Sweet Corn
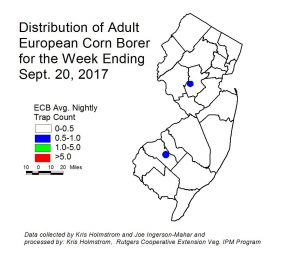 European corn borer (ECB) catches are still very low, but enough adults were caughted this week to register a map image. This pest is not much of a threat at this point, with most remaining plantings in silk. ECB feeding in less mature NJ sweet corn plantings is nearly non-existent now. Sprays for fall armyworm and corn earworm will manage any ECB larvae at this time. [Read more…]
European corn borer (ECB) catches are still very low, but enough adults were caughted this week to register a map image. This pest is not much of a threat at this point, with most remaining plantings in silk. ECB feeding in less mature NJ sweet corn plantings is nearly non-existent now. Sprays for fall armyworm and corn earworm will manage any ECB larvae at this time. [Read more…]
Veg IPM Update: Week Ending 9/20/17
Veg IPM Update: Week Ending 9/13/17
Sweet Corn
European corn borer (ECB) catches remain too low to register a map image. This flight has been extremely low and very spotty. ECB feeding in NJ sweet corn plantings is nearly non-existent now. What remains has been overshadowed by fall armyworm (FAW) feeding. Check 5 plants each in 10 random locations for a 50 plant sample. Look for “shot-hole” injury, and consider treating when the number of infested (from ECB or FAW) plants in a 50 plant sample exceeds 12%. Once plants hit full tassel, ECB larvae will move downward on the stalk and re-enter the plant near the area where ears are forming. This can result in direct injury to the ear. For growers who still have corn that has yet to silk, consider an insecticide application at the full tassel stage to target ECB larvae as they migrate downward. This application can eliminate larvae that have escaped any earlier insecticide applications. [Read more…]
Veg IPM Update: Week Ending 9/06/17
Sweet Corn
European corn borer (ECB) catches are very low, and with cooler evening temperatures through the weekend, not enough ECB have been captured to register a map image. This flight has been extremely low and very spotty. ECB feeding in NJ sweet corn plantings is nearly non-existent now. What remains has been overshadowed by fall armyworm (FAW) feeding. Check 5 plants each in 10 random locations for a 50 plant sample. Look for “shot-hole” injury, and consider treating when the number of infested (from ECB or FAW) plants in a 50 plant sample exceeds 12%. As infested plants proceed to the pre-tassel stage, live larvae and damage may be found in the emerging tassels. Once plants hit full tassel, ECB larvae will move downward on the stalk and re-enter the plant near the area where ears are forming. This can result in direct injury to the ear. Growers should consider an insecticide application at the full tassel stage to target ECB larvae as they migrate downward. This application can eliminate larvae that have escaped any earlier insecticide applications. [Read more…]
Veg IPM Update: Week Ending 8/30/17
Sweet Corn
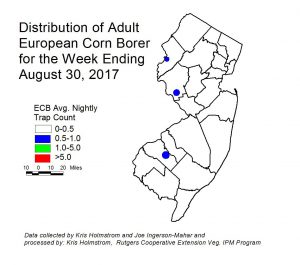 European corn borer (ECB) catches have remained very low, but blacklight traps have captured just enough to register a map image (see map at left). This flight has been extremely low and very spotty. ECB feeding in NJ sweet corn plantings remains very low, and has been largely obscured by fall armyworm (FAW) feeding. Check 5 plants each in 10 random locations for a 50 plant sample. Look for “shot-hole” injury, and consider treating when the number of infested (from ECB or FAW) plants in a 50 plant sample exceeds 12%. As infested plants proceed to the pre-tassel stage, live larvae and damage may be found in the emerging tassels. Once plants hit full tassel, ECB larvae will move downward on the stalk and re-enter the plant near the area where ears are forming. This can result in direct injury to the ear. Growers should consider an insecticide application at the full tassel stage to target ECB larvae as they migrate downward. This application can eliminate larvae that have escaped any earlier insecticide applications. [Read more…]
