Greetings from the Veg IPM team!
Sweet Corn
Corn earworm moth captures are increasing, leading to 3- or 4-day spray intervals being needed throughout the state. When temperatures are high (>85 degrees F), shorten the spray interval by one day. Rotation is important for avoiding resistance, and there are four IRAC groups that are registered in silking sweet corn: 1 (carbamates), 3 (pyrethroids), 5 (spinosyns), and 28 (diamides). Corn earworm is at least partly resistant to several pyrethroids, so a spray program should not rely solely on pyrethroids, although they can be useful in tank-mixes or as pre-mixed products, such as Besiege or Elevest (Group 28 + Group 3). For detailed information about resistance and potential spray programs, the University of Delaware has an excellent resource on corn earworm management.
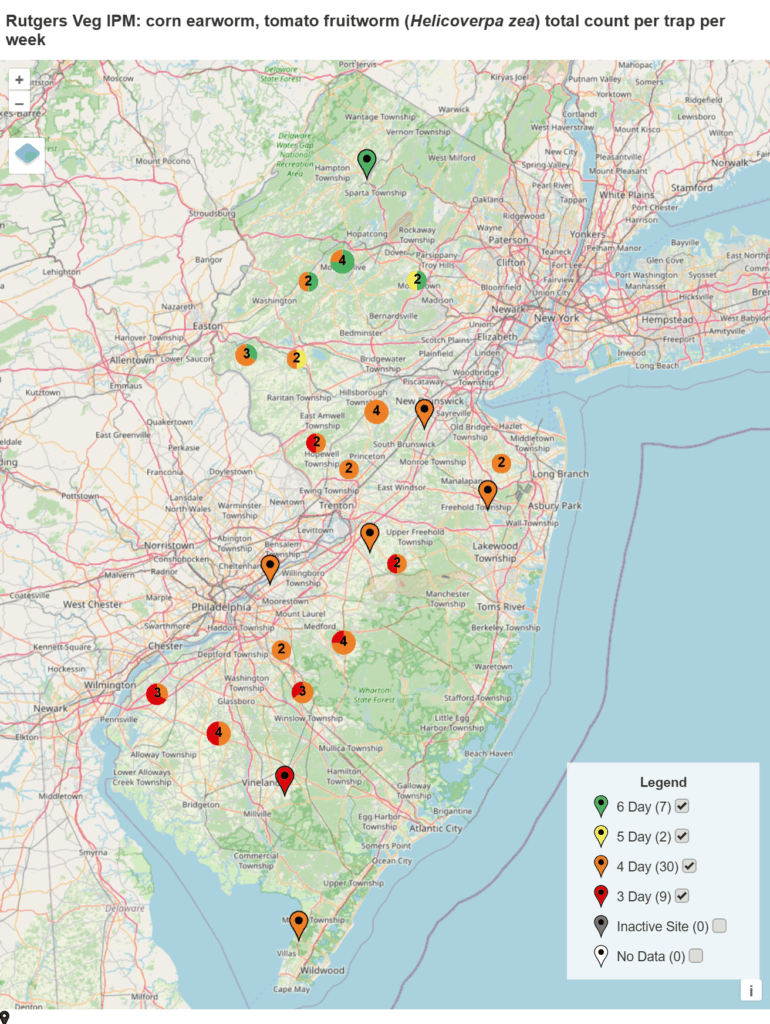
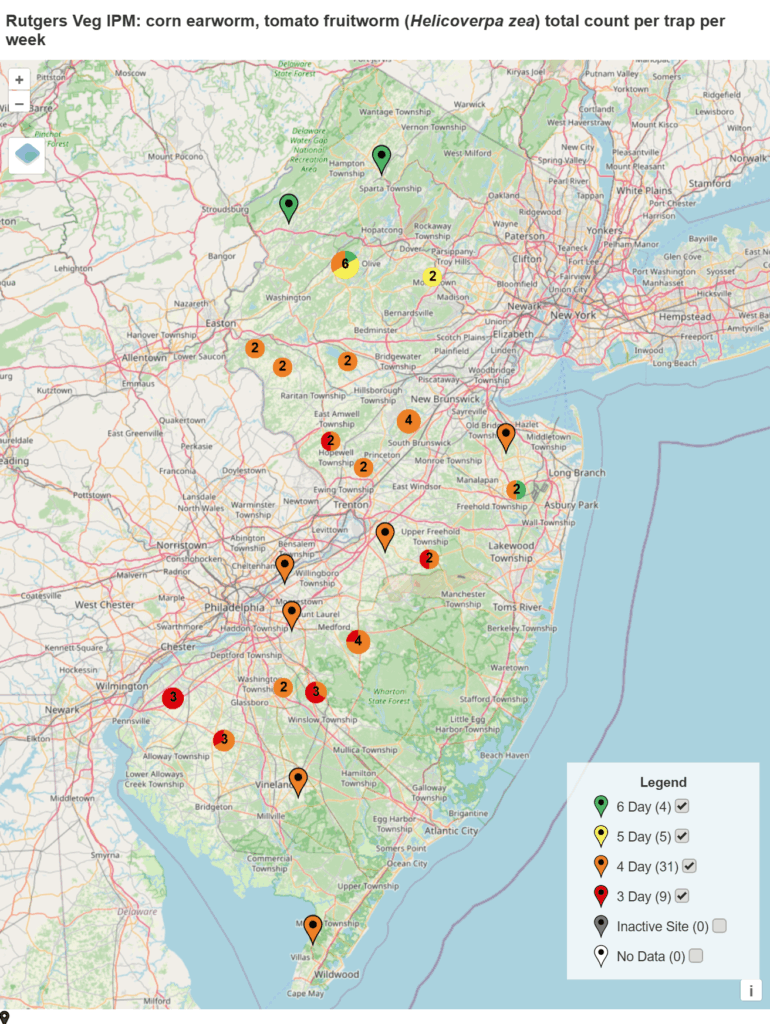
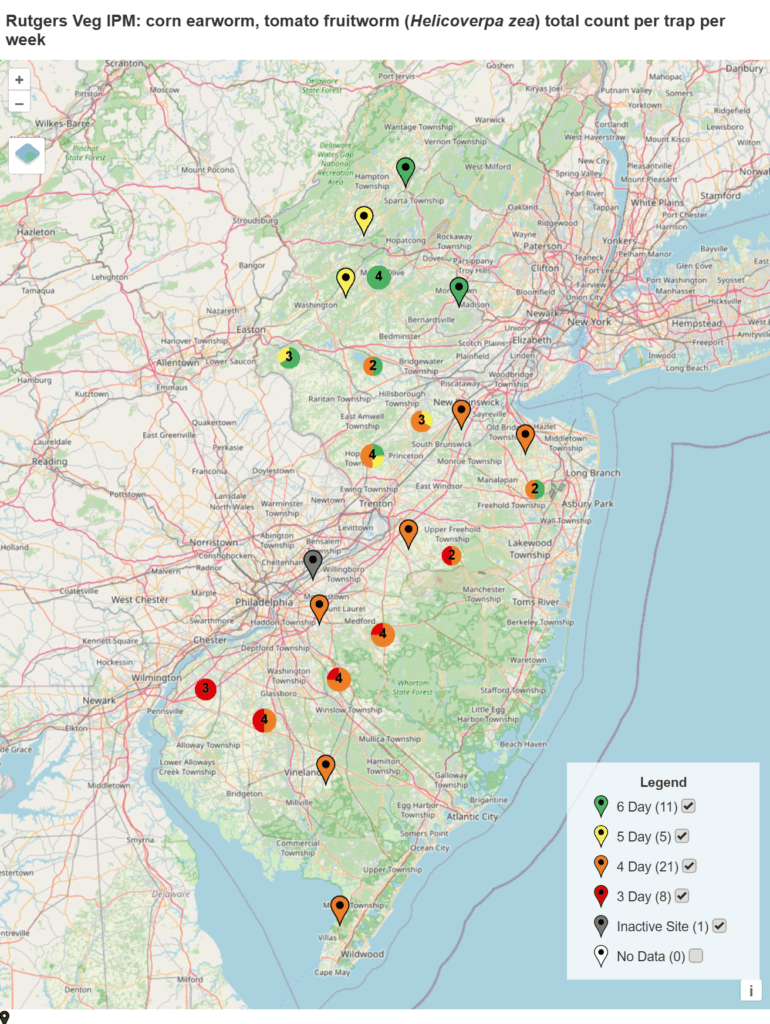
Spray intervals based on nightly pheromone moth captures for the southern part of New Jersey. Note that not all locations in the IPM program are currently trapping. This map is based on the following thresholds: 0 moths = 6-7 day schedule, 1 moth = 5 day spray schedule, 2-20 moths = 4 day spray schedule, 20+ moths = 3 day spray schedule.
