By Katarzyna Madalinska, Megan Muehlbauer, George Hamilton, and Anne L. Nielsen
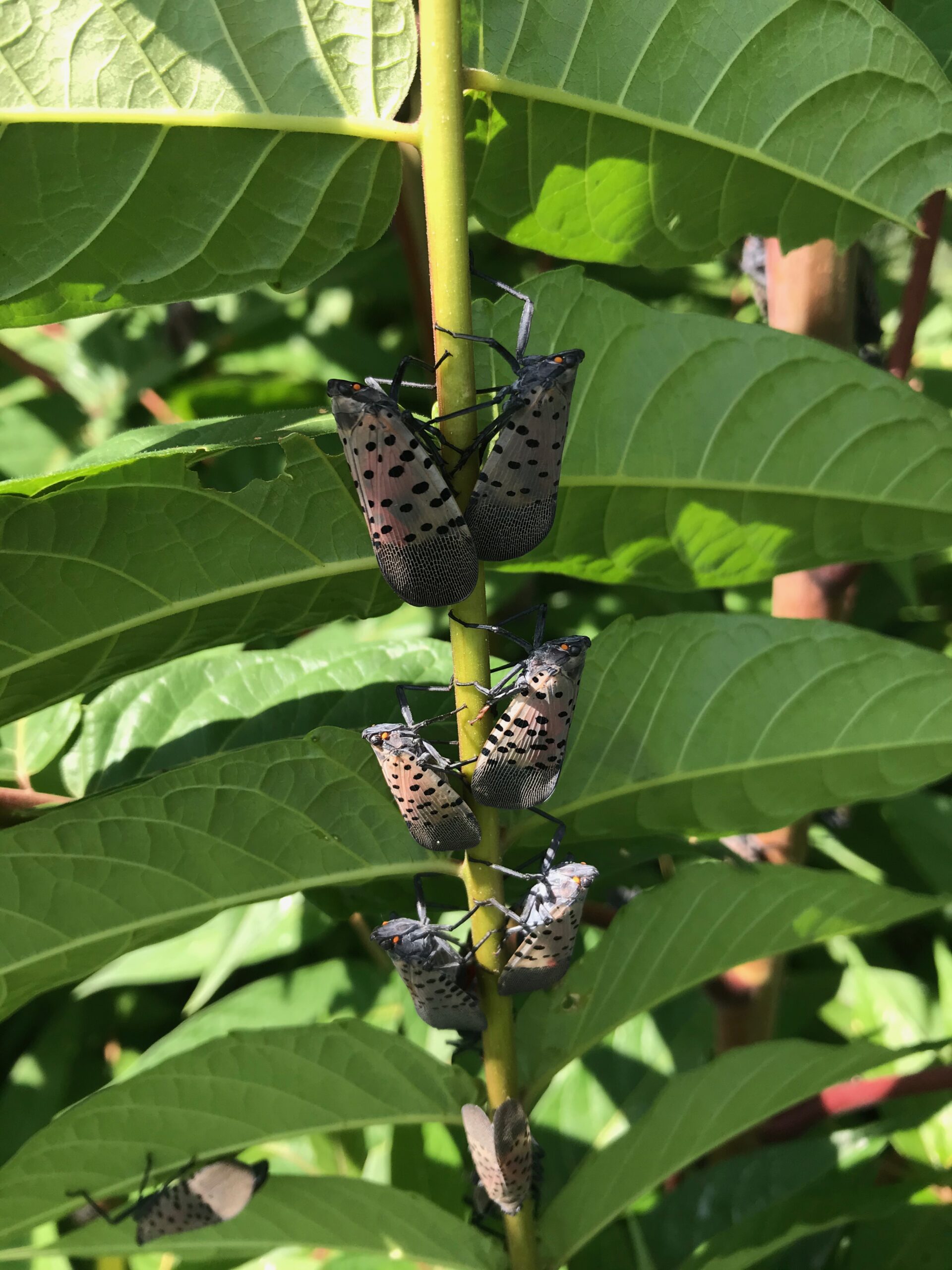

Spotted lanternfly adults congregating on tree of heaven
Spotted lanternfly was first found in northern NJ in 2018. Since then, populations are rapidly increasing and will substantially surpass those seen in 2019. Management of this pest is critical as we are still in the exponential growth phase of the population. There has been a 1300% increase in nymphs reported this year, which will most likely reflect higher numbers of adult SLF from previous years. This means that pressure from SLF adults will be felt more intensely by more vineyards this year.
The predominant life stage of the spotted lanternfly (SLF) seen across New Jersey during this time of year is the adult stage. That does not mean you will not see juveniles as well, which can appear black with white spots or their last juvenile stage which are red with black and white spots. The adult stage will be present until first frost.
