Cucurbit powdery mildew (CPM), caused by Podosphaera xanthii, is one the most important diseases of cucurbit crops throughout the world. The pathogen is an obligate parasite, just like cucurbit downy mildew, meaning it needs a living host in order to survive. In northern regions that have a killing frost in the fall the pathogen will die out when the crop freezes. Not being able to overwinter, the pathogen must be re-introduced each spring or summer in the mid-Atlantic region. The pathogen accomplishes this by re-infecting cucurbit crops in the spring as they are planted up the east coast starting in Florida, then the Carolina’s, Virginia, and so forth. By late May, as soon as cucurbit crops begin to germinate in the mid-Atlantic region, the potential threat for potential powdery mildew infections begin. [Read more…]
Vegetable Crops Edition
Seasonal updates and alerts on insects, diseases, and weeds impacting vegetable crops. New Jersey Commercial Vegetable Production Recommendations updates between annual publication issues are included.
Subscriptions are available via EMAIL and RSS.
Quick Links:
 NJ Commercial Vegetable Production Recommendations
NJ Commercial Vegetable Production Recommendations
 Rutgers Weather Forecasting - Meteorological Information important to commercial agriculture.
Rutgers Weather Forecasting - Meteorological Information important to commercial agriculture.
Tobacco Streak Virus (TSV) found on tomato in New Jersey
Tobacco Streak Virus (TSV) was found on fresh-market tomato this past week in southern New Jersey. TSV has a host range of close to 200 species, including cranberry, tobacco, tomato, pepper, asparagus, bean, soybean, mustard, radish, a number of ornamental hosts as well as weeds such as thistle, field bindweed, and jimson weed. Like Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus (TSWV), the Tobacco Streak Virus is also vectored by thrips. TSV can be seed-borne (reported in some hosts), spread via pollen, and mechanically transmitted. Symptoms can vary significantly depending on the host. Infected plants may have downward leaf curling, show black streaks on leaves and stems, chlorosis, stunted growth, deformed growing tips, ring spots, and flower drop. There is no genetic resistance to TSV in tomato and management should focus on keeping thrips populations as low as possible, scouting on a regular, removing infected plants, and knowing your weed population (as a potential source). The only method to correctly identify TSV is through serological tests such as ELISA.
For more information on Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus please click here.
Veg IPM update 7/4/25
Greetings from the Veg IPM team! We hope that you’re all enjoying the holiday and the nice weather for this weekend.
Sweet Corn
Moth captures in much of the state (see map) have decreased over the past week and a half, but a 4-day spray schedule is still necessary for most growers at this time. When temperatures are high (>85 degrees F), shorten the spray interval by one day. Rotation is important for avoiding resistance, and there are four IRAC groups that are registered in silking sweet corn: 1 (carbamates), 3 (pyrethroids), 5 (spinosyns), and 28 (diamides). Corn earworm is at least partly resistant to several pyrethroids, so a spray program should not rely solely on pyrethroids, although they can be useful in tank-mixes or as pre-mixed products, such as Besiege or Elevest (Group 28 + Group 3). For detailed information about resistance and potential spray programs, the University of Delaware has an excellent resource on corn earworm management. We’ve also seen some very minor instances of European corn borer, beet armyworm, and corn earworm feeding in pre-silking corn, as well as our first sighting of fall armyworm (found in Burlington County). In the pre-tassel stage, we use a treatment threshold of 12% infestation of these types of caterpillars, and sightings have been far below this so far.