Fall armyworm (FAW) infestations are beginning to pick up in some locations. Young larvae will cause damage known as “window paning”, in which the top surface of the leaf is eaten away, leaving behind thin, white, membranous-looking scratch marks. As the larvae age, these feeding marks become more ragged (A). The damage can look somewhat similar to European corn borer feeding, but FAW damage will be more severe and will lead down into the whorl. The caterpillars will have a dark head capsule with a distinct, inverted Y-shaped suture (B). We recommend using products other than diamides (IRAC Group 28) when treating whorl-stage infestations, as diamides are important to save for silk protection. Effective products include Lannate (Group 1A), Radiant (Group 5), Intrepid (Group 18), Intrepid Edge (5+18), and Avaunt (Group 22). Note that Avaunt can only be used through tassel push.
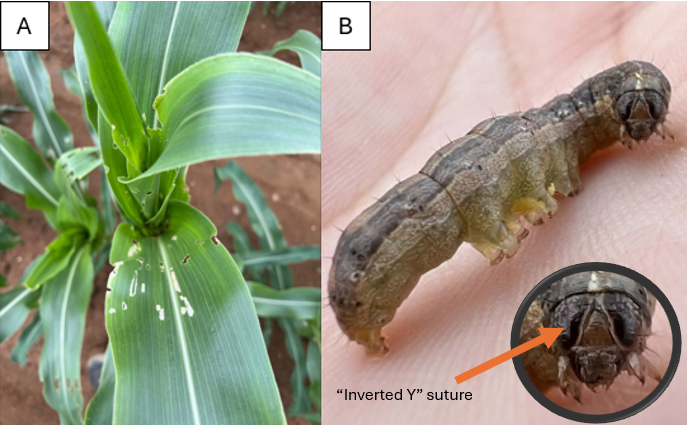

Fall armyworm damage (A) and larva (B). Note the distinct suture on the head, which will differentiate FAW from other caterpillar pests of corn. Photos by Amanda Quadrel
We are seeing a significant amount smut it sweet corn. Normally, smut infects the ears, however we have seen smut growths on vegetative stages (leaves and tassels) as well. Smut was prevalent in our area in 2024, and you can read more about it in an update written last year. Smut is rarely economic and there are no effective treatments for it. Being able to correctly identify it can help rule out other plant problems.
