Vegetable Crops Edition
Seasonal updates and alerts on insects, diseases, and weeds impacting vegetable crops. New Jersey Commercial Vegetable Production Recommendations updates between annual publication issues are included.
Subscriptions are available via EMAIL and RSS.
Quick Links:
 NJ Commercial Vegetable Production Recommendations
NJ Commercial Vegetable Production Recommendations
 Rutgers Weather Forecasting - Meteorological Information important to commercial agriculture.
Rutgers Weather Forecasting - Meteorological Information important to commercial agriculture.
EPA Requests Stakeholder Input on Proposed Training Program for Healthcare Providers to Address Pesticide Injuries
NJ Fish & Wildlife Announces Change in Southern Deer Forum Location
Attention All NJ Deer Hunters!
The southern Deer Hunter Forum hosted by NJ Fish & Wildlife to discuss preliminary proposals on simplifying NJ’s deer hunting regulations has changed locations.
Formerly scheduled to be held at Batsto Village State Park, the Southern Deer Forum WILL NOW BE HELD at Stockton University to better accommodate expected attendance. Details follow.Southern Deer Hunter Forum – October 5, 2023, starting at 6:30 p.m. at Stockton University – 101 Vera King Farris Dr., Galloway, NJ. **Attendees should park in the North Lot and the meeting will take place in the Lodge At Lakeside. (Campus map attached as the Lodge is not visible from the parking lot)
And don’t forget the Central Deer Hunter Forum on September 28, 2023, starting at 6:30 p.m. at the Rutgers EcoComplex – 1200 Florence Columbus Rd., Bordentown, NJ.
Corn Tar Spot Found in New Jersey
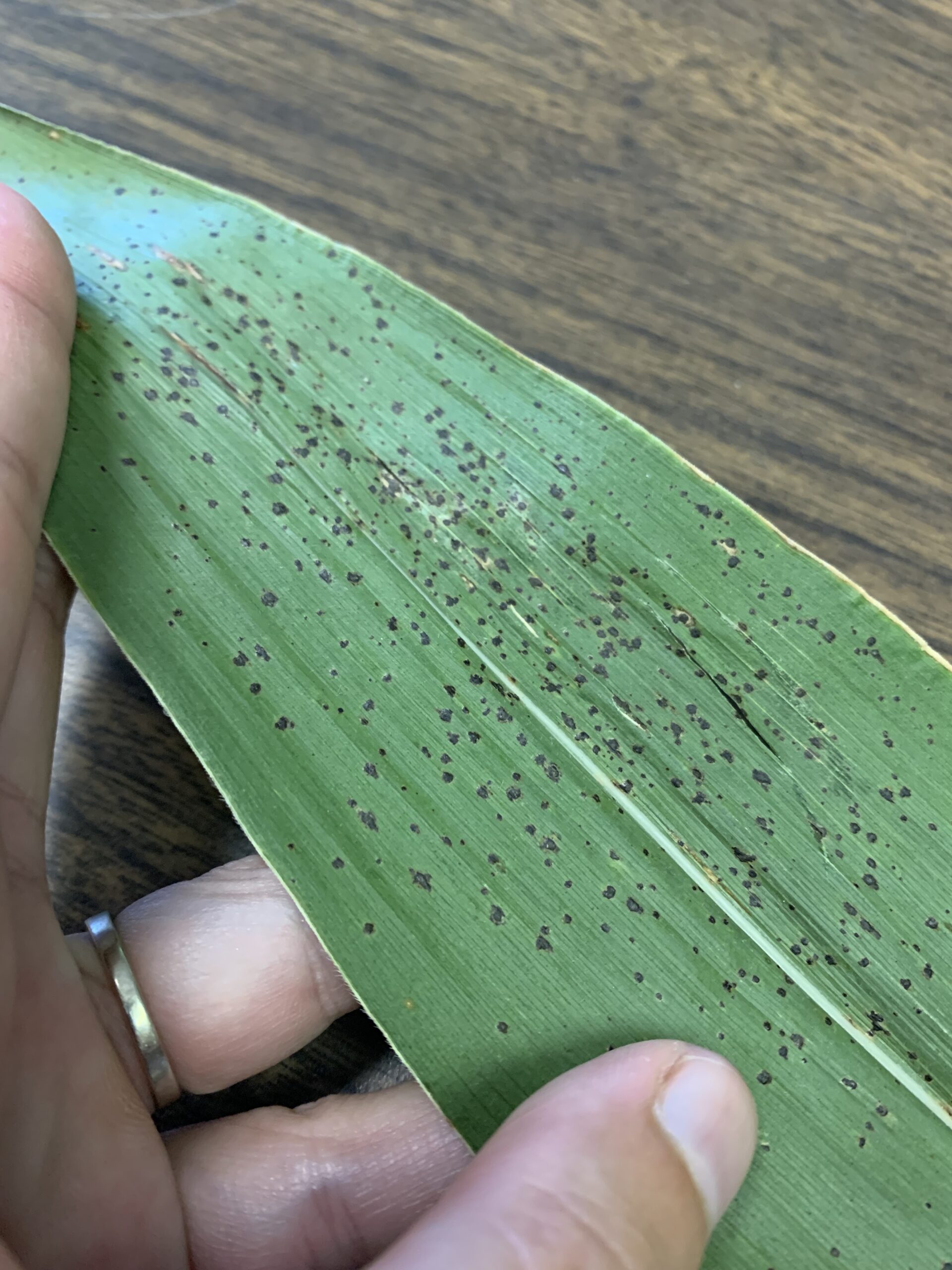

Corn Tar Spot. Photo Credit: Alyssa A. Collins, Penn State.