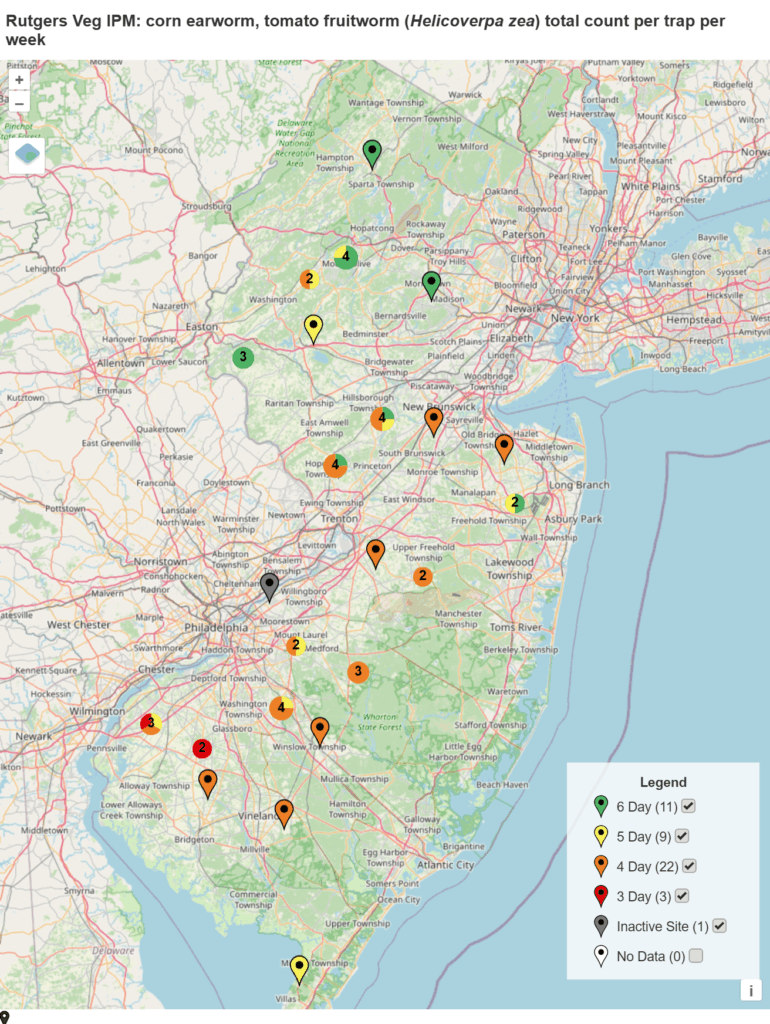
Spray intervals based on nightly pheromone moth captures for the southern part of New Jersey. Note that not all locations in the IPM program are currently trapping. This map is based on the following thresholds: 0 moths = 6-7 day schedule, 1 moth = 5 day spray schedule, 2-20 moths = 4 day spray schedule, 20+ moths = 3 day spray schedule.
Tomatoes
Throughout New Jersey we’re continuing to see high thrips counts both in tunnels and in the field, although numbers have been higher in tunnels. We consider more than 5 thrips on 10 leaves a high count. Other guides suggest 3-5 thrips per flower or the presence of stippling damage on fruit to be a treatment threshold. Thrips management is especially important because of their ability to vector tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV), a growing concern in New Jersey where we have resistance-breaking strains. TSWV has already been seen on farms this season. Thrips management can be especially challenging in high tunnels due to a lack of products. Minecto Pro (IRAC 28 + 6) and Exirel (IRAC 28) can be used in tunnels, but only suppress thrips populations (this means they reduce numbers, but do not eradicate them). In the field, Entrust/Radiant (IRAC 5) can be used as well as Torac (IRAC 21A) and Harvanta (IRAC 28). We do not recommend pyrethroids or neonicotinoids for thrips due to resistance in different thrips species. Refer to the previous link for a complete list of best management practices for thrips and TSWV.