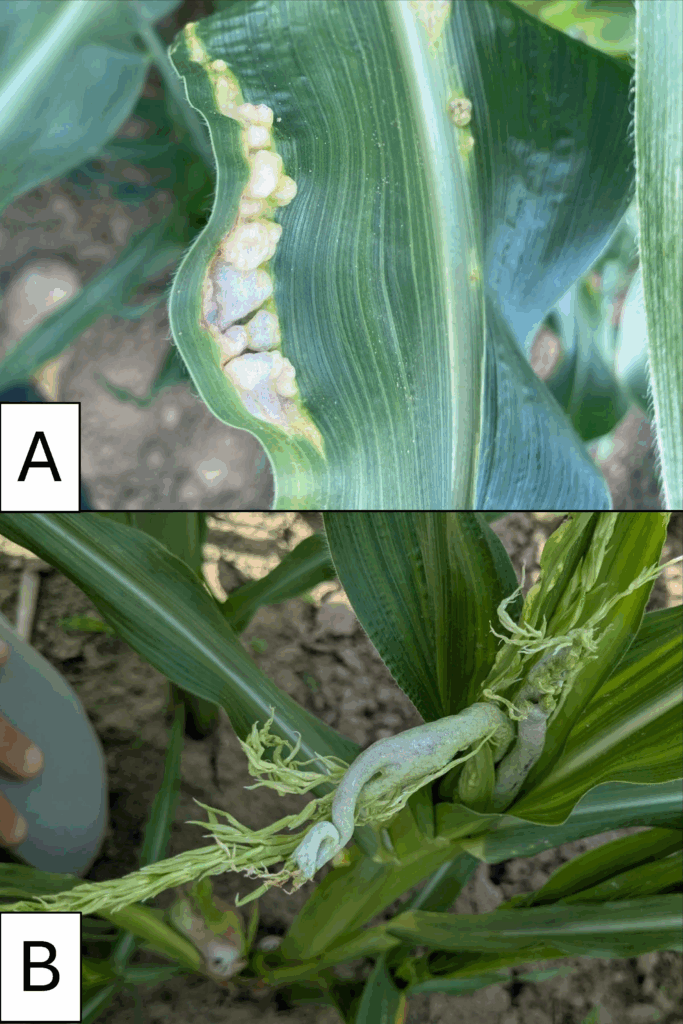

Corn smut in A) whorl-stage leaves, and B) pre-tassel tassels. Pictures by Renee Carter (A) and Nick Vergara (B)
Tomatoes
Throughout New Jersey we’re continuing to see high thrips counts both in tunnels and in the field, although numbers have been higher in tunnels. We consider more than 5 thrips on 10 leaves a high count. Other guides suggest 3-5 thrips per flower or the presence of stippling damage on fruit to be a treatment threshold. Thrips management is especially important because of their ability to vector tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV), a growing concern in New Jersey where we have resistance-breaking strains. We have seen several locations in our scouting program with small outbreaks of TSWV (in both peppers and tomatoes) so far. Scouting and roguing out these plants while continuing to manage thrips should help prevent serious losses. Additionally, follow best management practices for reducing TSWV risk throughout the season.
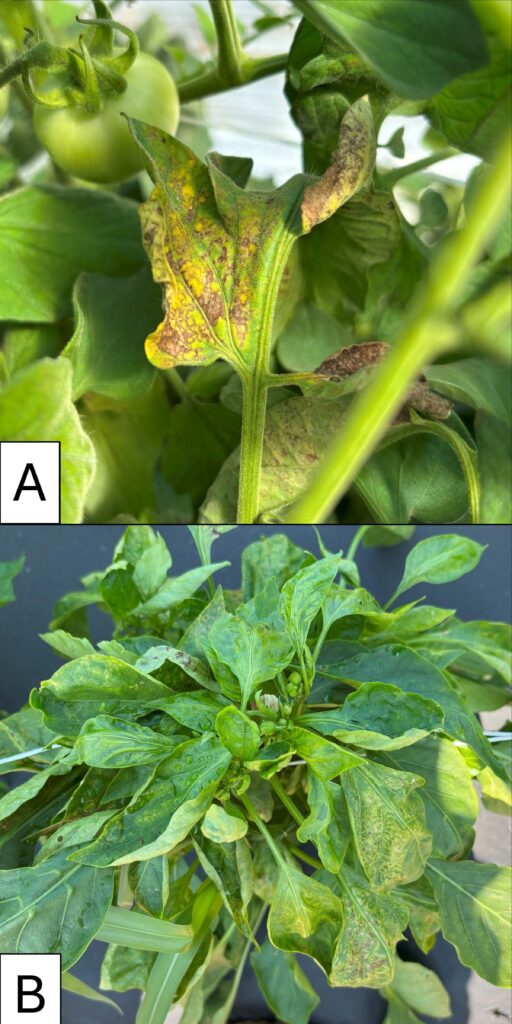

A) TSWV on a tomato leaf. Note the circle-shaped brown lesions. B) TSWV on a pepper plant. Note the distortion of leaves all over the plant as well as the yellow wavy lines and circles visible on leaves. Photos by Maria Cramer.
