With higher temperatures increasing hatch times and spring grains like wheat and rye have drying down, thrips may be more prevalent in vegetable crops, especially when small grains are adjacent to vegetable fields. Thrips are very small and often missed if casually looking at a plant since they hide in blossoms, under sepals, on under sides of leaves and other protected areas on the stems, leaves and flowers. To scout for thrips, look at plant parts mentioned above. It is also important to dissect a flower, pulling back petals and sepals to find hiding thrips. It is difficult to see thrips with the naked eye. Therefore, the use of a hand lens will help.
Most adult thrips are elongate, slender, very small (less than 1/20 inch long), and have long fringes on the margins of both pairs of their long, narrow wings. Immature thrips (called larvae or nymphs) are oblong or slender and elongate and lack wings. Most thrips range in color from translucent white or yellowish to dark brown or black.
Females of most plant-feeding species lay their elongate, cylindrical to kidney-shaped eggs on or into leaves, buds, or other locations where larvae feed. Thrips have several generations (up to about eight) a year. When the weather is warm, the life cycle from egg to adult may be completed in as short a time as 2 weeks.
Thrips will feed on most all vegetable crops – solanaceous crops like eggplant, tomatoes, peppers, white potatoes, cucurbit crops like cucumber, squash and melons, bean crops, allium crops like onions, garlic and leeks and others. This is a photo I took last week of Thrips damage and slender yellow thrips on leaves in a tomato field in Gloucester County.
Thrips feeding on plants can damage fruit, leaves, and shoots and very noticeably affect plants’ appearance. Leaves may be speckled on the top surface from feeding on under sides of leaves by the insect’s sucking mouthparts. High populations often cause significant damage to leaves that may at first glance mimic a foliar disease, but upon closer examination is thrips damage. Damage to fruit, like tomatoes may not appear until fruit ripen and can be seen as gold flecks on red tomato fruit. For many thrips species, by the time their damage is seen, such as after flowers open or fruit forms, the thrips may no longer be present.
Once thrips are identified, control can be difficult when they are found in high numbers. Preventative measures like the use of row covers and reflective mulch have some success. Both conventional and organic insecticides labeled for thrips control can be found in the Rutgers Commercial Vegetable Production Recommendations guide under the sections for individual vegetable crops. Always read the pesticide label for instructions, safety precautions, application rates and restrictions. Since thrips hide in tight areas of plant parts it is important to have good coverage and penetration when applying insecticides to reduce the population of this hard to control pest.
For more detailed information about thrips see the Rutgers Fact Sheet https://njaes.rutgers.edu/pubs/publication.php?pid=FS291
Archives for June 2025
Thrips Active in Vegetable Crops
Fruit IPM Report June 17, 2025
Peach:
Bacterial Spot: Fruit symptoms from this set of infections have begun to appear in southern counties. So far fruit symptoms are very low and only in highly susceptible varieties. Peaches are at or past pit hardening and fruit now has some resistance to bacterial spot. Infections can still occur but will be less unsightly and may still make grade. Growers should continue to manage using Oxytetracycline and lower rates of copper, especially around rainy periods and severe weather.
Rusty Spot: Rusty spot infections are appearing on fruit across New Jersey and ongoing until pit hardening. Maintain coverage through second cover with effective materials such as Rally, Rhyme, or potassium bicarbonate products. Other choices include Flint Extra, Inspire Super, and Luna Sensation.
Peach Scab: Maintain good coverage with captan or other effective fungicides until July in orchards where scab was an issue last year.
Oriental Fruit Moth: A biofix point for OFM was set on 4/2 for southern counties and 4/17 in northern counties. Treatment timings targeting the second generation are shown in the table below.
| OFM 2nd Generation Timing | ||||
| Insecticide Type | ||||
| County/Region | Degree Days by 6/16 base 45 | Conventional
1150-1200 1450-1500 |
Intrepid/Rimon
1050-1150 1300-1400 |
Diamides/Virus
1075-1150 1375-1450 |
| Gloucester – Southern | 1265 | 1st –past
2nd – June 23-26 |
1st –past
2nd – June 17-20 |
1st –past
2nd – June 20-23 |
| Middlesex – Northern | 1110 | 1st – June 18-20
2nd – too far off |
1st – June 13-18
2nd – too far off |
1st – June 14-18
2nd – too far off |
Tarnished Plant Bugs and Other Catfacing Insects: Tarnished plant bug and other catfacing insects are active, and activity is increasing with dry weather and summer temperatures. There has been very little recent fruit feeding observed.