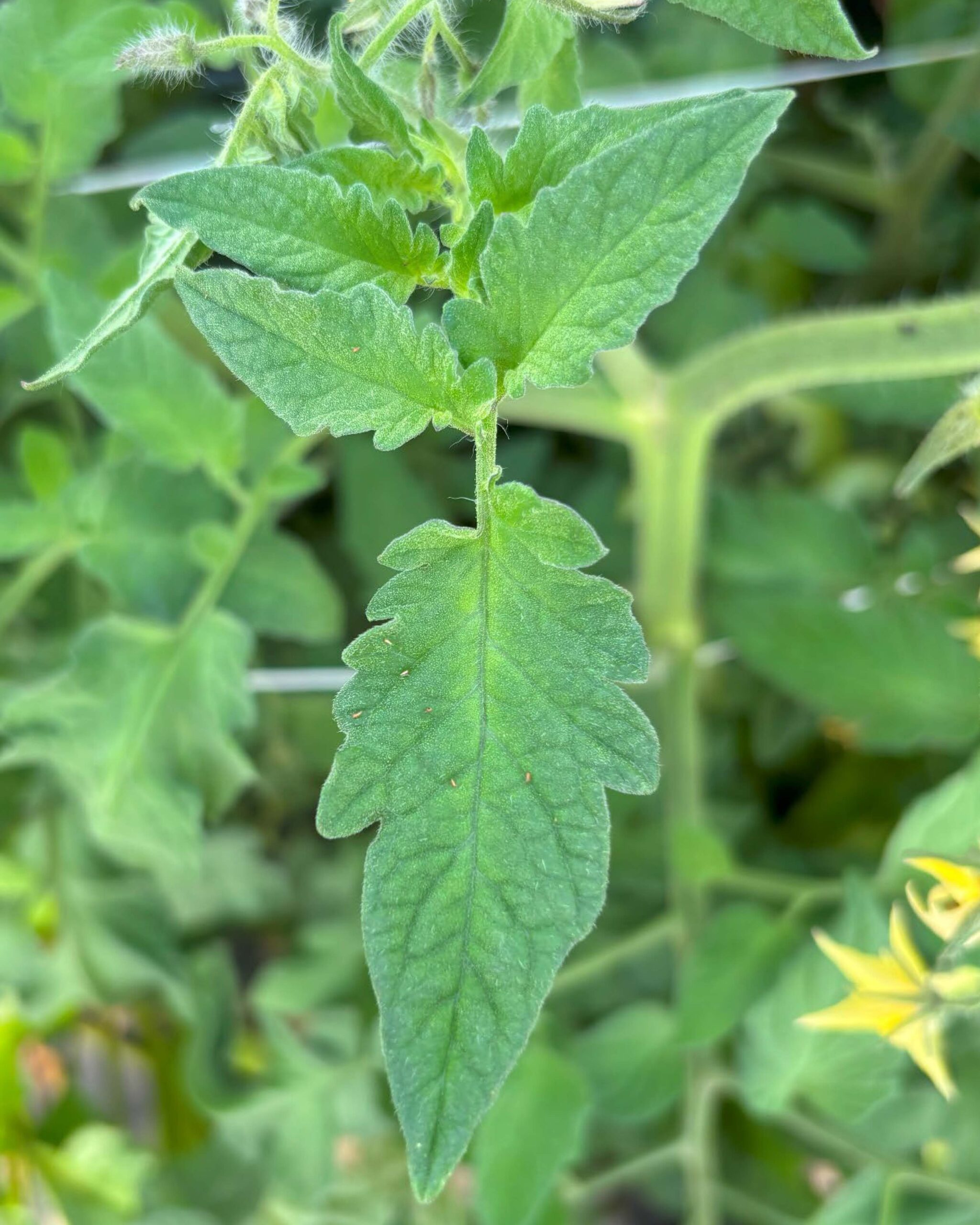

Thrips on a tomato leaf. Photo by Maria Cramer.
Caterpillar pests have begun showing up in southern NJ plantings in the last week. We’ve seen some fruit damage, and tomato fruitworm (AKA corn earworm), beet armyworm, and hornworms on plants and fruit. There are no reliable thresholds for determining when to spray for these caterpillar pests, however scouting and consulting the corn earworm pressure map for the state will help give a sense of risk to the crop. When corn earworm pressure indicates a 3 or 4 day spray interval in corn (2-20 moths per night) as is currently the case in much of the state, tomatoes should be scouted weekly for feeding damage. Pyrethroid resistance is widespread in tomato fruitworm/corn earworm and beet armyworm, so other classes of insecticides should be used if management is needed.
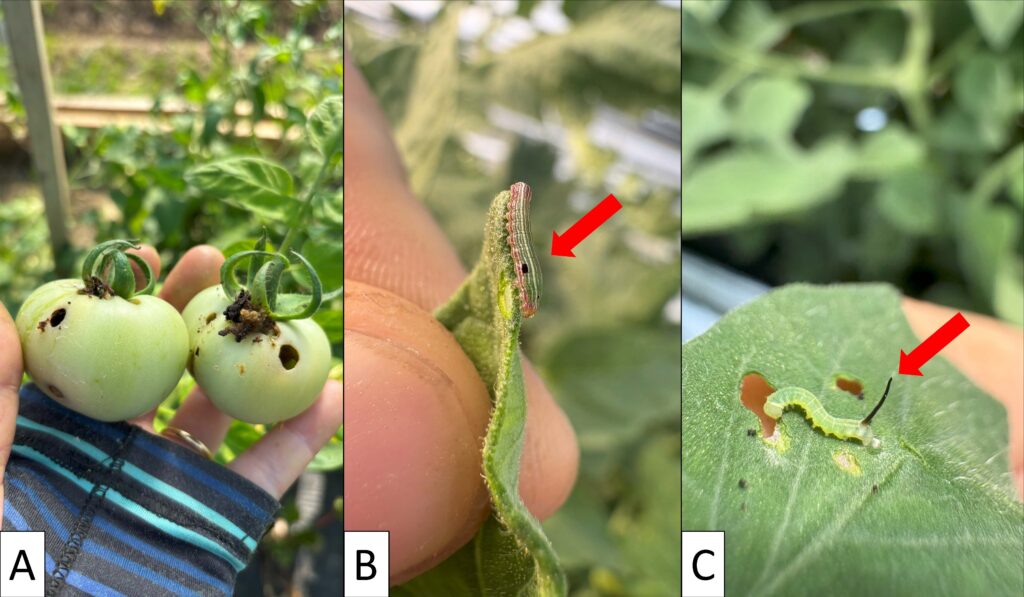

Caterpillars in tomatoes: A) Tomato fruitworm feeding holes (photo: Maria Cramer), B) A beet armyworm with red arrow indicating distinctive black dot on the side of the caterpillar above its front set of legs (photo: Kris Szymanski), and C) A very small tomato hornworm with red arrow indicating the horn (photo: Kris Szymanski).