Caterpillar pests have begun showing up in throughout the state. We’ve seen some fruit damage, and tomato fruitworm (AKA corn earworm), beet armyworm, and hornworms on plants and fruit. There are no reliable thresholds for determining when to spray for these caterpillar pests, however scouting and consulting the corn earworm pressure map for the state will help give a sense of risk to the crop. When corn earworm pressure indicates a 3 or 4 day spray interval in corn (2-20 moths per night) as is currently the case in much of the state, tomatoes should be scouted weekly for feeding damage. Pyrethroid resistance is widespread in tomato fruitworm/corn earworm and beet armyworm, so other classes of insecticides should be used if management is needed.
With consistent hot temperatures, we’re seeing more spider mites in tomato plantings. Spider mites tend to be worse in hot, dry conditions, and especially thrive in tunnels. Their populations often dramatically increase following broad-spectrum insecticides, which reduce their natural enemies. The first sign of their presence is often light-colored stippling seen on the top surface of tomato leaves. The mites causing this damage are usually found on the undersides of leaves. For spider mites, Nealta (IRAC 25) and Oberon (IRAC 23) are effective materials that are more friendly to beneficial insects, but Portal (IRAC 21A) and other materials can also be used to manage populations.
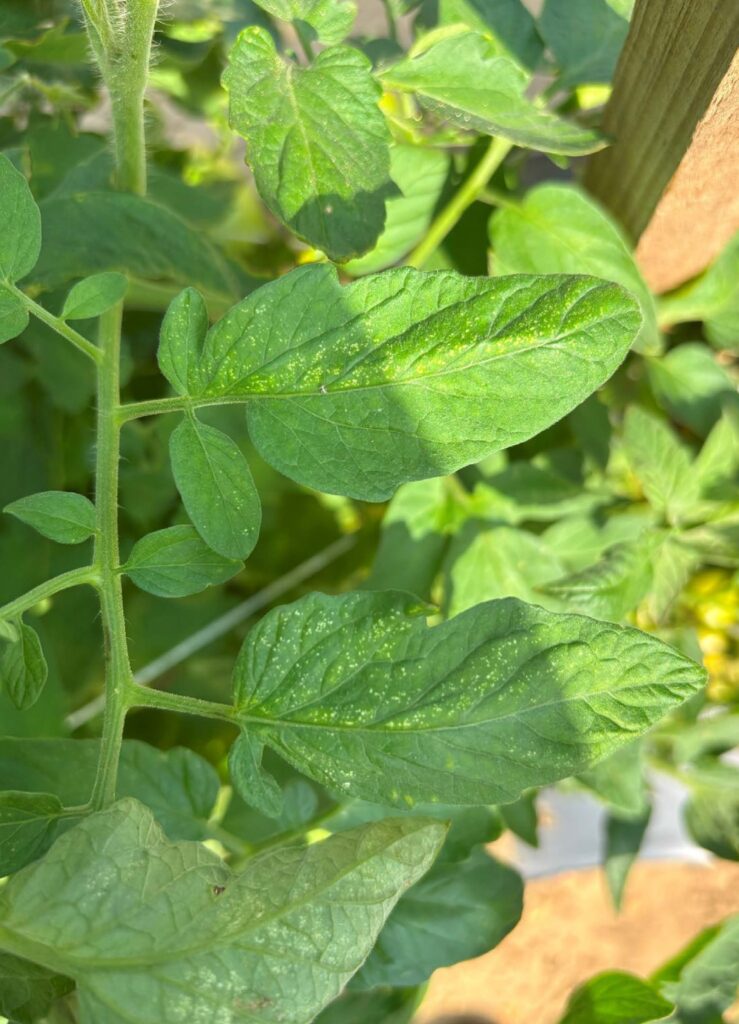

Spider mite stippling visible when looking at tomato leaves from above. The spider mites are found on the undersides of the leaves. Photo by Maria Cramer.
