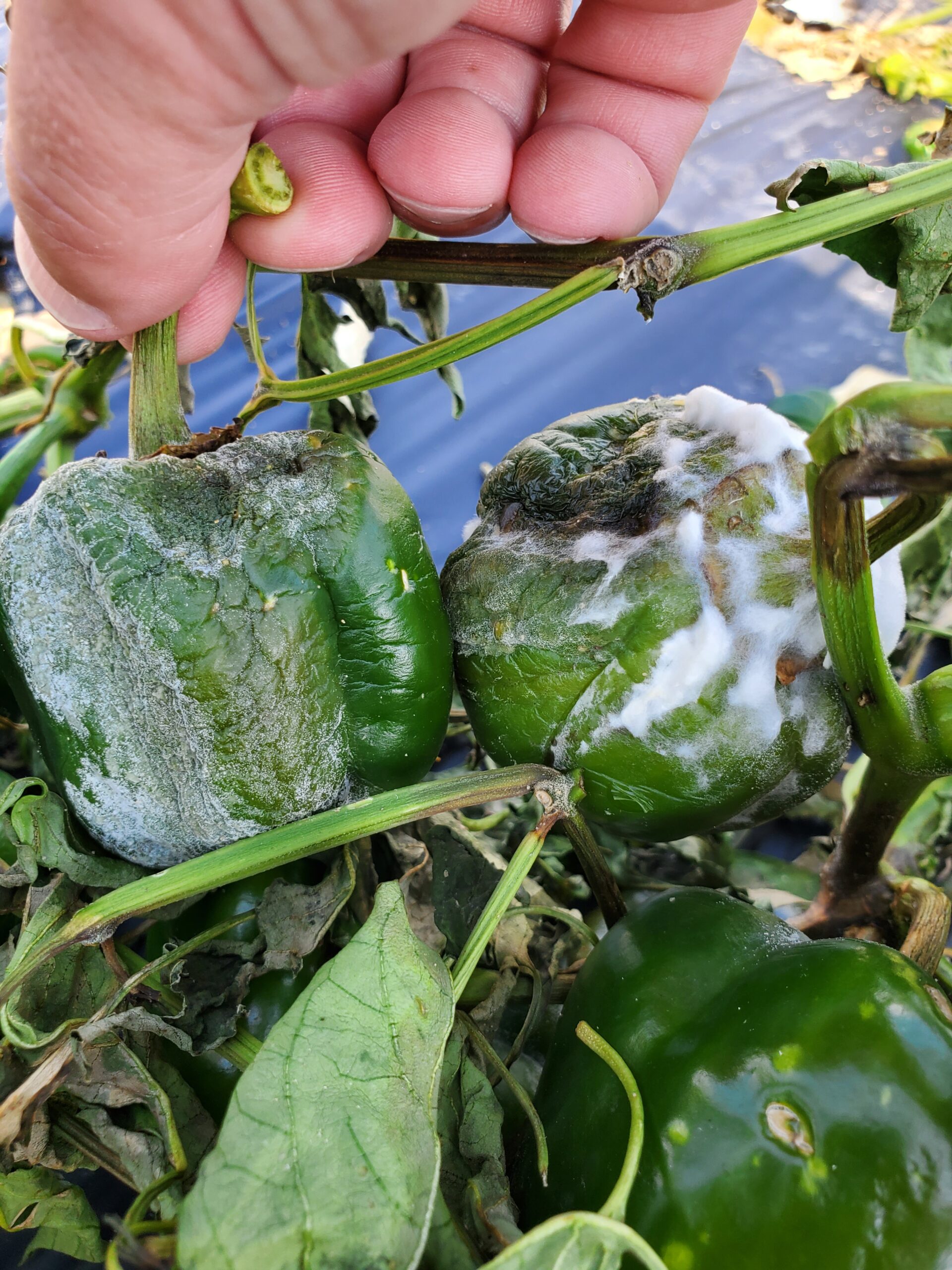
The cucurbit growing season is well under way in New Jersey and the rest of the mid-Atlantic region. Below are links to useful resources for the identification and management of important cucurbit diseases.