We’re also seeing limited aphid and spider mite activity in tomatoes. If dealing with primarily aphids, products such as Beleaf (IRAC 29) are recommended, especially if plants have reached the flowering stage. However, natural enemies often control aphids, so if counts are low and natural enemies like lacewings, lady beetles, or parasitoid wasps are present, you may avoid sprays. For spider mites, Nealta (IRAC 25) is an effective material that is more friendly to beneficial insects, but Portal (IRAC 21A) and other materials can also be used to manage populations.
Peppers
In terms of most insect pests, peppers have been looking very good. We have seen aphids, spider mites, and thrips at low levels so far, however it’s important to keep in mind that thrips can transmit TSWV to peppers as well, and so monitoring and staying on top of thrips populations is crucial.
In southern New Jersey, pepper weevils are periodically introduced from other regions of the United States via the processing industry, so we have been using pheromone traps to monitor their populations. Single pepper weevils have been found on traps at locations in Cumberland and Salem counties. Because established pepper weevil populations are virtually impossible to eradicate and can lead to total losses, the presence of a single weevil triggers routine insecticide applications through the end of pepper harvest. Many populations of pepper weevils are resistant to pyrethroids, and insecticide classes should be rotated when managing them to prevent further resistance. Currently available chemistries suppress, but do not eradicate, pepper weevils. Read more about pepper weevil biology and management here. If you think you may have pepper weevil on your farm or are interested in monitoring, please contact Maria Cramer.
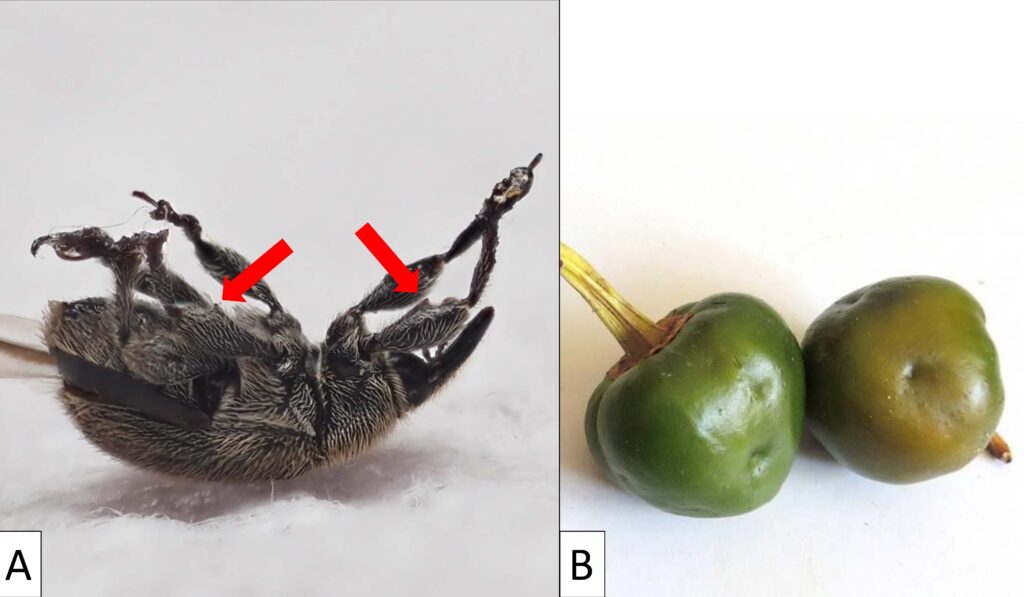
A) The first pepper weevil found in southern NJ in 2025. Red arrows indicate the characteristic spines found on the undersides of the legs which are key for identifying pepper weevil (photo: Maria Cramer). B) Dimpled pepper fruit indicate pepper weevil egg laying and can help confirm pepper weevil infestations (photo: Joe Ingerson-Mahar).
