Sweet Corn
Attention sweet corn growers! Please take a few moments to complete this survey. Rutgers IPM personnel expect to participate in grant funded research guided by grower responses. See the brief description below. Thank you for your help!
Corn Earworm Management in Sweet Corn Needs Assessment Survey
Dr. Kelly Hamby, Associate Professor/Extension Specialist with the Department of Entomology at University of Maryland, is leading a team of researchers, including Rutgers IPM staff, who have developed a survey to prioritize research and extension efforts for improving corn earworm management in sweet corn throughout the Northeast. We appreciate your participation in this survey and will use results to develop a grant proposal to try to get federal funding to address these needs.
Survey link: https://ume.qualtrics.com/jfe/form/SV_9vRh1xHnDp4KEaa
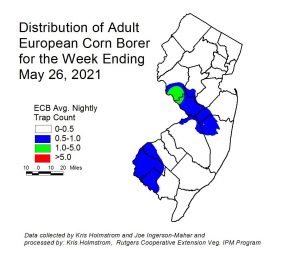
Low numbers of European corn borer (ECB) moths continue to be captured in parts of the state. Cool temperatures over the past weekend have likely suppressed activity, and warmer weather in the upcoming week may trigger a modest rebound. The highest adult activity is currently around the Atlantic-Camden County border (see map at right). Whorl corn is the primary target for egg laying, and injury as high as 16% of plants infested has been found up to northern Monmouth County this week. Feeding levels should rise over the next 3 weeks.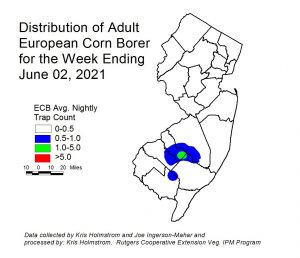
 Look for the characteristic “shot-hole” type of feeding (photo below at right) and consider treating when infested plants exceed 12% in a 50 plant sample. As plantings proceed to the pre-tassel stage, ECB larvae may be found in emerging tassels (see photo at left). It is a good idea to treat individual plantings as they move into the full tassel/first silk stage one time. This eliminates any ECB larvae that have emerged with the tassels as they begin to move down the stalk to re-enter near developing ears.
Look for the characteristic “shot-hole” type of feeding (photo below at right) and consider treating when infested plants exceed 12% in a 50 plant sample. As plantings proceed to the pre-tassel stage, ECB larvae may be found in emerging tassels (see photo at left). It is a good idea to treat individual plantings as they move into the full tassel/first silk stage one time. This eliminates any ECB larvae that have emerged with the tassels as they begin to move down the stalk to re-enter near developing ears.
Useful insecticides for this particular application include synthetic  pyrethroids (IRAC Grp 3), spinosyns (including OMRI approved Entrust) IRAC Grp 5), and diamides such as Coragen or Vantacor (IRAC Grp 28) or materials such as Besiege which include the active ingredient in Coragen. Synthetic pyrethroids alone should NOT be used for corn earworm (CEW) protection on silking corn. Control with these materials is very inconsistent.
pyrethroids (IRAC Grp 3), spinosyns (including OMRI approved Entrust) IRAC Grp 5), and diamides such as Coragen or Vantacor (IRAC Grp 28) or materials such as Besiege which include the active ingredient in Coragen. Synthetic pyrethroids alone should NOT be used for corn earworm (CEW) protection on silking corn. Control with these materials is very inconsistent.
The highest nightly trap catches of ECB for the week ending 6/02/21 are as follows:
| Elm 2 | Denville 1 | Pedricktown 1 |
| Asbury 1 | Medford 1 | Sergeantsville 1 |
| Clinton 1 | Milford 1 | Tabernacle 1 |
| Dayton 1 | New Egypt 1 | Woodstown 1 |
 Articles in this section contain information helpful to the NJ commercial organic grower.
Articles in this section contain information helpful to the NJ commercial organic grower.