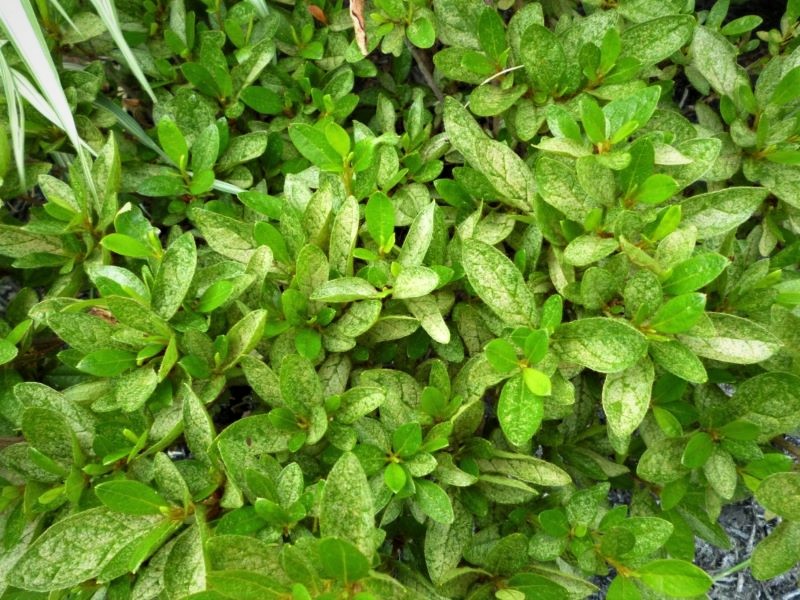
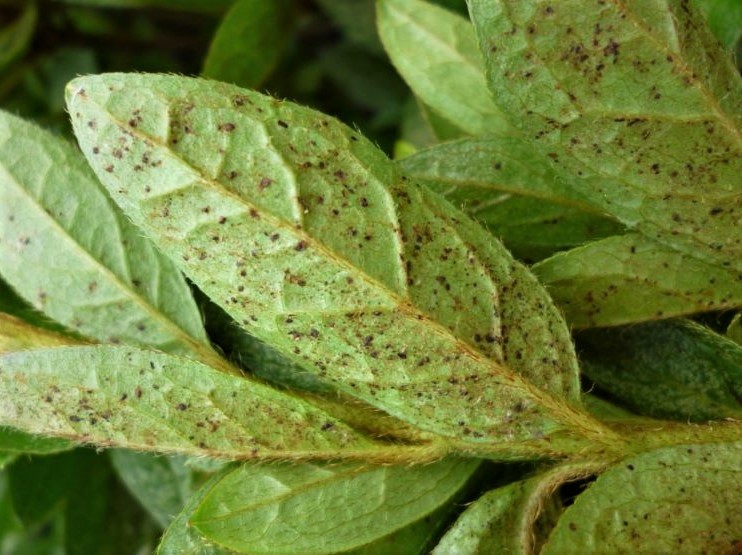
Based on our degree-day (DD) model for Sparganothis fruitworm, peak flight is expected at around 884 DD (see chart). As of June 22, Sparganothis fruitworm has accumulated 827 DD (using April 15 as biofix; a biofix more realistic to New Jersey practices). Based on the April 15 biofix, egg laying should have been initiated. However, I do not expect peak flight and those eggs to start hatching until mid-next week. Larval injury to fruit usually begins after the eggs hatch. If treatment is required (based on pheromone trap counts), sprays should be done 10-14 days after peak moth captures, ca. 7-11 July. If Sparganothis fruitworm pressure has been high, it may be advisable to treat 3 weeks after the moth flight began (i.e., around 1-4 July) and again 10 days later. When bees are present your option is to use an insect growth regulator such as Confirm or Intrepid. Our “standard” recommendation has been, however, to wait until bees are removed to apply an insecticide. Your post-bloom options include Altacor, Delegate, Exirel, or Intrepid. The timing of insecticide application is critical; so, if needed, do not wait too long to manage this pest.
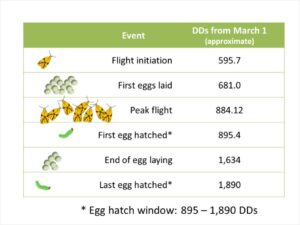
Degree-day model for Sparganothis fruitworm







