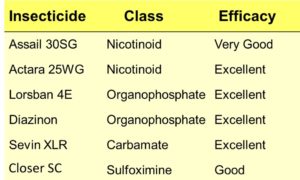
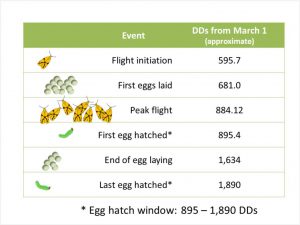
From early July through the first half of September, our attention turns to peach harvests. And for disease control, a great deal of focus is on preventing brown rot development in the ripening fruit. Failure to effectively manage brown rot during the first half of the harvest season can set you up for significant yield loss in the second half of the season, especially if rains become frequent. Infected, sporulating fruit from early maturing cultivars provides fuel (inoculum) for infection of the mid- and late-maturing cultivars. Remember, the harvest season is one big epidemic for brown rot.
This article is a continuation of my earlier article titled “Improving your early season peach brown rot control program” (plant-pest-advisorty.rutgers.edu, April 17, 2019). This former publication discussed blossom blight control as well as quiescent / latent infections occurring in young, green fruit. If you haven’t read this article, or forgot much of it, now is a good time to read or review it. I assume you followed the advice of the former article and therefore do not have significant latent infection lurking in your fruit!