Diagnosing important diseases in cucurbit crops
Cucurbit Powdery and Downy Mildew: A Tale of Two Pathogens
The downy mildew forecasting website
Preparing for cucurbit downy mildew in 2023
Preparing for cucurbit powdery mildew in 2023
Preparing for Anthracnose and Alternaria Leaf Blights in Cucurbit Crops
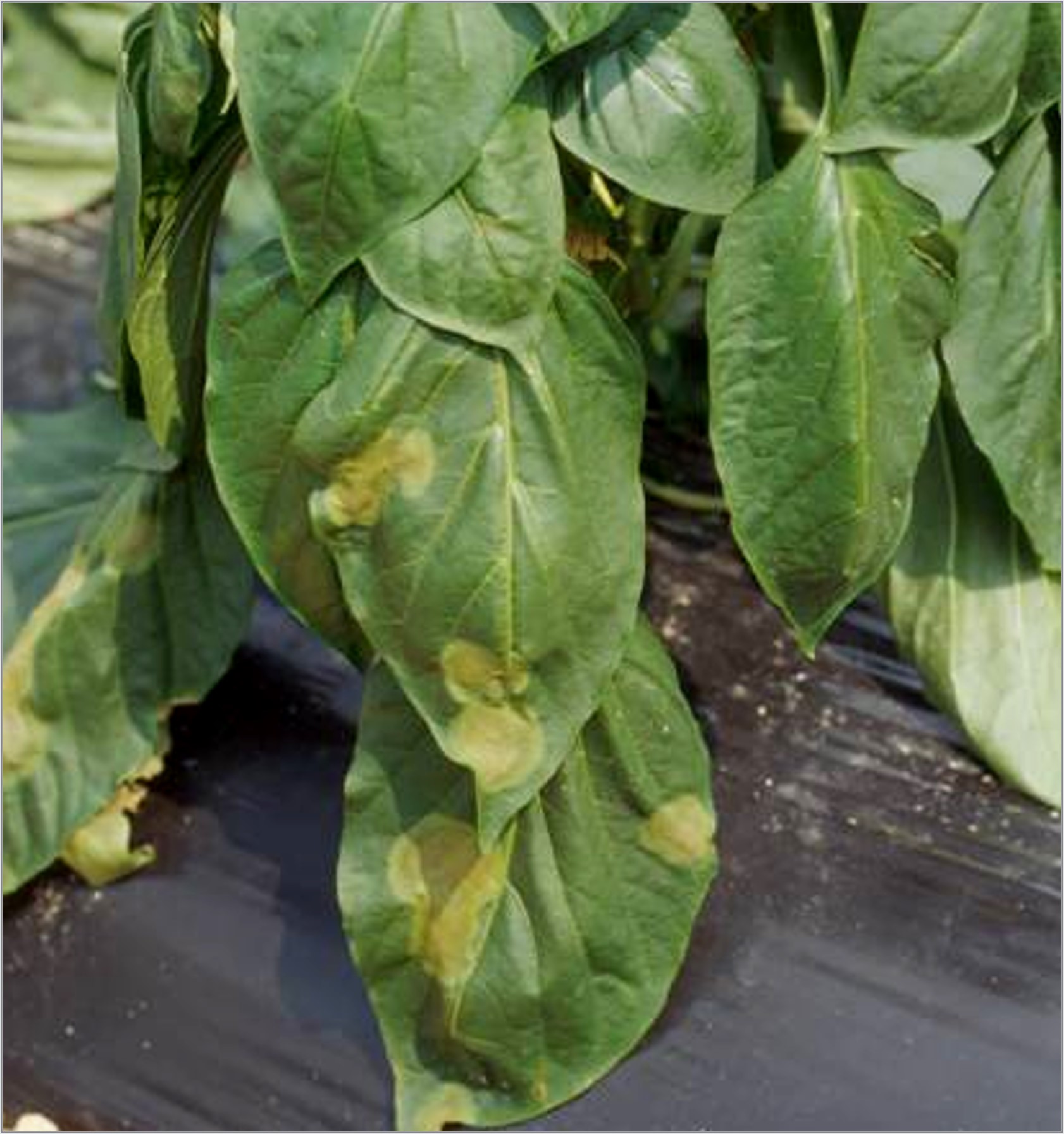
Recognizing and controlling Angular leaf spot in cucurbits
Recognizing and controlling Plectosporium blight in cucurbits