Cole Crops
We are no longer seeing many flea beetles in cole crops, but we continue to see caterpillar activity. Treatment thresholds vary between crops and growth stage, but for heading cole crops between early vegetative and cupping, the treatment threshold is 30%. As heads form, the treatment threshold goes down to just 5% infestation. Sprayable Bt products (IRAC 11A) such as Dipel, Xentari, or Javelin can be effective on young imported cabbage worm caterpillars. Other materials approved for caterpillar control include Entrust/Radiant (IRAC 5), Proclaim (IRAC 6), Torac (IRAC 21A), and Exirel (IRAC 28). Diamondback moth (the primary caterpillar found in southern NJ) has resistance to many insecticide groups, and pyrethroids (IRAC 3A) are not effective for their management. For Bt products and contact insecticides, coverage on the undersides the leaves is essential.

Left: Diamondback moth caterpillar, showing characteristic tapering at each end. Right: Imported cabbageworm caterpillar showing characteristic fuzziness. Pictures by Maria Cramer.
Diseases
With the heavy rainfall over the last week, conditions have been favorable for diseases to spread. We’re still seeing bacterial and fungal issues in peppers and tomatoes, but we have also started to see issues like Alternaria in cole crops. To prevent the spread of disease, avoid working fields when foliage is wet and continue to use resistant varieties when possible. In tunnels, leaf mold is becoming a prevalent problem as well. Be sure to vent the structure regularly to reduce humidity. Mural (FRAC 7 + 11) is labeled for greenhouse use.
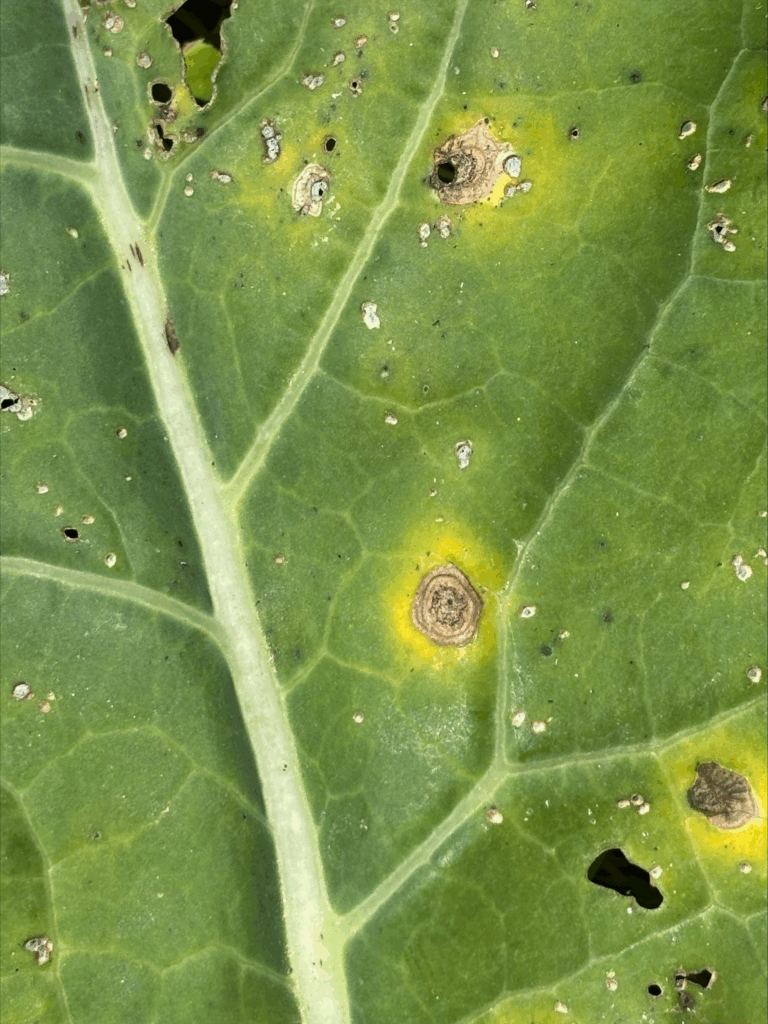

Alternaria on broccoli. Photo by Amanda Quadrel
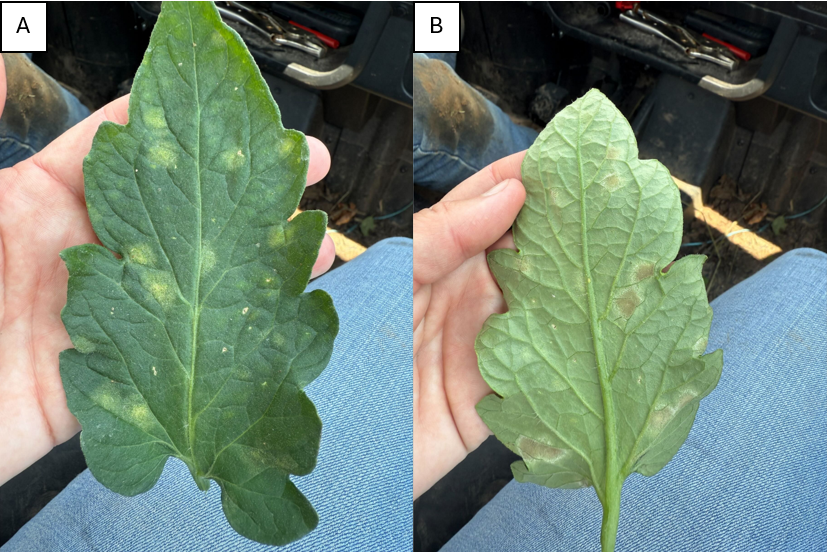

Photo showing leaf mold symptoms on the upper (A) and lower (B) surface of the leaves. Photo by Darcy Perehinys
As always, please consult the Mid-Atlantic Commercial Vegetable Production Guide for a comprehensive list of materials that are labeled for specific crops and pests. As always, be sure to follow label rates and application instructions.
