Populations of the cranberry toad bug, Phylloscelis rubra (Figure 1), have increased in the last week in some beds. In a recent study, we showed that even relatively low densities of this insect can cause significant injury to cranberries (Rodriguez-Saona et al. 2020. Characterizing the Feeding Injury Caused by Phylloscelis rubra (Hemiptera: Dictyopharidae) to Cranberries, Journal of Insect Science, 20 (6), 37, https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/ieaa143). Thus, monitoring for this insect from the end of July through mid-August is critical.

Figure 1. Cranberry toad bug
Life cycle. Cranberry toad bugs feed only on cranberries. This insect has a single generation per year (Figure 2). It overwinters as eggs. The nymphs appear by the end of June through early September, and the adults from end of July through October (harvest). Eggs are laid from end of August through October.
Damage. Feeding damage can be noticed in two stages. 1st-stage feeding damage on vines causes closing in (towards the branch) of the leaves on the new growth. 2nd-stage feeding causes changed in color (reddish to brown) of new growth. The damage can be seen from July until harvest. This damage will cause dying of the branch and the berries to shrivel up (Figure 3). Heavy infestation will result in dwarfed berries.
Management. To determine infestation, lightly sweep problematic beds (bugs should be easy to catch in sweep nets as they are very active). Currently there is no threshold established for this pest. Thus, insecticide applications should be based on the relative number of bugs per sweep compared with other sites and previous history of infestation. If needed, growers can use the following control options: Sevin 4F (broad-spectrum carbamate), Diazinon, Imidan 70W (broad-spectrum organophosphates), and Actara or Assail 30SG (neonicotinoid insecticides, effective against piercing-sucking insects). If infestation is high, treatments should be applied now (mid-August) for best control.

Figure 3. Cranberry toad bug injury
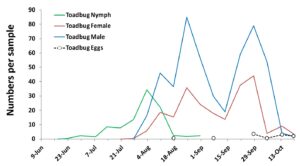
Figure 2. Cranberry toad bug phenology