Peppers
In terms of most insect pests, peppers have been looking very good. We have seen aphids, spider mites, and thrips at low levels so far, however it’s important to keep in mind that thrips can transmit TSWV to peppers as well, and so monitoring and staying on top of thrips populations is crucial. As with tomatoes, finding and roguing out infected plants is important as well. See previous section for an example of TSWV symptoms in peppers.
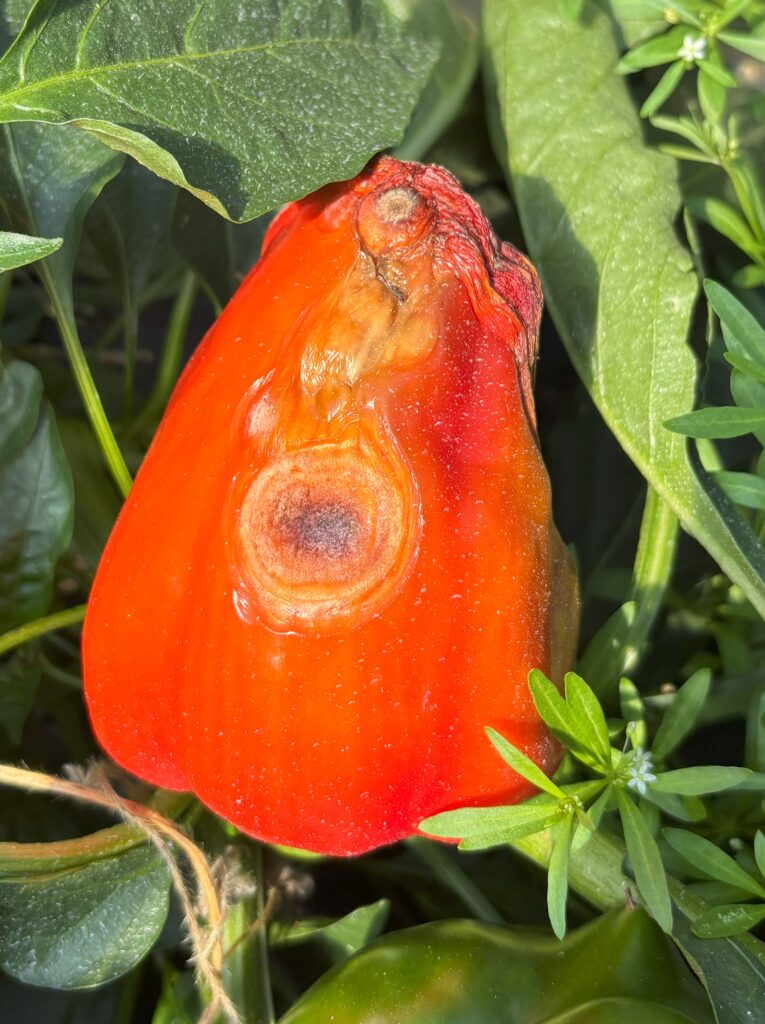

Anthracnose on ripe pepper fruit. Note concentric circles and sporulation. Picture by Maria Cramer.
With drying weather, peppers have been fairly disease-free, but we have seen instances of anthracnose. Anthracnose is an important disease to scout for and be able to identify as removing infected fruit and strip-picking surrounding fruit is key to managing its spread. Your fungicide program can also help manage anthracnose — for more information, read more here.
As a reminder, in June we saw several pepper weevils on pepper weevil traps in Cumberland and Salem Counties. Read more about pepper weevil biology and management here. If you think you may have pepper weevil on your farm or are interested in monitoring, please contact Maria Cramer.
