Redroot and smooth pigweeds reproduce in abundance by seed which is easily transported across a farm. Using knowledge about the life cycle of this weed is important when making management decisions that require time and effort throughout a growing season. Learn more about non-herbicide management methods to control smooth and redroot pigweed populations on your farm by using the smooth and redroot pigweed decision tool fact sheet and a companion presentation. These resources are one of a five-part weed management series created by Extension Specialist Thierry Besancon and County Agricultural Agent Meredith Melendez, funded by USDA Specialty Crop Block Grant AM190100. You can provide feedback through an online survey about these resources.
Vegetable Crops Edition
Seasonal updates and alerts on insects, diseases, and weeds impacting vegetable crops. New Jersey Commercial Vegetable Production Recommendations updates between annual publication issues are included.
Subscriptions are available via EMAIL and RSS.
Quick Links:
 NJ Commercial Vegetable Production Recommendations
NJ Commercial Vegetable Production Recommendations
 Rutgers Weather Forecasting - Meteorological Information important to commercial agriculture.
Rutgers Weather Forecasting - Meteorological Information important to commercial agriculture.
Redroot and Smooth Pigweed: Non-Herbicide Management Options in Specialty Crops
Vegetable IPM Update 09/21/22
Sweet Corn
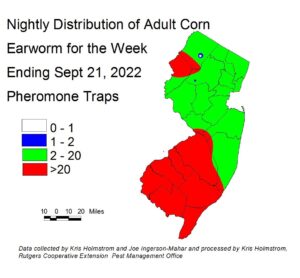
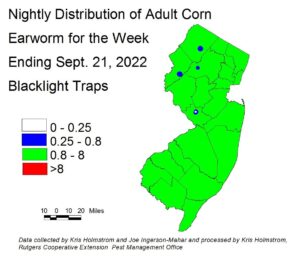 Corn earworm (CEW) moth captures from both blacklight traps and pheromone traps have declined significantly, with cooler night temperatures. Pheromone traps in northern Warren County and parts of Burlington County are highest at this time, although data from a number of southern sites is not currently available. Both trap types are in general agreement as to spray schedules. CEW populations can increase or decline with changes in night temperatures. Growers should be on alert for large CEW migrations should NJ experience tropical weather systems. Check this publication weekly for CEW status. The number of pheromone traps deployed is much lower, resulting in much broader color bands on the map. It is also important to understand that pheromone traps are more sensitive than blacklight traps, and thresholds are adjusted to account for the higher catches typical of this trap type. Remaining silking corn is at risk of CEW infestation at this time. On the blacklight map (left), green areas represent a 3-day silk spray schedule. On the pheromone map (below right), red represents a 3-day spray schedule, green represents a 4-day schedule. Be sure to access information from this publication in the upcoming weeks to determine how frequently you should treat silking sweet corn to protect it from CEW infestation.
Corn earworm (CEW) moth captures from both blacklight traps and pheromone traps have declined significantly, with cooler night temperatures. Pheromone traps in northern Warren County and parts of Burlington County are highest at this time, although data from a number of southern sites is not currently available. Both trap types are in general agreement as to spray schedules. CEW populations can increase or decline with changes in night temperatures. Growers should be on alert for large CEW migrations should NJ experience tropical weather systems. Check this publication weekly for CEW status. The number of pheromone traps deployed is much lower, resulting in much broader color bands on the map. It is also important to understand that pheromone traps are more sensitive than blacklight traps, and thresholds are adjusted to account for the higher catches typical of this trap type. Remaining silking corn is at risk of CEW infestation at this time. On the blacklight map (left), green areas represent a 3-day silk spray schedule. On the pheromone map (below right), red represents a 3-day spray schedule, green represents a 4-day schedule. Be sure to access information from this publication in the upcoming weeks to determine how frequently you should treat silking sweet corn to protect it from CEW infestation.
The highest nightly blacklight trap catches of CEW for the week ending 09/21/22 are as follows:
| Crosswicks 7 | Hackettstown 3 | Hillsborough 2 |
| Georgetown 5 | South Branch 3 | Long Valley 2 |
| Bellemeade 4 | Cinnaminson 2 | Medford 2 |
| Denville 4 | Dayton 2 | Old Bridge 2 |
The highest nightly pheromone trap catches of CEW for the week ending 09/21/22 are as follows:
| Allamuchy 46 | Farmingdale 10 |
| Georgetown 30 | Woodstown 9 |
| Folsom 28 | Dayton 4 |
| South Branch 21 | Matawan 4 |
Silking Spray Schedules*:
South – 3 days
Central – 3 days
North – 3 days
*These recommendations are based on regional catches. Adhere to tighter spray schedules if indicated by local trap catches. Synthetic pyrethroids alone should NOT be used for corn earworm (CEW) protection on silking corn, or for fall armyworm (FAW) management at any stage. Control with these materials is very inconsistent. Utilize materials in IRAC groups 5 and 28, or combination products that include IRAC group 28 for best control. See the Sweet Corn section of the 2020-21 Commercial Vegetable Production Guide for selections.