Green Peach Aphid: Green peach aphid counts have decreased significantly at most farm sites, but a few scouted blocks had pressure above threshold. If more than 1 colony of aphids are found in nectarines, or 2-3 colonies are found in peaches, an insecticide for aphids is needed. See the NJ Commercial Tree Fruit Production Guide for recommended materials and rates.
Scale Insects: White peach scale and San Jose scale crawlers began emergence around May 26 and will continue emergence for up to 6 weeks (Figure 1). Control options during crawler emergence include Neonicitiniods (suppression only), Sivanto, and the IGR’s Esteem and Centaur. See the NJ Commercial Tree Fruit Production Guide and the product labels for more information.

Figure 1. Scale feeding on apple.
Thrips: Increased thrips activity was recorded last week. Thrips damage appears as “silvering” and usually appears on fruit close to harvest. If populations are high, damage can be extensive. Delegate or Entrust at the highest labeled rate are the usual recommended materials for thrips in stone fruit. These materials all have short PHI’s and may be applied close to harvest when damage typically appears. Thrips have also been observed to mark cherries. Damage is different than peach and appears as a dark streak in a similar pattern as silvering. See the NJ Commercial Tree Fruit Production Guide for more information.
Apples and Pears:
Diseases: Now that primary scab has ended, the focus turns toward summer diseases such as fruit rots (Bitter rot), and sooty blotch and fly speck. Bitter rot control has been difficult at best in recent years even where management programs have been rigorous. Research has suggested products such as Merivon, Luna Sensation, Inspire Super, Omega, and Aprovia may be effective, and longtime reliable broad spectrum fungicides such as captan and ziram should provide control. Experience has suggested that the addition of phosphorous acid products such as Prophyt or Rampart to captan sprays may improve control. Observations are that these products improve control of other summer diseases such as sooty blotch and flyspeck, and may help suppress scab infections where present. Scab symptoms are appearing in some orchards statewide.
Fire Blight: Fire Blight symptoms began appearing in southern county apple orchards the week of 5/19. Typically it is recommended to cut out infected limbs; however, this is a practical decision that must be made. This blog post from Michigan State may be helpful to decide whether it is worth cutting out infected tissue. Once the terminal buds set, typically in July, infected wood should be removed to prevent colonization by the bitter rot pathogen.
Codling Moth (CM): A codling moth biofix was set in southern counties on 4/28 and in northern counties on 4/30. Trap captures increased in some orchards this week. Second generation timings are updated below. Rimon is not recommended for this and later generations.
| Codling Moth Degree Day Timing – Second Generation | ||||||||
| Application and Insecticide Type | ||||||||
| County Area | Biofix | Rimon:
75-100DD + 14-17 days later
|
Intrepid
1150 + 1450 DD Diamides – Altacor, Voliam mixes: (150-200 DD) |
Madex
1250 DD + every 7-9 days during brood hatch (later if first spray is an IGR) |
Standard Insecticides – Delegate, Avaunt, OP’s, carbamates, pyrethroids
1250 DD + 1550 DD
|
|||
| DD | 1150 | 1450 | 1250 | 1250 | 1550 | |||
| Southern | April 28 | past | past | too far off | too far off | too far off | too far off | too far off |
| Northern | April 30 | past | past | too far off | too far off | too far off | too far off | too far off |

Figure 2. Aphids on fruit.
Wooly Apple Aphid (WAA); Green Apple (Spirea) Aphids (GAA): GAA colonies are being observed, some above threshold in some apple blocks (Figures 2 & 3). GAA is generally a pest that can be tolerated in orchards where beneficial insects are present. Generally treatment thresholds for GAA are if 50% of the shoots are infested where no beneficial insects are present. WAA aerial colonies are also forming in orchards statewide. See the NJ Commercial Tree Fruit Production Guide for more information on effective products at this time.

Figure 3. Green apple aphid colonies on younger branches.
Pear: Pear psylla are still actively laying eggs and nymphs continue to hatch. Options for control include spinosyn products such as Delegate and Entrust, and the neonicotinoids (IRAC group 4A). The addition of 0.25-1 gal of summer oil may improve control. Other options at this time include products containing abamectin. Be sure to read and follow the label instructions regarding the addition of penetrants for abamectin products.
