Sweet Corn
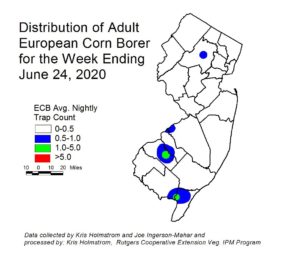
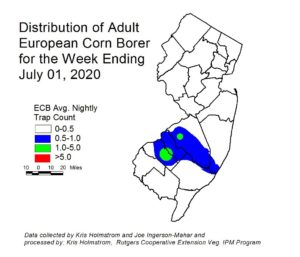 European corn borer (ECB) moth catches have remained steady at very low levels over the past week. At this time, activity is highest in Gloucester and Camden counties (see ECB map at left). Catches are widely dispersed. Above threshold (12%) larval infestations continue into the northern counties. Larval infestations should be expected to continue for another week or so.
European corn borer (ECB) moth catches have remained steady at very low levels over the past week. At this time, activity is highest in Gloucester and Camden counties (see ECB map at left). Catches are widely dispersed. Above threshold (12%) larval infestations continue into the northern counties. Larval infestations should be expected to continue for another week or so.
The highest nightly trap catches of ECB for the week ending 7/01/20 are as follows:
| Medford 2 | Elm 1 | Springdale 1 |
| Blairstown 1 | Long Valley 1 | Tabernacle 1 |
| Downer 1 | New Egypt 1 | |
| Eldora 1 | Port Colden 1 |
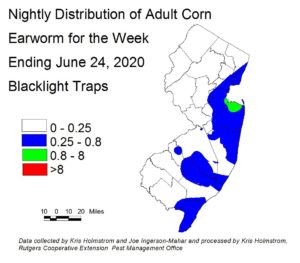
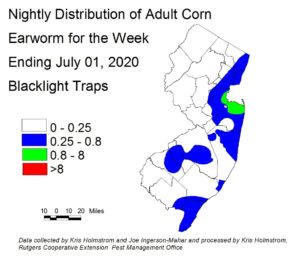 Corn earworm (CEW) moth captures stayed largely unchanged in blacklight traps this past week. This lingering population is somewhat heavier than normal for this time of year, and silking corn will need protection from this pest. Blacklight catches were highest overall along the coast (see map at left).
Corn earworm (CEW) moth captures stayed largely unchanged in blacklight traps this past week. This lingering population is somewhat heavier than normal for this time of year, and silking corn will need protection from this pest. Blacklight catches were highest overall along the coast (see map at left).
The highest nightly trap catches of CEW in black light traps for the week ending 7/01/20 are as follows:
| Matawan 4 | Eldora 1 | Pedricktown 1 |
| Allentown 1 | Elm 1 | Sergeantsville 1 |
| Cinnaminson 1 | Green Creek 1 | Springdale 1 |
| Downer 1 | Milltown 1 | Tabernacle 1 |
 Articles in this section contain information helpful to the NJ commercial organic grower.
Articles in this section contain information helpful to the NJ commercial organic grower.