The Vegetable IPM Program wishes to thank the following Field Technicians, without whom much of the information presented weekly here would not be available:
Southern team: Renee Carter, Kris Szymanski, and Nick Vergara
Northern team: Martina Lavender, Coco Lin, and Cassandra Dougherty
Vegetable Disease Update – 7/3/25
Collar rot on fresh-market tomato has been reported sporadically around the state over the past week. For more information please click here.
White mold and Southern blight have been reported this past week on fresh-market tomato in both high tunnels and fields in southern New Jersey.
Cucurbit downy mildew was reported in MI this past week. There have been no reports of CDM in the region to date.
Wet weather brings on the development of Phytophthora blight.
Preparing for Pepper anthracnose this growing season.
Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus (TSWV) has been reported in southern New Jersey. For more information please click here.
Veg IPM update 6/27/25
Greetings from the Veg IPM team! We hope you all stayed cool during the heat wave this past week!
Sweet Corn
Early plantings of sweet corn are silking throughout New Jersey. Moth captures in much of the state (see map) have generally decreased, but a 4-day spray schedule is still necessary for most growers at this time. When temperatures are high (>85 degrees F), shorten the spray interval by one day. Rotation is important for avoiding resistance, and there are four IRAC groups that are registered in silking sweet corn: 1 (carbamates), 3 (pyrethroids), 5 (spinosyns), and 28 (diamides). Corn earworm is at least partly resistant to several pyrethroids, so a spray program should not rely solely on pyrethroids, although they can be useful in tank-mixes or as pre-mixed products, such as Besiege or Elevest (Group 28 + Group 3). For detailed information about resistance and potential spray programs, the University of Delaware has an excellent resource on corn earworm management. We’ve also seen some instances of European corn borer and corn earworm feeding in tassels of scouted corn, but for the most part, their numbers have not been high enough to warrant control efforts prior to silking.