Grape: The biofix in southern counties for Grape berry moth (GBM) was 5/24. Model timing will predict IGR and diamide materials for the second generation. The model works best when growers record their own bloom dates and use the Grape Berry Moth model at NEWA. The timing is set at 810 degree days base 470F for the second generation treatments using Diamides or Intrepid. Other materials may be applied a few days later. Given the current weather patterns, this should be about the last week of June in southern counties. As for diseases we are seeing low levels of phomopsis on older leaves in some vineyards.
Blueberry: Spotted-wing drosophila (SWD) and Oriental beetle (OB) captures increased from the previous week. The first catch of Blueberry Maggot (BBM) was recorded on June 12. For weekly reports on blueberry pests and recommendations read the Rutgers Blueberry Bulletin.
Phenology Table: Based on annual observations made in Gloucester County.
| Pest Event or Growth Stage | Approximate Date | 2025 Observed Date |
| Bud Swell (Redhaven/PF-17) | March 23 +/- 15 Days | March 30 |
| 1/4″ Green Tip Red Delicious | March 31 +/- 13 Days | March 30 |
| Pink Peach (Redhaven/PF-17) | April 4 +/- 15 Days | April 1 |
| Tight Cluster Red Delicious | April 9 +/- 13 Days | April 5 |
| Full Bloom Peach (Redhaven/PF-17) | April 9 +/- 14 Days | April 10 |
| Pink Apple (Red Delicious) | April 14 +/- 12 Days | April 16 |
| Full Bloom Apple (Red Delicious) | April 22 +/- 11 Days | April 25 |
| Petal Fall (Redhaven) | April 22 +/- 10 Days | April 19 |
| Petal Fall (Red Delicious) | April 27 +/- 13 Days | May 2 |
| Shuck Split (Redhaven) | April 30 +/- 11 Days | April 26 |
| Pit Hardening | June 15 +/- 9 Days | June 15 |
Tree Fruit Trap Captures – Southern Counties
| Week Ending | STLM | TABM-A | CM | BMSB | OFM-A | DWB | OFM-P | TABM-P | LPTB | PTB |
| 4/5/2025 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/12/2025 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/21/2025 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 36 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/27/2025 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 5/2/2025 | 517 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
| 5/9/2025 | 159 | 4 | 10 | 0 | 3 | 16 | 5 | 4 | 46 | 0 |
| 5/16/2025 | 91 | 11 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 36 | 2 | 14 | 69 | 0 |
| 5/23/2025 | 299 | 21 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 23 | 1 | 26 | 23 | 0 |
| 5/30/2025 | 399 | 14 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 41 | 1 | 11 | 10 | 3 |
| 6/6/2025 | 733 | 13 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 36 | 2 | 12 | 29 | 1 |
| 6/13/2025 | 684 | 19 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 81 | 2 | 17 | 22 | 8 |
Tree Fruit Trap Captures – Northern Counties
| Week Ending | STLM | TABM-A | CM | BMSB | OFM-A | DWB | OFM-P | TABM-P | LPTB | PTB | AMBROSIA BEETLE |
| 4/5/2025 | 387 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/21/2025 | 435 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/27/2025 | 26 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 72 |
| 5/2/2025 | 86 | 0 | 0.33 | 0 | 72.5 | 0 | 47.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 136 |
| 5/9/2025 | 56 | 0 | 5.3 | 0 | 58.8 | 0 | 22.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 145 |
| 5/16/2025 | 13.75 | 2.6 | 7.3 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50.5 |
| 5/23/2025 | 4.8 | 10.3 | 10.5 | 0 | 0.6 | 31.25 | 4.2 | 0 | 14.6 | 1 | 22.2 |
| 5/30/2025 | 2.2 | 4.8 | 1.8 | 0 | 0 | 12.4 | 9.6 | 0 | 9.6 | 1.9 | 22.1 |
| 6/6/2025 | 3 | 4.83 | 2.8 | 0.25 | 0 | 20 | 4.1 | 0 | 21.2 | 1.8 | 40.3 |
| 6/13/2025 | 65 | 20 | 11.4 | 0.6 | 0 | 12.3 | 4 | 0 | 10.5 | 1.5 | 59.2 |
Forest Tree and Plant Identification Program Offered This Summer

Scan QR code or the link below!
Forest Tree & Plant Identification Outdoor Lessons for Land Stewards
Veg IPM update 6/12/25
Greetings from the Veg IPM team!