The presence of Corn Tar Spot (Phyllachora maydis) has been confirmed in New Jersey. Laboratory examination of a corn sample from New Jersey revealed the presence of tar spot. Tar spot is a foliar disease of corn that commonly occurs throughout Mexico, Central America, South America, and the Caribbean. The disease was identified in the United States for the first time in 2015 in northern Illinois and Indiana. Tar spot is caused by the fungus Phyllachora maydis and can cause severe yield loss on susceptible hybrids. In the Midwest severe tar spot outbreaks have been reported to reduce yield by more than 60 bushels per acre. It has also been observed that stalk rot and lodging are increased when tar spot severity is high. Corn at any developmental stage is susceptible to infection by the tar spot fungus when conditions are favorable. Tar spots appear as small, raised, black spots scattered across the upper and lower leaf surfaces. The pathogen that causes tar spot overwinters on infested corn residue on the soil surface, and it is thought that high relative humidity and prolonged leaf wetness favor disease development. You can diagnose corn tar spot in the field by examining corn leaves for the presence of black, tar-like spots. In the United States tar spot has been observed mostly during mid- to late grain fill (growth stages R3-R6) on leaves below or near the ear leaf.
Understanding and management of this disease in the United States is limited because of its very recent history. Management practices that may help reduce tar spot development and severity include the following:
Residue Management – In order to reduce over wintering inoculum, tilling and burying residue is recommended to promote decomposition of crop residue.
Crop Rotation– This helps reduce primary inoculum. We are still learning about the length of time to rotate out of corn.
Variety Selection – Avoid varieties that are or may be susceptible to tar spot.
Fungicides – The use of fungicides is still developing in the management of this disease. Several fungicides have been identified with efficacy on tar spot. Some of these products have 2ee labels that are not applicable in all states. Data on timing of application, effectiveness and economic returns are still being developed.
Vegetable IPM Update 9/20/23
Sweet Corn
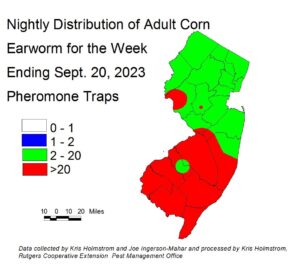 Northern and central blacklight traps and all pheromone traps continue to catch corn earworm (CEW) moths, although recent night temperatures in the low 50s have depressed numbers somewhat this week. Pheromone trap information is available from all northern and central sites, with now very limited input from southern New Jersey. We will use a combination of pheromone and blacklight trap types to derive silk spray schedules by region. We are now only able to check many traps on a weekly basis, as our student help has returned to their studies. This can give some areas an artificially high or low appearance of activity. Nonetheless, very high pheromone trap catches continue into Morris County. Red areas on the pheromone trap map (at upper right) indicate a 3-day spray schedule. Although the green areas indicate a 4 day schedule, blacklight trap catches in those areas remain consistent with a 3-day schedule. This is reflected in the suggested spray schedules below. Cool evening temperatures may further suppress activity temporarily. If this occurs and trap types are in agreement, more relaxed silk spray schedules may be suggested. Silking corn is at high risk of CEW infestation at this time. Be sure to access information from this publication in the upcoming weeks to determine how frequently you should treat silking sweet corn to protect it from CEW infestation.