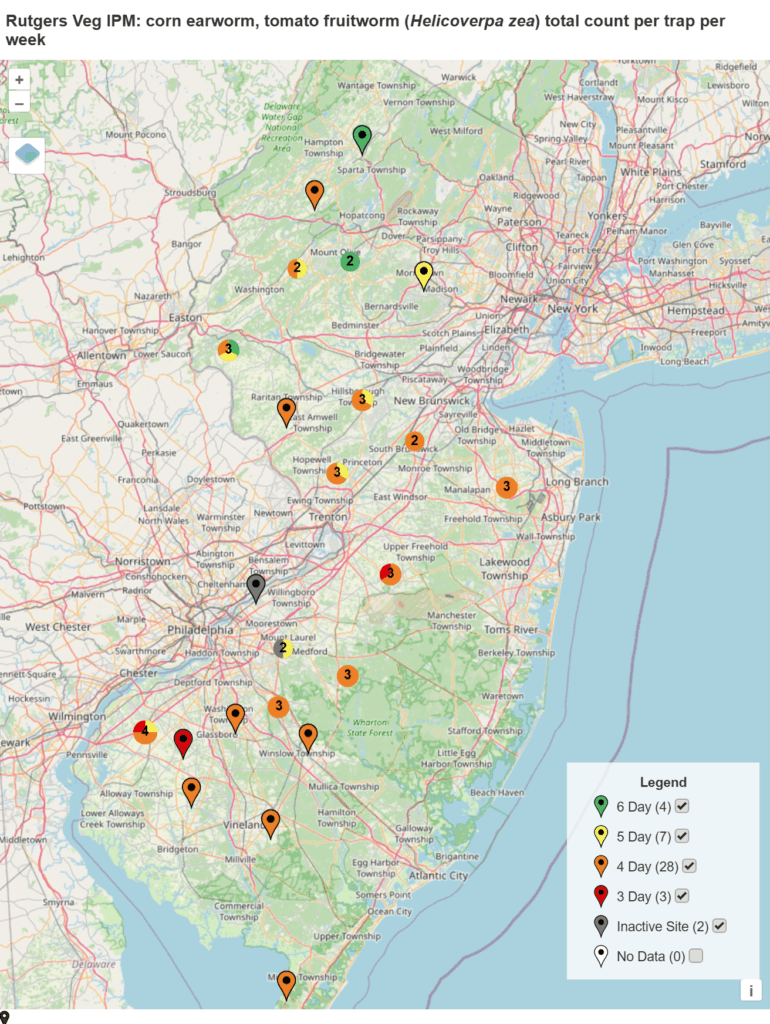
Spray intervals based on nightly pheromone moth captures for the southern part of New Jersey. Note that not all locations in the IPM program are currently trapping. This map is based on the following thresholds: 0 moths = 6-7 day schedule, 1 moth = 5 day spray schedule, 2-20 moths = 4 day spray schedule, 20+ moths = 3 day spray schedule
Tomatoes
Throughout New Jersey we’re continuing to see high thrips counts both in tunnels and in the field, although numbers have been higher in tunnels. We consider more than 5 thrips on 10 leaves a high count. Other guides suggest 3-5 thrips per flower or the presence of stippling damage on fruit to be a treatment threshold. Thrips management is especially important because of their ability to vector tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV), a growing concern in New Jersey where we have resistance-breaking strains. TSWV has already been seen on farms this season. Thrips management can be especially challenging in high tunnels due to a lack of products. Minecto Pro (IRAC 28 + 6) and Exirel (IRAC 28) can be used in tunnels, but only suppress thrips populations (this means they reduce numbers, but do not eradicate them). In the field, Entrust/Radiant (IRAC 5) can be used as well as Torac (IRAC 21A) and Harvanta (IRAC 28). We do not recommend pyrethroids or neonicotinoids for thrips due to resistance in different thrips species. Refer to the previous link for a complete list of best management practices for thrips and TSWV.
We’re also seeing limited aphid and spider mite activity. If dealing with primarily aphids, products such as Beleaf (IRAC 29) are recommended, especially if plants have reached the flowering stage. However, natural enemies often control aphids, so if counts are low and natural enemies like lacewings, lady beetles, or parasitoid wasps are present, you may avoid sprays. For spider mites, Nealta (IRAC 25) is an effective material that is more friendly to beneficial insects, but Portal (IRAC 21A) and other materials can be used to manage populations. Colorado potato beetles are especially prevalent in eggplants. Please consult the Mid-Atlantic Commercial Vegetable Production guide for appropriate materials for CPB control.

Thrips on a tomato leaf. Photo by Maria Cramer.
Cole Crops

Flea beetle surrounded by feeding damage. Picture by Maria Cramer.
Flea beetle activity seems to be slowing down some, but they are still active in some cole crops. This year, they have been especially prevalent in lacinato kale, Napa cabbage and bok choy. Young plants are especially vulnerable to attack from flea beetles. The treatment threshold for flea beetles in heading cole crops is 50% infestation.