Sweet Corn
Early plantings of sweet corn are silking throughout New Jersey. Moth captures in much of the state (see map) are indicating that 4 day spray intervals are necessary, with pockets of higher pressure requiring 3 day intervals, and a few with lower pressure, indicating 5 or 6 day intervals. Rotation is important for avoiding resistance, and there are four IRAC groups that are registered in silking sweet corn: 1 (carbamates), 3 (pyrethroids), 5 (spinosyns), and 28 (diamides). Corn earworm is at least partly resistant to several pyrethroids, so a spray program should not rely solely on pyrethroids, although they can be useful in tank-mixes or as pre-mixed products, such as Besiege or Elevest (Group 28 + Group 3). For detailed information about resistance and potential spray programs, the University of Delaware has an excellent resource on corn earworm management. We’ve also seen some instances of European corn borer and corn earworm feeding in tassels of scouted corn, but for the most part, their numbers have not been high enough to warrant control efforts prior to silking.
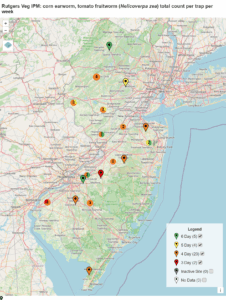
Spray intervals based on nightly pheromone moth captures for the southern part of New Jersey. Note that not all locations in the IPM program are currently trapping. This map is based on the following thresholds: 0 moths = 6-7 day schedule, 1 moth = 5 day spray schedule, 2-20 moths = 4 day spray schedule, 20+ moths = 3 day spray schedule.
Tomatoes
In southern New Jersey we’re seeing high thrips counts both in tunnels and in the field, although numbers have been higher in tunnels. We consider more than 5 thrips on 10 leaves a high count. Other guides suggest 3-5 thrips per flower or the presence of stippling damage on fruit to be a treatment threshold. Thrips management is especially important because of their ability to vector tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV), a growing concern in New Jersey where we have resistance-breaking strains. TSWV has already been seen on farms this season. Thrips management can be especially challenging in high tunnels due to a lack of products. Minecto Pro (IRAC 28 + 6) and Exirel (IRAC 28) can be used in tunnels, but only suppress thrips populations (this means they reduce numbers, but do not eradicate them). In the field, Entrust/Radiant (IRAC 5) can be used as well as Torac (IRAC 21A) and Harvanta (IRAC 28). We do not recommend pyrethroids or neonicotinoids for thrips due to resistance in different thrips species. Refer to the previous link for a complete list of best management practices for thrips and TSWV.