Cole Crops
We are no longer seeing many flea beetles in cole crops, but we continue to see caterpillar activity. Treatment thresholds vary between crops and growth stage, but for heading cole crops between early vegetative and cupping, the treatment threshold is 30%. As heads form, the treatment threshold goes down to just 5% infestation. Sprayable Bt products (IRAC 11A) such as Dipel, Xentari, or Javelin can be effective on young imported cabbage worm caterpillars. Other materials approved for caterpillar control include Entrust/Radiant (IRAC 5), Proclaim (IRAC 6), Torac (IRAC 21A), and Exirel (IRAC 28). Diamondback moth (the primary caterpillar found in southern NJ) has resistance to many insecticide groups, and pyrethroids (IRAC 3A) are not effective for their management. For Bt products and contact insecticides, coverage on the undersides the leaves is essential.

Left: Diamondback moth caterpillar, showing characteristic tapering at each end. Right: Imported cabbageworm caterpillar showing characteristic fuzziness. Pictures by Maria Cramer.
Pumpkins and Other Cucurbits
Cucurbit downy mildew was first reported on 7/11/25 on cucumbers in central NJ and has been found on cucumbers and cantaloupe at the Snyder Research Farm in Pittstown. Growers should be applying protectants on cucumbers and cantaloupes for cucurbit downy mildew at this time. As of this post, we haven’t found any instances of the disease on pumpkins, squash, or watermelon. For information on how to build an effective cucurbit down mildew control program, please reference this post by Dr. Andy Wyenandt and consult the Mid-Atlantic Production Guide for additional materials that can be used.
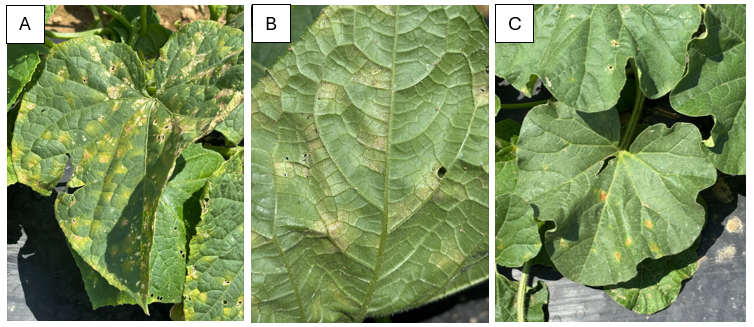
Cucurbit downy mildew symptoms on the upper surface (A) and underside (B) of cucumber leaves and symptoms on cantaloupe (C). Photos by Amanda Quadrel
In pumpkins, we’ve seen few insect issues, although adult squash bugs and egg masses are starting to appear. Consider treating for squash bug if you see more than one egg mass or group of nymphs per plant (see photos below).
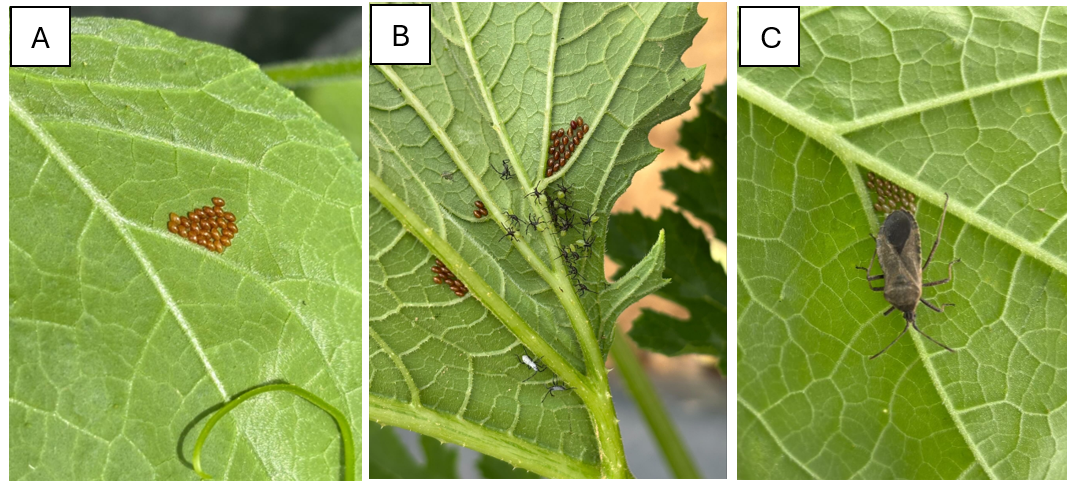
Squash bug eggs (A), newly hatched nymphs (B), and an adult (C). Photos by Amanda Quadrel
Powdery mildew is also beginning to pick up. If more than one leaf in a 50 leaf sample is infected, fungicide programs for powdery mildew should be initiated.
