House Agriculture Committee Farm Bill Review
“An integral part of the oversight and review process of the 2018 Farm Bill and further preparation for the 2023 Farm Bill is getting direct input from producers, stakeholders, and consumers on how various farm bill programs are working for them” – Click here to add your comments into the form posted on the House Agriculture Committee website with the option to answer the following questions:
- Which programs included in the 2018 Farm Bill do you think are performing well?
- Are there any new programs or ideas that you or the organization that you represent would like to see considered for the 2023 Farm Bill?
- Which programs included in the 2018 Farm Bill do you think could be improved upon or should be reconsidered?
Guidance on Farm Bill Sections.
“The farm bill refers to an authorization of mandatory and discretionary spending bills appropriated to provide assistance related to food and farms. It is a multi-year law that is primarily executed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and it governs a wide variety of agricultural and food programs” – Farm Bureau.org. Click here for a short summary and video on the history of the farm bill.
Title I, Commodity Programs. Under this authorization, USDA is reauthorized to provide and improve commodity and marketing loans, sugar, dairy and disaster programs. In addition to the links below for the farm bill overview, see the ERS link at https://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/farm-economy/farm-commodity-policy/title-i-crop-commodity-program-provisions-after-enactment-of-the-agriculture-improvement-act-of-2018/
Title II, Conservation. To read more about this title go to https://www.thefarmbill.com/title-2-other-conservation
or read more in https://sgp.fas.org/crs/misc/IF11199.pdf
Title III, Trade. To read more about this title go to https://www.thefarmbill.com/title-3-trade-programs
Title IV, Nutrition. To read more about this title go to https://www.thefarmbill.com/title-4-snap
Use the same website to scroll through each of the remaining titles:
Title V, Credit
Title VI, Rural Development
Title VII, Research, Extension, and Related Matters
Title VIII, Forestry
Title IX, Energy
Title X, Horticulture
Title XI, Crop Insurance. To read more about this title you can also go to https://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/farm-economy/farm-commodity-policy/crop-insurance-program-provisions-title-xi/
Title XII, Miscellaneous
 ave an idea you would like to try on your farm that is related to sustainable agriculture?
ave an idea you would like to try on your farm that is related to sustainable agriculture?  Here is a checklist of questions to ask and sellers to answer to ensure the fodder purchased is fit for livestock consumption and priced accordingly.
Here is a checklist of questions to ask and sellers to answer to ensure the fodder purchased is fit for livestock consumption and priced accordingly.
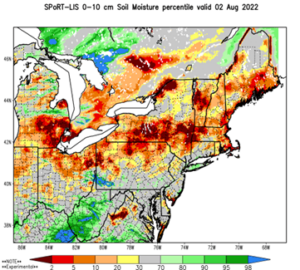 , soil moisture for surface to ten cm depth readings shifted from below the 3-percentile category for much of the county on August 1st to the 30th percentile as of August 2, but a large area of production remains in the five to ten percentile.
, soil moisture for surface to ten cm depth readings shifted from below the 3-percentile category for much of the county on August 1st to the 30th percentile as of August 2, but a large area of production remains in the five to ten percentile.