Peach:
Oriental Fruit Moth (OFM): Overall, OFM trap captures have been low and treatments should be over for the third generation flight statewide. Additional treatments should be made if trap captures are over 6 moths per trap.
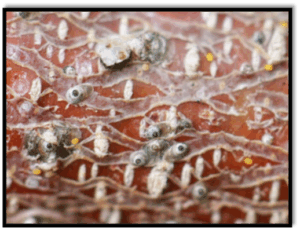
Scale Insects: Scale crawler emergence is past peak and declining. White Peach scale has a third generation in September and San Jose scale may have a third generation in October. Options at this point include Group 4A products labelled for scale including Assail, and the bioinsecticide Venerate. Venerate has a 0-day PHI, making it useful for blocks near or at harvest (Figure 1).

Figure 1. San Jose scale on apple.
Lesser Peachtree Borer (LPTB) and Peachtree Borer (PTB): Trap counts for borers have been high at several farms this season throughout the state (Figure 2). Where mating disruption is not being used, trunk sprays using pyrethroids can be applied early to mid-September followed by an additional application in mid to late September. Since this would be a labor intensive practice it would be most efficient to give priority to younger and most productive orchards. See the NJ Tree Fruit Production for effective materials and rates.

Figure 2. Lesser peachtree borer adult.
Apples and Pears:
Summer Diseases: Disease control is over for Early season apple varieties. Mid to late season varieties will need further applications on a two-week schedule until mid-September for sooty blotch and fly speck. See the NJ Tree Fruit Production guide for effective materials.
Brown Marmorated Stink Bugs (BMSB): Brown Marmorated Stink bug and native stinkbug populations have been low this season, although we have seen an increase in trap captures at some farms. If stinkbugs are a concern for your orchard, see the NJ Tree Fruit Production guide for effective materials.
Codling Moth (CM): Most orchards have very low CM pressure. Additional treatments should be made if trap captures are over 5 moths/trap.
Phenology Table: Based on annual observations made in Gloucester County.
| Pest Event or Growth Stage | Approximate Date | 2025 Observed Date |
| Bud Swell (Redhaven/PF-17) | March 23 +/- 15 Days | March 30 |
| 1/4″ Green Tip Red Delicious | March 31 +/- 13 Days | March 30 |
| Pink Peach (Redhaven/PF-17) | April 4 +/- 15 Days | April 1 |
| Tight Cluster Red Delicious | April 9 +/- 13 Days | April 5 |
| Full Bloom Peach (Redhaven/PF-17) | April 9 +/- 14 Days | April 10 |
| Pink Apple (Red Delicious) | April 14 +/- 12 Days | April 16 |
| Full Bloom Apple (Red Delicious) | April 22 +/- 11 Days | April 25 |
| Petal Fall (Redhaven) | April 22 +/- 10 Days | April 19 |
| Petal Fall (Red Delicious) | April 27 +/- 13 Days | May 2 |
| Shuck Split (Redhaven) | April 30 +/- 11 Days | April 26 |
| Pit Hardening | June 15 +/- 9 Days | June 15 |
Tree Fruit Trap Captures – Southern Counties
| Week Ending | STLM | TABM-A | CM | BMSB | OFM-A | DWB | OFM-P | TABM-P | LPTB | PTB |
| 4/5/2025 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/12/2025 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/21/2025 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 36 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/27/2025 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 5/2/2025 | 517 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