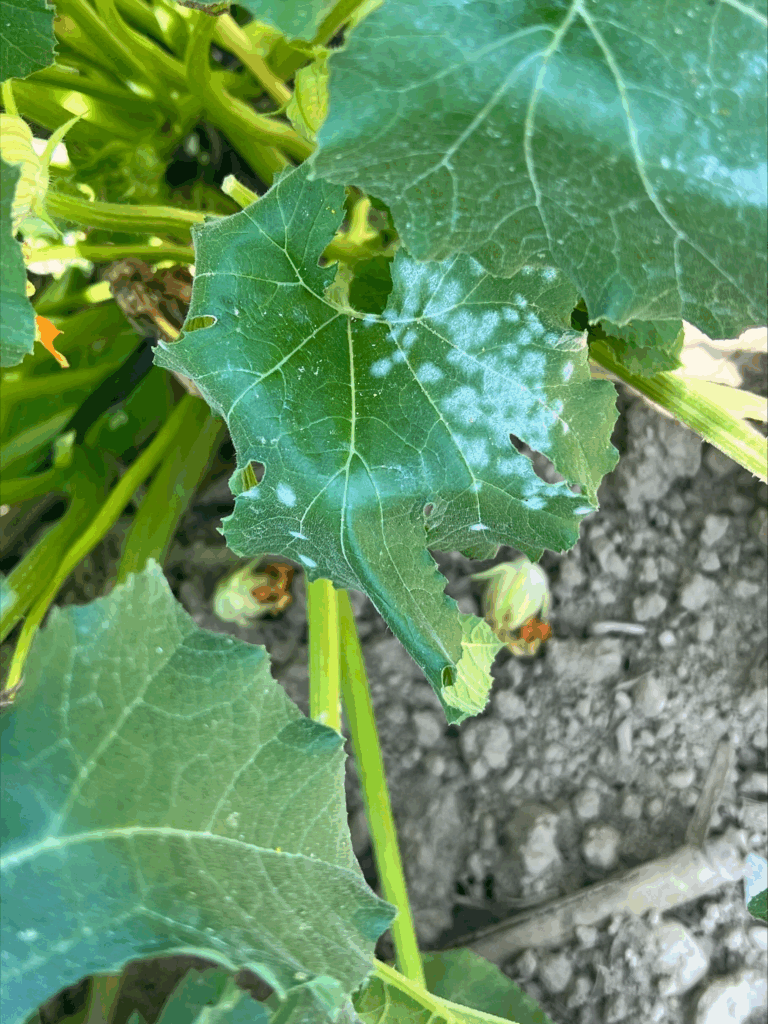
Powdery mildew on pumpkin leaf. Photo by Amanda Quadrel.
We have also seen isolated cases of anthracnose, bacterial wilt, plectosporium, and phythophthora root rot. A preventative diseases management plan based on recommendations from the Mid-Atlantic Production Guide is important for suppressing many of these diseases. If you suspect diseases in your pumpkins (or other cucurbits), reference the “Diagnosing important diseases in Cucurbit crops” guide or send/bring samples to Rutger’s Plant Diagnostic Lab.
As always, please consult the Mid-Atlantic Commercial Vegetable Production Guide for a comprehensive list of materials that are labeled for specific crops and pests. As always, be sure to follow label rates and application instructions.
The Vegetable IPM Program wishes to thank the following Field Technicians, without whom much of the information presented weekly here would not be available:
Southern team: Renee Carter, Kris Szymanski, and Nick Vergara
Northern team: Martina Lavender, Coco Lin, and Cassandra Dougherty