We’re also seeing limited aphid and spider mite activity. If dealing with primarily aphids, products such as Beleaf (IRAC 29) are recommended, especially if plants have reached the flowering stage. However, natural enemies often control aphids, so if counts are low and natural enemies like lacewings, lady beetles, or parasitoid wasps are present, you may avoid sprays. For spider mites, Nealta (IRAC 25) is an effective material that is more friendly to beneficial insects, but Portal (IRAC 21A) and other materials can be used to manage populations. Colorado potato beetles are especially prevalent in eggplants. Please consult the Mid-Atlantic Commercial Vegetable Production guide for appropriate materials for CPB control.
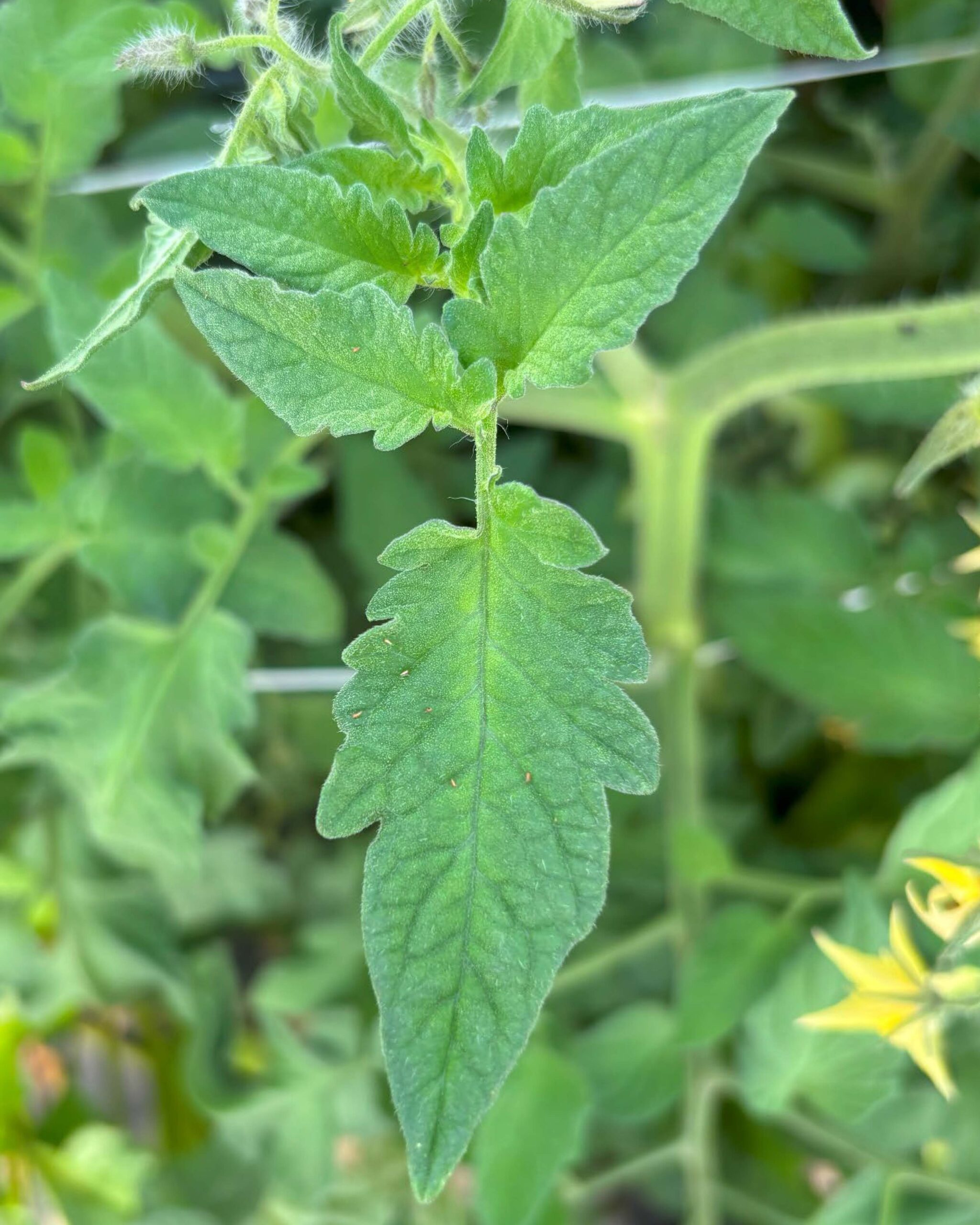

Thrips on a tomato leaf. Photo by Maria Cramer.
Peppers
Peppers have been relatively pest-free so far this season, other than patches of aphids and a few disease issues. As in tomatoes, aphids are often controlled by natural enemies, and using selective insecticides can favor natural enemy activity preventing outbreaks. Before fruit set, the threshold for treatment is 10 aphids per leaf. After fruit set the threshold is 5 aphids per leaf. There are many products registered for aphids in peppers. similar to tomatoes, if only dealing with aphids, we recommend using Beleaf (IRAC 29).
Cole Crops

Flea beetle surrounded by feeding damage. Picture by Maria Cramer.
Flea beetle activity seems to be slowing down some, but they are still active in various cole crops. This year, they have been especially prevalent in lacinato kale, Napa cabbage and bok choy. Young plants are especially vulnerable to attack from flea beetles. The treatment threshold for flea beetles in heading cole crops is 50% infestation.

Left: Diamondback moth caterpillar, showing characteristic tapering at each end. Right: Imported cabbageworm caterpillar showing characteristic fuzziness. Pictures by Maria Cramer.
We continue to see caterpillar activity in heading cole crops. Treatment thresholds vary between crops and growth stage, but for heading cole crops between early vegetative and cupping, the treatment threshold is 30%. For very small caterpillars, sprayable Bt products (IRAC 11A) such as Dipel, Xentari, or Javelin can be effective on young imported cabbage worm caterpillars. Other materials approved for caterpillar control include Entrust/Radiant (IRAC 5), Proclaim (IRAC 6), Torac (IRAC 21A), and Exirel (IRAC 28). Diamondback moth (the primary caterpillar found in southern NJ) has resistance to many insecticide groups, and pyrethroids (IRAC 3A) are not effective for their management. For Bt products and contact insecticides, coverage on the undersides the leaves is essential.
As always, please consult the Mid-Atlantic Commercial Vegetable Production Guide for a more comprehensive list of materials that are labeled for specific crops and pests. As always, be sure to follow label rates and application instructions.