Northern and central blacklight traps and all pheromone traps continue to catch corn earworm (CEW) moths, although recent night temperatures in the low 50s have depressed numbers somewhat this week. Pheromone trap information is available from all northern and central sites, with now very limited input from southern New Jersey. We will use a combination of pheromone and blacklight trap types to derive silk spray schedules by region. We are now only able to check many traps on a weekly basis, as our student help has returned to their studies. This can give some areas an artificially high or low appearance of activity. Nonetheless, very high pheromone trap catches continue into Morris County. Red areas on the pheromone trap map (at upper right) indicate a 3-day spray schedule. Although the green areas indicate a 4 day schedule, blacklight trap catches in those areas remain consistent with a 3-day schedule. This is reflected in the suggested spray schedules below. Cool evening temperatures may further suppress activity temporarily. If this occurs and trap types are in agreement, more relaxed silk spray schedules may be suggested. Silking corn is at high risk of CEW infestation at this time. Be sure to access information from this publication in the upcoming weeks to determine how frequently you should treat silking sweet corn to protect it from CEW infestation.
The highest nightly blacklight trap catches of CEW for the week ending 9/20/23 are as follows:
| Georgetown 12 | Allentown 4 | South Branch 3 |
| Hackettstown 8 | Hillsborough 4 | Chester 2 |
| Princeton 8 | Lawrenceville 3 | Dayton 2 |
| Bellemeade 5 | Oldwick 3 | Pennington 2 |
The highest nightly pheromone trap catches of CEW for the week ending 9/20/23 are as follows:
| Woodstown 88 | Green Creek 25 | Farmingdale 10 |
| East Vineland 60 | Sparta 22 | Matawan 9 |
| Georgetown 46 | Chester 20 | Berlin 8 |
| Snyder Farm (Hunterdon) 33 | Califon 14 | Dayton 6 |
Silking Spray Schedules*:
South – 3 days
Central – 3 days
North – 3 days
*These recommendations are based on regional catches. Adhere to tighter spray schedules if indicated by local trap catches. Synthetic pyrethroids alone should NOT be used for corn earworm (CEW) protection on silking corn, or for fall armyworm (FAW) management at any stage. Control with these materials is very inconsistent.
Cole Crops
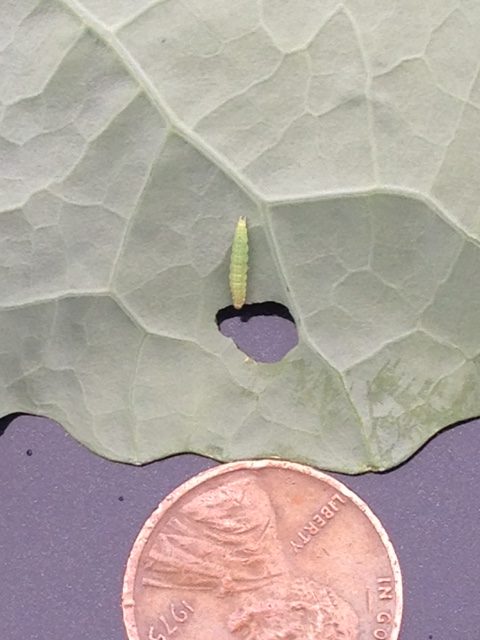 With fall plantings now underway, it is typical for diamondback moth larvae ((DBM) see photo at right) to become the dominant caterpillar pest in many cole crop fields. This pest can multiply quickly, with a generation completed in under 2 weeks with high temperatures. Furthermore, this pest is not responding to chlorantraniliprole (Coragen) in many parts of the state. Effective materials continue to be IRAC 5 materials (spinosyns), and the IRAC 6 material, ememectin benzoate (Proclaim). Consultants and scouts report good efficacy with the IRAC 21A, tolfenpyrad (Torac) . Be sure to check the Cole Crops Section of the 2022-23 Commercial Guide for specifics, as PHI’s and crop labels vary. It is important to return to treated fields within 2-3 days to assess the efficacy of the insecticide applications. Effective materials should eliminate DBM larvae within 48 hours.