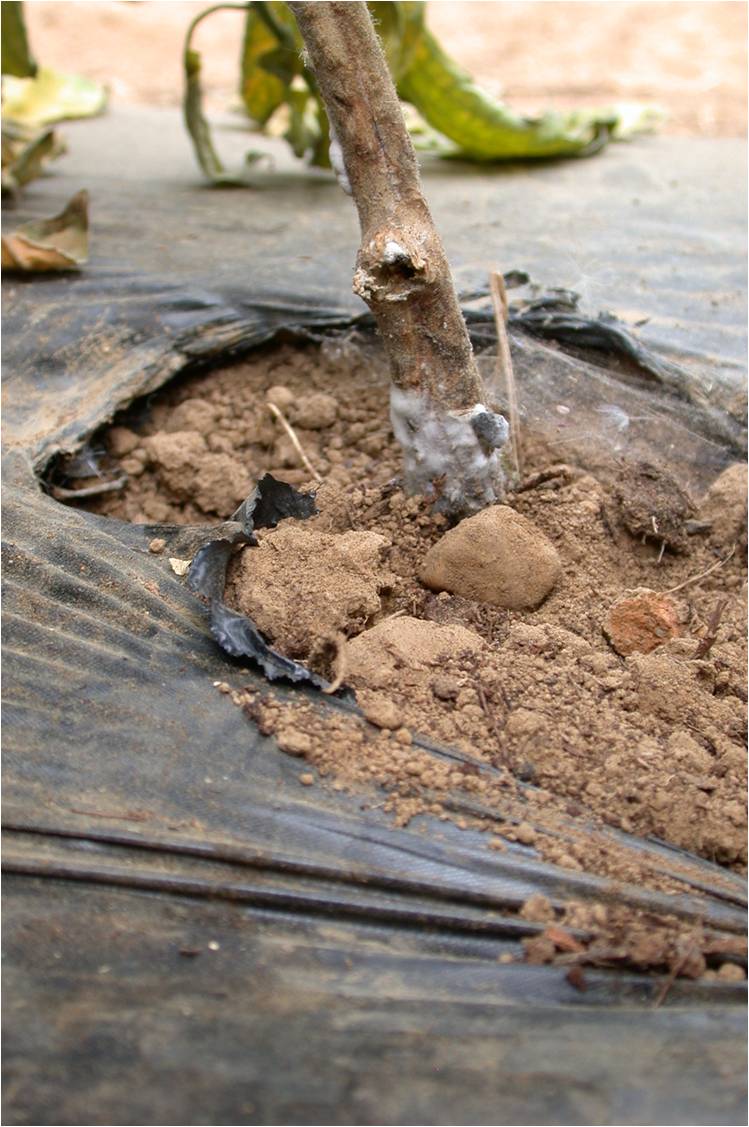
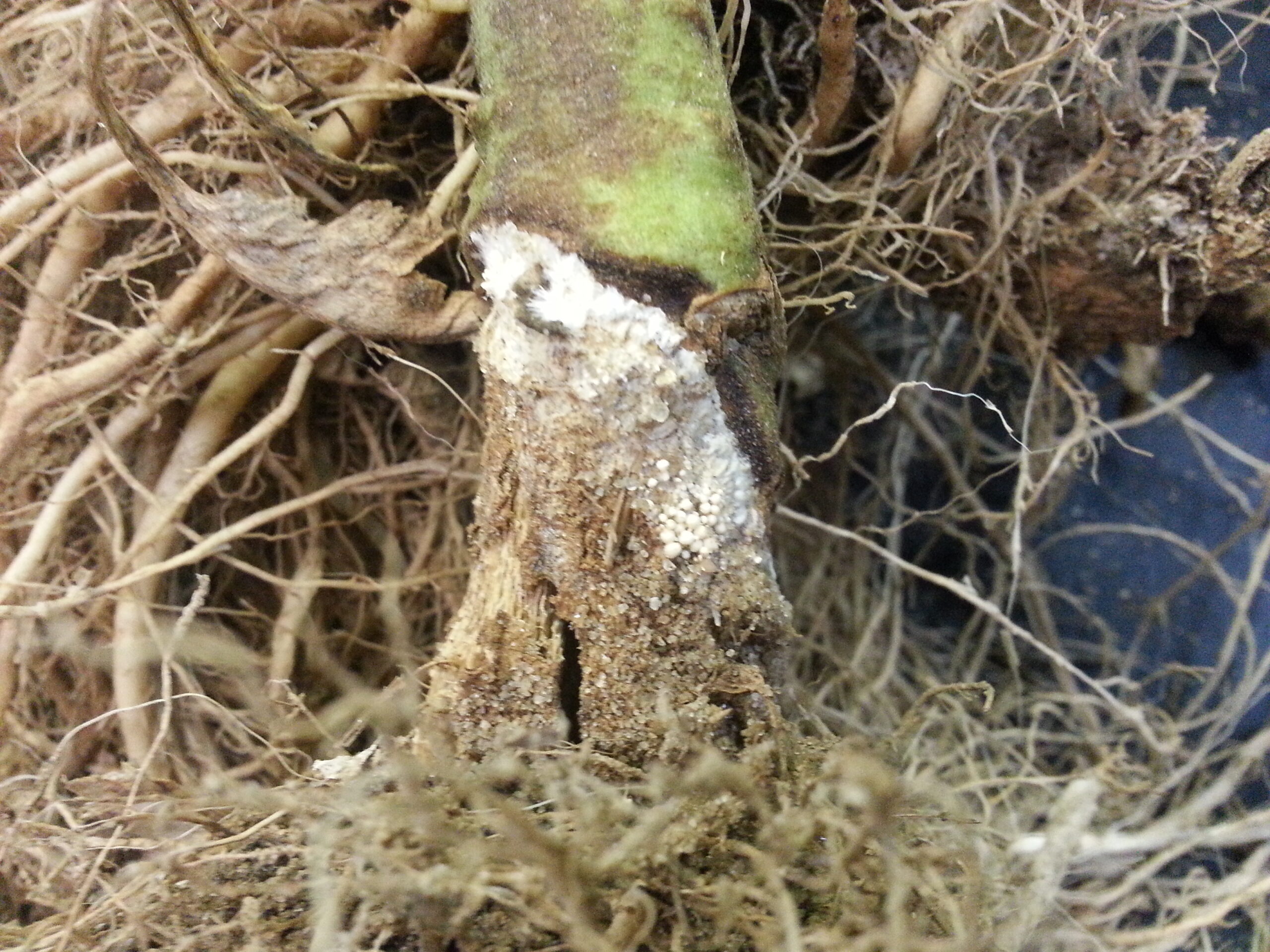
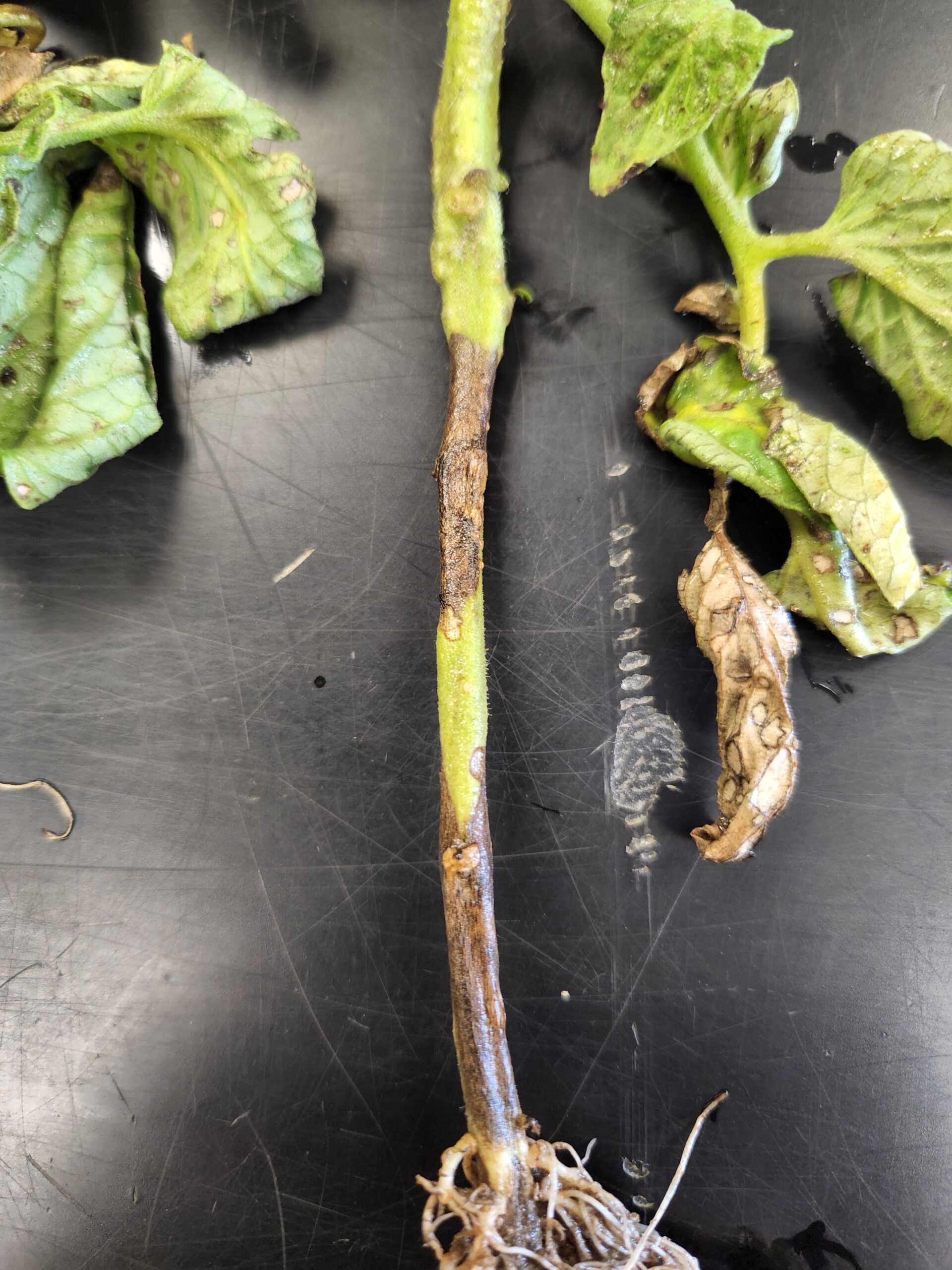