Fall armyworm (FAW) is less of an issue with dwindling whorl stage corn. Areas with extremely late plantings, especially along the bayshore and Atlantic coastal areas, may experience continued infestations. FAW can be tough to manage because it is resistant to synthetic pyrethroid insecticides (IRAC 3A) and because larvae are often covered by their own droppings, making contact with the insecticide more difficult. Treat when 12% or more plants exhibit FAW injury alone, or in combination with ECB injury. As a rule, insecticides that are most effective on CEW will also adequately control FAW.
Tomatoes
 Consideration should be given to protecting tomato plantings from CEW in tomatoes (called the fruitworm, when found in tomatoes). Larger populations locally, (>20 CEW/night) in local pheromone traps are a signal that growers should be inspecting tomato plantings at least weekly for signs of fruit injury. Typically, the female CEW moth lays eggs in blossom clusters near the outer canopy of the plant. Larvae hatching from these eggs begin feeding on the nearest fruit (photo at left), making damage very visible while walking the planting. At the first sign of this injury, growers should initiate control, with insecticides in the IRAC 5 and 28 classes most effective, with short PHIs. There are a number of effective insecticides listed in the Tomato Section from the 2022-23 Guide.
Consideration should be given to protecting tomato plantings from CEW in tomatoes (called the fruitworm, when found in tomatoes). Larger populations locally, (>20 CEW/night) in local pheromone traps are a signal that growers should be inspecting tomato plantings at least weekly for signs of fruit injury. Typically, the female CEW moth lays eggs in blossom clusters near the outer canopy of the plant. Larvae hatching from these eggs begin feeding on the nearest fruit (photo at left), making damage very visible while walking the planting. At the first sign of this injury, growers should initiate control, with insecticides in the IRAC 5 and 28 classes most effective, with short PHIs. There are a number of effective insecticides listed in the Tomato Section from the 2022-23 Guide.
Peppers
One additional farm has been found with pepper weevil in the Hammonton area. At one of the earlier infested farms, the weevil population seems to have exploded. This may be because the pheromone traps weren’t in that location of the field. The pheromone traps are the best monitoring tool that we have but placing them in a field is difficult. We try to visualize where vehicles would most likely be slowing down or stopping and set traps in those areas. Research conducted in the ’90s suggested that 10 traps be set per acre. On a practical scale, this is undoable. So while pheromone traps are very useful, they are not infallible.
Some farmers have expressed concerns about the lures on the traps that would lure the weevils into the fields. A pepper field is what the weevils are looking for. Once in the field, they may be attracted to the traps. When the first weevil is caught, we don’t know if this is the only weevil or represents some greater number of weevils.
The best control rotations for pepper weevil include Vydate, a neonicotinoid (Actara, Admire, Assail, others), a diamide (Exirel, Harvanta), and possibly Torac. University of Georgia researchers have found that all populations of pepper weevil that they have tested are resistant to pyrethroids. Since we don’t know where the weevils come from that we find here in New Jersey, farmers probably shouldn’t rely on pyrethroids being effective. Refer to the Rutgers Fact Sheet, FS1330: Monitoring and Management of Pepper Weevil in New Jersey (Rutgers NJAES) for more details on monitoring pepper weevil populations.
Beet armyworm adults (BAW) continue to be captured over the past week. Nightly counts include:
| Woodstown 57 |
| Jones Island 20 |
Growers in Gloucester, Salem and Cumberland counties should monitor pepper fields weekly for signs of feeding. BAW larvae (photo at left) feed in the developing foliage in terminal growth of plants. Initially, leaves are skeletonized, but as larvae grow, they will move onto fruit and damage these as well.  As with other armyworms, BAW is difficult to control with pyrethroid insecticides. Effective materials include spinosyns (IRAC 5) and diamides (IRAC 28).
As with other armyworms, BAW is difficult to control with pyrethroid insecticides. Effective materials include spinosyns (IRAC 5) and diamides (IRAC 28).