With fall plantings now underway, it is typical for diamondback moth larvae ((DBM) see photo at right) to become the dominant caterpillar pest in many cole crop fields. This pest can multiply quickly, with a generation completed in under 2 weeks with high temperatures. Furthermore, this pest is not responding to chlorantraniliprole (Coragen) in many parts of the state. Effective materials continue to be IRAC 5 materials (spinosyns), and the IRAC 6 material, ememectin benzoate (Proclaim). Consultants and scouts report good efficacy with the IRAC 21A, tolfenpyrad (Torac) . Be sure to check the Cole Crops Section of the 2022-23 Commercial Guide for specifics, as PHI’s and crop labels vary. It is important to return to treated fields within 2-3 days to assess the efficacy of the insecticide applications. Effective materials should eliminate DBM larvae within 48 hours.
 Recent farm visits in the northern half of the state have revealed high numbers of Hawaiian beet webworm (HBWW) moths in weedy areas (photo at left). Galinsoga patches seem to be favored by the moths. Injury to host crops (beet greens, swiss chard, spinach) has been reported from Middlesex County, and has been observed by IPM staff in Hunterdon County. Growers in all counties would be wise to check plantings of these hosts at least weekly for the presence of foliar injury. Numerous holes in leaves, with larvae on the lower leaf surfaces (photo at right). Recommended insecticides may be found in the Spinach Section of the 2022-23 Commercial Guide.
Recent farm visits in the northern half of the state have revealed high numbers of Hawaiian beet webworm (HBWW) moths in weedy areas (photo at left). Galinsoga patches seem to be favored by the moths. Injury to host crops (beet greens, swiss chard, spinach) has been reported from Middlesex County, and has been observed by IPM staff in Hunterdon County. Growers in all counties would be wise to check plantings of these hosts at least weekly for the presence of foliar injury. Numerous holes in leaves, with larvae on the lower leaf surfaces (photo at right). Recommended insecticides may be found in the Spinach Section of the 2022-23 Commercial Guide.
Beet Armyworm
Pheromone catches of beet armyworm are high in some southern NJ areas at this time. 148 moths per night in Woodstown and 7 per night in East Vineland have been reported. 
 This pest (photo at near left) has the ability to defoliate pepper plants and damage fruit, and can cause severe damage on other crops (see photo of chard at far left). BAW is resistant to pyrethroid insecticides, and other materials should be used in response to infestations. Effective materials include spinosyns (IRAC 5) and diamides (IRAC 28).
This pest (photo at near left) has the ability to defoliate pepper plants and damage fruit, and can cause severe damage on other crops (see photo of chard at far left). BAW is resistant to pyrethroid insecticides, and other materials should be used in response to infestations. Effective materials include spinosyns (IRAC 5) and diamides (IRAC 28).
Attention Deer Hunters – NJ Fish & Wildlife Forums on Simplified Hunting Regulations
NJ Fish & Wildlife is looking for your input and will be hosting three Deer Hunter Forums to discuss preliminary proposals on simplifying NJ’s deer hunting regulations.
Hunters are asked to attend for discussions of ideas on how to make deer hunting regulations less complicated and less expensive.
Your feedback is crucial to keep deer hunting a treasured tradition and valuable wildlife management tool in the Garden State!
The first Forum for North Jersey took place last week. The remaining two are scheduled as follows:
- Central – September 28, 2023, at 6:30 p.m.
- Rutgers EcoComplex – 1200 Florence Columbus Rd., Bordentown, NJ
- South – October 5, 2023 at 6:30, p.m.
- Batsto Village State Park Visitor’s Center – 31 Batsto Rd., Hammonton, NJ
Source: https://dep.nj.gov/njfw/news-2023-08-24-upcoming-deer-hunter-forums/
Sunscald Injury on Cucurbit Fruit
Extended periods of long, hot dry weather can cause pumpkin fruit to seemingly mature quicker (i.e., turn orange). Sunscald injury occurs when cucurbit fruit are suddenly exposed to direct sunlight during the latter stages of fruit ripening during the fall. Sunscald injury often occurs after plants prematurely defoliate due to powdery mildew or downy mildew infection or when vines collapse due to Phytophthora blight or bacterial wilt.
Symptoms of sunscald injury include the collapsing of rind tissue on the side of the fruit which is in direct afternoon sunlight. Sunscald injury often develops as a pinkish-red color on exposed fruit which becomes flat in appearance. Over time fruit tissue may become tan to brown and secondary pathogens often invade the sunscald injured areas of the fruit.
To help reduce the potential for sunscald injury on pumpkin and other winter squash fruit, maintain weekly protectant fungicide programs to help retain foliage for as long as necessary, especially if fruit are going to be left in the field for long periods.