Our current understanding of SLF adult behavior may aid in targeting management in vineyards. Right now, adult SLF are congregating in large numbers on hardwood trees along hedgerows or in bordering woods. It can be useful to identify one or a few spots around your vineyard where large numbers of SLF are feeding. One option for action at this time could be to target these trees with a backpack sprayer
using an insecticide labeled for SLF control as well as labeled for the tree species being treated. This is expected to decrease populations in general before they start reproducing but MAY not result in a decrease of pressure within the vineyard. While adults may be observed in the vineyard, right now SLF movement into the vineyard is minimal and is expected to dramatically increase in September and October. During the period of predicted peak SLF feeding within vineyards (September and October), the vines are storing carbohydrates for winter and excessive feeding by SLF can decrease winter hardiness by 1.5oC.
Movement into the vineyard will occur across several weeks and a strong edge effect will occur. However, SLF do not discriminate between vines that have been harvested or not. The treatment threshold used in South Korea is 10 SLF per vine, however, a more conservative threshold may be warranted to reduce populations and injury to the vines. If you can identify the more vulnerable parts of your vineyard you can target your insecticide application in those areas. The key is the application of an insecticide with long residual activity. There are several effective options for insecticide application (see Table 1).
Insecticides and their application rates are broken down in the table below. Be mindful of allowable uses and PHI when choosing an insecticide. After harvest there is more flexibility in insecticides available for application. We recommend the use of insecticides with a longer residual activity such as Bridgade post-harvest.
Table 1. Effectiveness of Insecticides Against Spotted Lanternfly Adults. SLF activity derived from PSU extension and Leach et al. Crop Protection 2019 v. 24 DOI:10.1016/j.cropro.2019.05.027
| Trade name | Rate per acre | Total Use | Systemic, Contact, Ingestion | PHI (days) | REI (hrs) | Days of activity | Labeled for SLF? | SLF activity |
| Malathion 8F | 1.88 pt | 1.88 pt | C, I | 3 | 36 | 3-7 | Yes, 2(ee) | Excellent |
| Baythroid XL | 2.4-3.2 oz | 12.8 | C, I | 3 | 12 | No | Good | |
| Scorpion 35SL | 5 fl oz (foliar) | 20.9 oz | S, C, I | 1 | 12 | <14 | Yes, 2(ee) | Exc. |
| Brigade 10WSB | 8-16 oz. | 16 oz | C, I | 30 | 12 | 21 | Yes, 2(ee) | Exc. |
| Mustang Maxx 0.8EC | 4 fl. oz. | 24 oz | C, I | 1 | 12 | <7 | Yes, 2(ee) | Good |
| Actara 25WDG | 3.5 oz | 7 oz. | S, C, I | 5 | 12 | <21 | Yes, 2(ee) | Exc. |
| Assail 30SG | 5.2 oz | 2/yr | S, C, I | 3 | 48 | 0 | Yes, 2(ee) on nymphs only | Good |
| Carbaryl 4L | 2 qt | 10 qt | C, I | 7 | 12 | <14 | No | Exc. |
| Avaunt 30DG | 6 oz | 2/yr | C, I | 7 | 12 | 0 | Yes, 2(ee) | Fair |
| Admire Pro | 1.4 fl oz | 2.8 oz | C, I | 0 | 12 | <7 | No | Good |
| Belay | 4-6 oz (foliar) | 1/yr | S, C, I | 0/30 | 12 | No | Good/Excellent | |
| Prepared by PennState with modifications by Anne Nielsen | ||||||||
There are several reasons to manage adult SLF in September and October during peak movement.
- Adults feed on the canes, cordon, and trunk of grape vines. Excessive feeding has been shown to lower winter hardiness by >1.5°C.
- SLF females lay egg masses in October. Killing females prior to egg laying will decrease population growth the following year.
In October, female SLF prefer to lay egg masses on a relatively smooth surface that is positioned horizontally. Within a vineyard, egg masses may be laid on posts, farm equipment, and the grape vines themselves. When looking for egg masses on your vines, be sure to examine any layers of peeling bark on the trunk or canes. However, if many egg masses are present in your vineyard, there are substantially more in any bordering wooded areas. Currently, we feel that management against the nymphs in the spring is more effective than targeting egg masses with an insecticide.
 When you’re working in the heat, safety comes first! With the OSHA-NIOSH Heat Safety Tool, you have vital safety information available whenever and wherever you need it – right on your mobile phone – for planning outdoor work activities based on how hot it feels throughout the day. Featuring real-time heat index and hourly forecasts, specific to your location, as well as occupational safety and health recommendations from OSHA and NIOSH.
When you’re working in the heat, safety comes first! With the OSHA-NIOSH Heat Safety Tool, you have vital safety information available whenever and wherever you need it – right on your mobile phone – for planning outdoor work activities based on how hot it feels throughout the day. Featuring real-time heat index and hourly forecasts, specific to your location, as well as occupational safety and health recommendations from OSHA and NIOSH.