Pumpkins and Winter Squash
Cucurbit downy mildew (CDM) is active on cucumbers in all parts of the state, and has recently been discovered on summer squash, butternut squash and pumpkins in various counties. As of Tuesday 9/20, the CDM forecast was for low risk of new infection in all of NJ. Heavier dews and occasional rain events are conducive to local spread, so fields that appear to have minimal or no infection can become heavily infected quickly. For regional information on this important disease, see the Cucurbit Downy Mildew Forecast webpage: http://cdm.ipmpipe.org/. It is advisable for all growers treat preventively for CDM on all vine crops at this time.
With mature fruit present, growers should check at least weekly for the presence of striped cucumber beetles (photo at right). This pest, which is important early in the life of the plants, again becomes economically significant with maturing fruit, as it can scar the rinds of pumpkins and other squashes. If cucumber beetles are found at more than 2 sites in a 10 site sample, and any fruit injury is detected, an insecticide application to prevent further injury may be warranted. For useful materials, see the Pumpkin and Winter Squash section of the 2022-23 Commercial Guide. Populations of melon aphids are present in some pumpkin and winter squash fields (see photo below at left). This pest has the ability to increase to extremely high population levels in fields. When this happens, their sticky droppings are deposited on fruit below the canopy. Sooty  mold fungus grows on this sticky coating, disfiguring fruit. Additionally, hornets are attracted to the aphid droppings; creating a potential issue in U-pick situations. Check fields weekly for the presence of melon aphid colonies developing on the undersides of leaves. If aphids are found in more than one sample site/10 sites, consider an insecticide application to limit population spread. There are a number of effective materials listed in the Pumpkin and Winter Squash section of the 2022-23 Commercial Guide. Avoid pyrethroid insecticides for aphids or other insect pests, as these can cause aphids to increase.
mold fungus grows on this sticky coating, disfiguring fruit. Additionally, hornets are attracted to the aphid droppings; creating a potential issue in U-pick situations. Check fields weekly for the presence of melon aphid colonies developing on the undersides of leaves. If aphids are found in more than one sample site/10 sites, consider an insecticide application to limit population spread. There are a number of effective materials listed in the Pumpkin and Winter Squash section of the 2022-23 Commercial Guide. Avoid pyrethroid insecticides for aphids or other insect pests, as these can cause aphids to increase.
Cole Crops
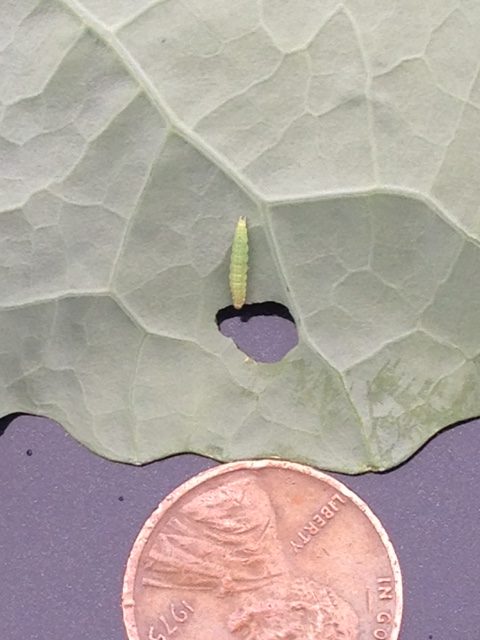 Diamondback moth larvae ((DBM) see photo at right) continues to be the dominant caterpillar pest in many cole crop plantings. This pest can multiply quickly, with a generation completed in under 2 weeks with high temperatures. Furthermore, it is apparent that this pest is not responding to chlorantraniliprole (Coragen) in many parts of the state. Effective materials continue to be IRAC 5 materials (spinosyns), other IRAC 28 products like Exirel, the IRAC 6 material, ememectin benzoate (Proclaim), and the carbamate (1A) Lannate. Lannate and Proclain have longer PHIs, so it is best to start with these if a DBM population is present. Transition to shorter PHI materials like the spinosyns or Exirel as harvest gets closer. Be sure to check the Cole Crops Section of the 2022-23 Commercial Guide for specifics, as PHI’s and crop labels vary. It is important to return to treated fields within 2-3 days to assess the efficacy of the insecticide applications. Effective materials should eliminate DBM larvae within 48 hours.
