Cranberry beds are in bloom. If insects have been effectively managed prior to bloom, we recommend no sprays at this time. A reminder: when bees are present your only choices of insecticides are insect growth regulators (IGRs) such as Intrepid 2F or Bt products such as DiPel.
During bloom we recommend monitoring insect populations using pheromone traps. Pheromone traps should be used particularly to monitor activity of Sparganothis fruitworm and blackheaded fireworm, two key pests in New Jersey.
Sparganothis fruitworm- Adult flight started a few weeks ago and we should be at peak flight activity by next week (see DD model below). Damage by the second generation larvae begins after the eggs hatch, usually 9-12 days after they are laid. These larvae will feed on foliage and fruit. Larvae will partially feed on berries, causes scoring of the fruit. However, particularly on Ben Lear, larvae may feed inside the fruit. Insecticide treatment should target small larvae. Pheromone traps can be utilized to time insecticides sprays. If treatment is required, sprays should be applied two weeks after peak moth flight and/or earlier if using an IGR. If trap counts indicate a low population that requires management, a single insecticide application may be made post-bloom. If trap counts are high, then an early application of an IGR may be used when the first eggs start to hatch. This would be followed by a second application soon after bloom. Your post-bloom options are Diazinon, Altacor, Delegate, or Intrepid.
As indicated above, controlling fruitworm populations is often very difficult and many require multiple applications depending on pest pressure. Sparganothis fruitworm populations in Massachusetts are resistant to organophosphate insecticides (e.g. Diazinon, Lorsban). Thus, organophosphates should be used with care, i.e., always rotate insecticides with different modes of action. Organophosphate insecticides will also negatively affect natural enemy populations. Delegate and Altacor are insecticides belonging to relatively new modes of action; these are registered against fruitworms and can be used as an alternative to organophosphates post-bloom.
Degree-day model for Sparganothis fruitworm
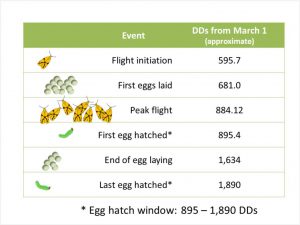
Sparganothis degree-day model benchmarks
The figure details life history benchmarks of interest for Sparganothis fruitworm and associated degree-day estimates from March 1. Flight initiation is predicted around 595 DD, at a lower temperature threshold of 50 °F. Based on this model Sparganothis fight was initiated in our region (Chatsworth, NJ) about a week ago. So far, we have accumulated (starting April 15) 763 DD, which means that egg laying has started (depending on the DD accumulations specific to your farm); however, eggs are not expected to hatch until later this month. Also, a reminder that a single insecticide application aimed at Sparganothis larvae will likely have the greatest effect if it is timed between the beginning and the peak egg-hatch/larval-emergence, which is approximately 895-1,400 DD. I will keep you updated on these DD predictions as the season progresses.