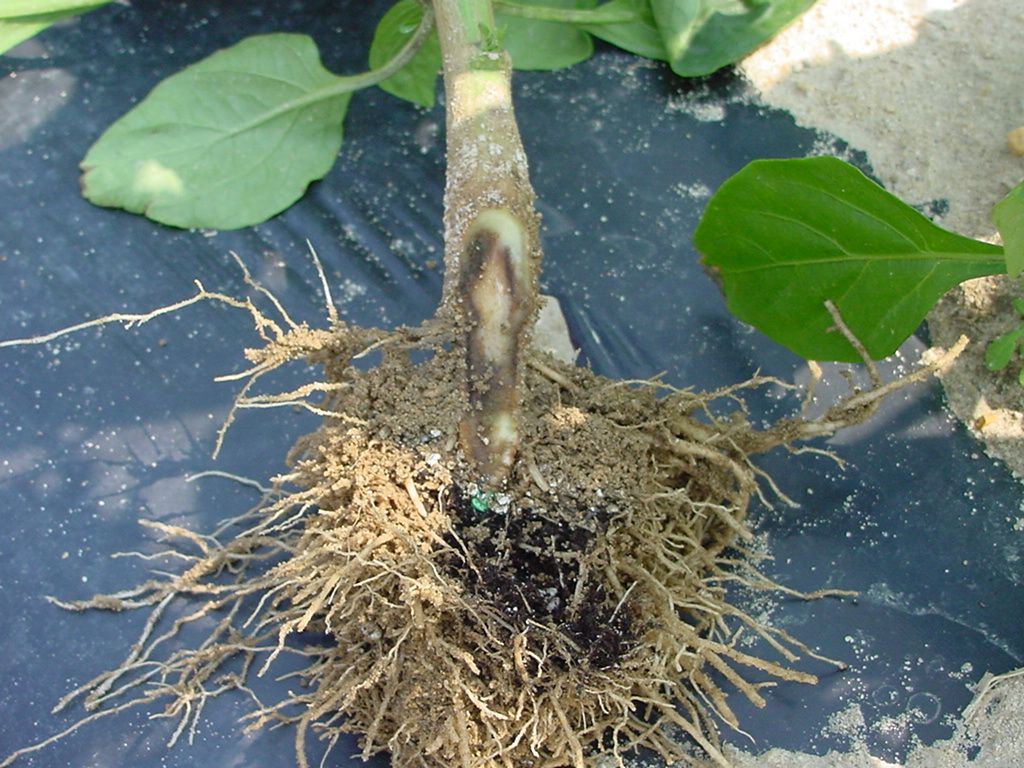
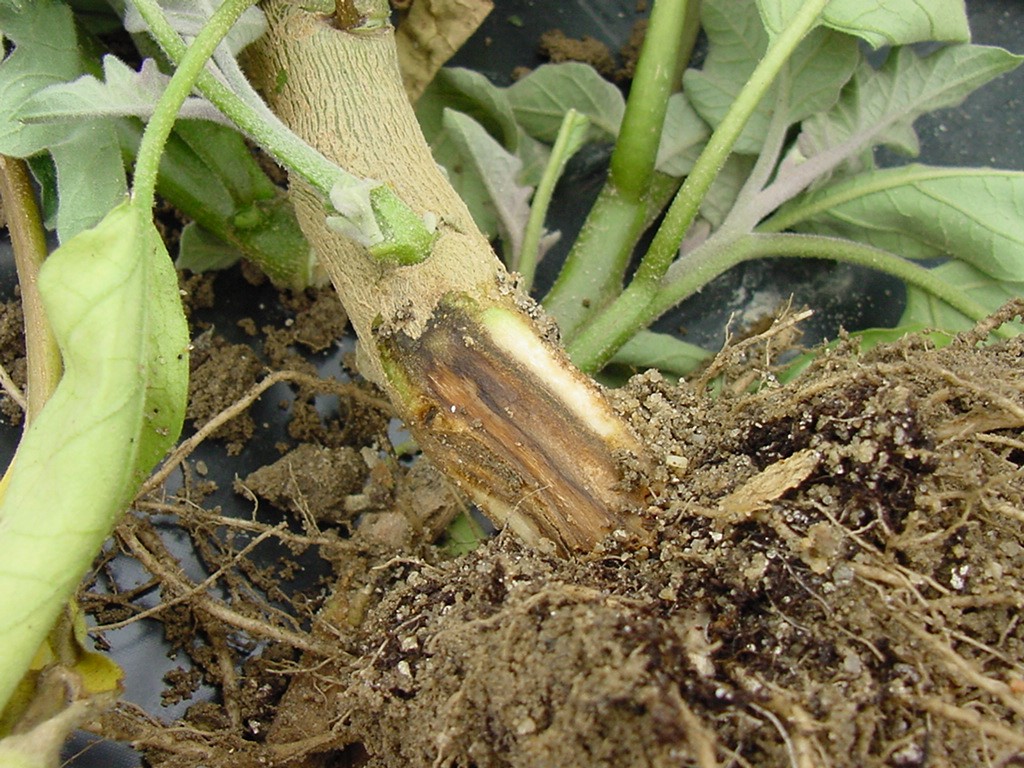
Controlling Phytophthora and Pythium root rots
Destroying cucurbit plantings after harvest