Diamondback moth larvae ((DBM) see photo at right) continues to be the dominant caterpillar pest in many cole crop plantings. This pest can multiply quickly, with a generation completed in under 2 weeks with high temperatures. Furthermore, it is apparent that this pest is not responding to chlorantraniliprole (Coragen) in many parts of the state. Effective materials continue to be IRAC 5 materials (spinosyns), other IRAC 28 products like Exirel, the IRAC 6 material, ememectin benzoate (Proclaim), and the carbamate (1A) Lannate. Lannate and Proclain have longer PHIs, so it is best to start with these if a DBM population is present. Transition to shorter PHI materials like the spinosyns or Exirel as harvest gets closer. Be sure to check the Cole Crops Section of the 2022-23 Commercial Guide for specifics, as PHI’s and crop labels vary. It is important to return to treated fields within 2-3 days to assess the efficacy of the insecticide applications. Effective materials should eliminate DBM larvae within 48 hours.
SARE Farmer Grants for 2023 – Webinar on October 4th
 Multiple Northeast SARE (Sustainable Agriculture Research and Education) grant recipient Tommye Lou Rafes, of T.L. Fruits and Vegetables in West Virginia, is sharing her experiences to help other farmers experiment with new ideas through the Farmer Grant program.
Multiple Northeast SARE (Sustainable Agriculture Research and Education) grant recipient Tommye Lou Rafes, of T.L. Fruits and Vegetables in West Virginia, is sharing her experiences to help other farmers experiment with new ideas through the Farmer Grant program.
At noon on October 4th, 2022, Rafes will join Northeast SARE Grant Coordinator Candice Huber for an informational webinar to assist farmers interested in applying for up to $30,000 in funding for projects beginning in March 2023. Registration is required and participants are encouraged to submit questions ahead of the event. The Call for Farmer Grant Proposals is currently available and the online system for submitting applications is opening soon. Applications are due November 15, 2022.
Northeast SARE Farmer Grants are perfect for farmers looking to grow through new practices. Rafes first learned about SARE while attending a Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) training. One of the professors hosting the meeting was a SARE reviewer who invited the attendees to apply for a grant. Rafes knew sustainable practices like using renewable-powered high tunnels to extend growing seasons could be good for business as well as the planet. “Growing in the winter months is a completely different way than you do in the summer months,” she said. “I decided to test varieties that were successful during the winter months as well as growing conditions that could be improved so that people would be more successful.”
Grant Coordinator Candice Huber says Farmer Grants are an opportunity for farmers to try things that could improve their operations. SARE funds can cover the farmer’s time on the project, any farm workers time spent on the project, supplies that are not capital purchase, technical support, soil testing and other budgeted items. Farmer grant projects generally are for one year.
If you have an idea and you need resources to really explore it, a Farmer Grant can connect you with those resources. This webinar will be a good starting point and participants must pre-register. See below.
To sign up for the October 4th webinar at 12:00PM go to https://us02web.zoom.us/webinar/register/6516611235851/WN_RoG_IkMmSDGsduZwmFgKkA
For information about the application for SARE Farmer grants see https://www.sare.org/wp-content/uploads/Northeast-SARE-Farmer-Grant-Call-for-Proposals.pdf
For general information about Northeast SARE go to Northeast SARE Home Page – SARE Northeast

Hairy Galinsoga: Non-Herbicide Management Options in Specialty Crops
Hairy galinsoga spreads throughout a farm by seeds that germinate quickly once exposed to light, with multiple generations in a growing season. Using knowledge about the life cycle of this weed is important when making management decisions that require time and effort throughout a growing season. Learn more about non-herbicide management methods to control hairy galinsoga populations on your farm by using the hairy galinsoga decision tool fact sheet and a companion presentation. These resources are one of a five-part weed management series created by Extension Specialist Thierry Besancon and County Agricultural Agent Meredith Melendez, funded by USDA Specialty Crop Block Grant AM190100. You can provide feedback through an online survey about these resources.
Cucurbit Downy Mildew Alert – 9/16/22 – Pumpkin and Butternut Squash
Cucurbit downy mildew has been confirmed on pumpkin and butternut squash in New Jersey. Cucurbit downy mildew was confirmed on summer squash in southern New Jersey a few weeks ago and cucumber earlier this season. Remember, some CDM isolates fall into Clade I which predominately infect watermelon, pumpkin, and squash, where other CDM isolates in Clade II predominately infect cucumber and cantaloupe. All cucurbit growers should scout on a regular basis and initiate a weekly CDM fungicide program.
For more information on CDM, the clades, and CDM control please click here.

Cucurbit downy mildew sporulating on the underside of an infected cucumber leaf.
Vegetable IPM Update 09/14/22
Note: Insect trap data are unavailable from much of southern New Jersey this past week due to staff shortages. No maps will appear in this edition. Maps will resume later in September as conditions permit. Interpretations from available data will continue in the absence of maps.
Sweet Corn
European corn borer (ECB) moth catches are nearly non-existent now. At this time, no feeding has been detected.