European corn borer (ECB) catches have remained very low, but blacklight traps have captured just enough to register a map image (see map at left). This flight has been extremely low and very spotty. ECB feeding in NJ sweet corn plantings remains very low, and has been largely obscured by fall armyworm (FAW) feeding. Check 5 plants each in 10 random locations for a 50 plant sample. Look for “shot-hole” injury, and consider treating when the number of infested (from ECB or FAW) plants in a 50 plant sample exceeds 12%. As infested plants proceed to the pre-tassel stage, live larvae and damage may be found in the emerging tassels. Once plants hit full tassel, ECB larvae will move downward on the stalk and re-enter the plant near the area where ears are forming. This can result in direct injury to the ear. Growers should consider an insecticide application at the full tassel stage to target ECB larvae as they migrate downward. This application can eliminate larvae that have escaped any earlier insecticide applications. [Read more…]
Veg IPM Update: Week Ending 8/23/17
Sweet Corn
European corn borer (ECB) catches have again declined to levels that do not permit a map image. This flight has been very sporadic. ECB feeding in NJ sweet corn plantings is very low, and has been largely obscured by fall armyworm (FAW) feeding. Check 5 plants each in 10 random locations for a 50 plant sample. Look for “shot-hole” injury, and consider treating when the number of infested (from ECB or FAW) plants in a 50 plant sample exceeds 12%. As infested plants proceed to the pre-tassel stage, live larvae and damage may be found in the emerging tassels. Once plants hit full tassel, ECB larvae will move downward on the stalk and re-enter the plant near the area where ears are forming. This can result in direct injury to the ear. Growers should consider an insecticide application at the full tassel stage to target ECB larvae as they migrate downward. This application can eliminate larvae that have escaped any earlier insecticide applications. [Read more…]
Veg IPM Update: Week Ending 8/16/17
Sweet Corn
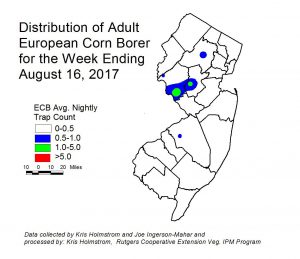 European corn borer (ECB) catches have been largely contained to Hunterdon and Somerset counties this past week (see ECB map at left). This flight has been very sporadic. ECB feeding in NJ sweet corn plantings is very low, and has been largely obscured by fall armyworm (FAW) feeding. Check 5 plants each in 10 random locations for a 50 plant sample. Look for “shot-hole” injury, and consider treating when the number of infested (from ECB or FAW) plants in a 50 plant sample exceeds 12%. As infested plants proceed to the pre-tassel stage, live larvae and damage may be found in the emerging tassels. Once plants hit full tassel, ECB larvae will move downward on the stalk and re-enter the plant near the area where ears are forming. This can result in direct injury to the ear. Growers should consider an insecticide application at the full tassel stage to target ECB larvae as they migrate downward. This application can eliminate larvae that have escaped any earlier insecticide applications. [Read more…]
European corn borer (ECB) catches have been largely contained to Hunterdon and Somerset counties this past week (see ECB map at left). This flight has been very sporadic. ECB feeding in NJ sweet corn plantings is very low, and has been largely obscured by fall armyworm (FAW) feeding. Check 5 plants each in 10 random locations for a 50 plant sample. Look for “shot-hole” injury, and consider treating when the number of infested (from ECB or FAW) plants in a 50 plant sample exceeds 12%. As infested plants proceed to the pre-tassel stage, live larvae and damage may be found in the emerging tassels. Once plants hit full tassel, ECB larvae will move downward on the stalk and re-enter the plant near the area where ears are forming. This can result in direct injury to the ear. Growers should consider an insecticide application at the full tassel stage to target ECB larvae as they migrate downward. This application can eliminate larvae that have escaped any earlier insecticide applications. [Read more…]
