When: May 20 (Tue) 5:00 PM
Where: Autumn Lake Winery: 870 W Malaga Rd, Williamstown, NJ 08094
Pesticide Credits: CORE; PP2; 1A; 10
PROGRAM
Welcome and Updates
Hemant Gohil, Gloucester County Extension Agent, Rutgers NJAES
Mark Hernandez, Owner, Autumn Lake Winery
Field Observations from the Wine Grape IPM Pilot Program
Janine Spies, Statewide Fruit IPM Program Leader, Rutgers NJAES.
2025 Recommendations for Disease Management
Peter Oudemans, Extension Specialist, Small Fruit Pathology, Rutgers NJAES.
Record Keeping Update for 2025
George Hamilton, Extension Specialist in Pest Management, Rutgers NJAES.
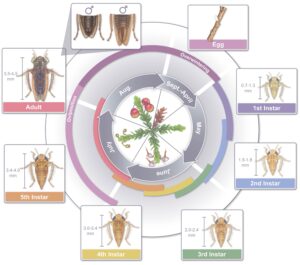
Grape Berry Moth in the Vineyard
Anne Nielsen, Extension Specialist in Fruit Entomology, Rutgers NJAES.
Crown Gall – Early Symptoms and Management
Hemant Gohil, Extension Agent, RCE of Gloucester County.
Grape Nutrition Update.
Gary Pavlis, Extension Agent, RCE of Atlantic County.
Pesticide recertification credits and adjourn.
Light fare will be provided. If you plan to attend, please email Joan Medany at jmedany@co.gloucester.nj.us or call 856-224-8030. For additional assistance, please get in touch with Hemant Gohil at 856-224-8029 before the meeting.