Left: Diamondback moth caterpillar, showing characteristic tapering at each end. Right: Imported cabbageworm caterpillar showing characteristic fuzziness. Pictures by Maria Cramer.
We continue to see caterpillar activity in heading cole crops. Treatment thresholds vary between crops and growth stage, but for heading cole crops between early vegetative and cupping, the treatment threshold is 30%. As heads form, the treatment threshold goes down to just 5% infestation. For very small caterpillars, sprayable Bt products (IRAC 11A) such as Dipel, Xentari, or Javelin can be effective on young imported cabbage worm caterpillars. Other materials approved for caterpillar control include Entrust/Radiant (IRAC 5), Proclaim (IRAC 6), Torac (IRAC 21A), and Exirel (IRAC 28). Diamondback moth (the primary caterpillar found in southern NJ) has resistance to many insecticide groups, and pyrethroids (IRAC 3A) are not effective for their management. For Bt products and contact insecticides, coverage on the undersides the leaves is essential.
Diseases
With the heavy rainfall over the last week, conditions have been favorable for diseases to spread. We’re still seeing bacterial and fungal issues in tomatoes, but we have also started to see issues like Alternaria in cole crops. To prevent the spread of disease, avoid working fields when foliage is wet and continue to use resistant varieties when possible. In tunnels, leaf mold is becoming a prevalent problem as well. Be sure to vent the structure regularly to reduce humidity. Mural (FRAC 7 + 11) is labeled for greenhouse use.

Alternaria on broccoli. Photo by Amanda Quadrel

Photo showing leaf mold symptoms on the upper (A) and lower (B) surface of the leaves. Photo by Darcy Perehinys
As always, please consult the Mid-Atlantic Commercial Vegetable Production Guide for a more comprehensive list of materials that are labeled for specific crops and pests. As always, be sure to follow label rates and application instructions.
Thrips Active in Vegetable Crops
With higher temperatures increasing hatch times and spring grains like wheat and rye have drying down, thrips may be more prevalent in vegetable crops, especially when small grains are adjacent to vegetable fields. Thrips are very small and often missed if casually looking at a plant since they hide in blossoms, under sepals, on under sides of leaves and other protected areas on the stems, leaves and flowers. To scout for thrips, look at plant parts mentioned above. It is also important to dissect a flower, pulling back petals and sepals to find hiding thrips. It is difficult to see thrips with the naked eye. Therefore, the use of a hand lens will help.
Most adult thrips are elongate, slender, very small (less than 1/20 inch long), and have long fringes on the margins of both pairs of their long, narrow wings. Immature thrips (called larvae or nymphs) are oblong or slender and elongate and lack wings. Most thrips range in color from translucent white or yellowish to dark brown or black.
Females of most plant-feeding species lay their elongate, cylindrical to kidney-shaped eggs on or into leaves, buds, or other locations where larvae feed. Thrips have several generations (up to about eight) a year. When the weather is warm, the life cycle from egg to adult may be completed in as short a time as 2 weeks.
Thrips will feed on most all vegetable crops – solanaceous crops like eggplant, tomatoes, peppers, white potatoes, cucurbit crops like cucumber, squash and melons, bean crops, allium crops like onions, garlic and leeks and others. This is a photo I took last week of Thrips damage and slender yellow thrips on leaves in a tomato field in Gloucester County.
Thrips feeding on plants can damage fruit, leaves, and shoots and very noticeably affect plants’ appearance. Leaves may be speckled on the top surface from feeding on under sides of leaves by the insect’s sucking mouthparts. High populations often cause significant damage to leaves that may at first glance mimic a foliar disease, but upon closer examination is thrips damage. Damage to fruit, like tomatoes may not appear until fruit ripen and can be seen as gold flecks on red tomato fruit. For many thrips species, by the time their damage is seen, such as after flowers open or fruit forms, the thrips may no longer be present.
Once thrips are identified, control can be difficult when they are found in high numbers. Preventative measures like the use of row covers and reflective mulch have some success. Both conventional and organic insecticides labeled for thrips control can be found in the Rutgers Commercial Vegetable Production Recommendations guide under the sections for individual vegetable crops. Always read the pesticide label for instructions, safety precautions, application rates and restrictions. Since thrips hide in tight areas of plant parts it is important to have good coverage and penetration when applying insecticides to reduce the population of this hard to control pest.
For more detailed information about thrips see the Rutgers Fact Sheet https://njaes.rutgers.edu/pubs/publication.php?pid=FS291