| 5/9/2025 | 159 | 4 | 10 | 0 | 3 | 16 | 5 | 4 | 46 | 0 |
| 5/16/2025 | 91 | 11 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 36 | 2 | 14 | 69 | 0 |
| 5/23/2025 | 299 | 21 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 23 | 1 | 26 | 23 | 0 |
| 5/30/2025 | 399 | 14 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 41 | 1 | 11 | 10 | 3 |
| 6/6/2025 | 733 | 13 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 36 | 2 | 12 | 29 | 1 |
| 6/13/2025 | 684 | 19 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 81 | 2 | 17 | 22 | 8 |
| 6/20/2025 | 724 | 24 | 2 | 0.5 | 1 | 60 | 1 | 23 | 19 | 12 |
| 6/27/2025 | 932 | 5 | 1 | 0.8 | 1 | 40 | 0 | 5 | 24 | 14 |
| 7/4/2025 | 643 | 0 | 0 | 0.75 | 1 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 16 |
| 7/11/2025 | 194 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 | 18 | 8 | 0 | 24 | 15 |
| 7/18/2025 | 190 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 16 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 12 |
| 7/25/2025 | 222 | 2 | 1 | 1.6 | 0 | 16 | 1 | 2 | 12 | 21 |
| 8/1/2025 | 450 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 24 | 2 | 1 | 21 | 18 |
| 8/8/2025 | 523 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 35 | 5 | 2 | 30 | 19 |
| 8/15/2025 | 595 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 37 | 1 | 2 | 32 | 15 |
| 8/22/2025 | 125 | 5 | 0 | 3.75 | 1 | 49 | 4 | 4 | 40 | 14 |
Tree Fruit Trap Captures – Northern Counties
| Week Ending | STLM | TABM-A | CM | BMSB | OFM-A | DWB | OFM-P | TABM-P | LPTB | PTB | AMBROSIA BEETLE |
| 4/5/2025 | 387 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/21/2025 | 435 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4/27/2025 | 26 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 72 |
| 5/2/2025 | 86 | 0 | 0.33 | 0 | 72.5 | 0 | 47.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 136 |
| 5/9/2025 | 56 | 0 | 5.3 | 0 | 58.8 | 0 | 22.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 145 |
| 5/16/2025 | 13.75 | 2.6 | 7.3 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50.5 |
| 5/23/2025 | 4.8 | 10.3 | 10.5 | 0 | 0.6 | 31.25 | 4.2 | 0 | 14.6 | 1 | 22.2 |
| 5/30/2025 | 2.2 | 4.8 | 1.8 | 0 | 0 | 12.4 | 9.6 | 0 | 9.6 | 1.9 | 22.1 |
| 6/6/2025 | 3 | 4.83 | 2.8 | 0.25 | 0 | 20 | 4.1 | 0 | 21.2 | 1.8 | 40.3 |
| 6/13/2025 | 65 | 20 | 11.4 | 0.6 | 0 | 12.3 | 4 | 0 | 10.5 | 1.5 | 59.2 |
| 6/20/2025 | 26 | 26 | 8 | 0.75 | 1 | 13 | 4.5 | 0 | 11 | 0.75 | 52 |
| 6/27/2025 | 145 | 19 | 6 | 1.3 | 6 | 35 | 5.4 | 0 | 16 | 1.6 | 38 |
| 7/4/2025 | 212 | 6 | 3 | 0.6 | 12.5 | 40 | 2 | 0 | 8.4 | 1.1 | 27 |
| 7/11/2025 | 125 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 0.14 | 5 | 41 | 3 | 0 | 20 | 4.5 | 48 |
| 7/18/2025 | 64 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.16 | 2 | 42 | 2 | 0 | 8.4 | 1.9 | 64 |
| 7/25/2025 | 110.5 | 0.4 | 2.3 | 0.24 | 7.5 | 44 | 4 | 0 | 6.8 | 12.2 | 69 |
| 8/1/2025 | 132 | 0.5 | 2.8 | 0.4 | 5.7 | 42.5 | 2.9 | 0 | 8 | 6.2 | 71.5 |
| 8/8/2025 | 157 | 1.9 | 0.6 | 0.41 | 6 | 27.8 | 8.3 | 0 | 10.8 | 5.5 | 78 |
| 8/15/2025 | 36.8 | 2 | 2.6 | 0.3 | 2.9 | 25.8 | 2 | 0 | 11.6 | 4.8 | 24 |
| 8/22/2025 | 25 | 6 | 1.4 | 0.05 | 1.6 | 40.4 | 7 | 0 | 18 | 4.8 | 67.6 |
Grape

Figure 3. Sour rot of grapes.
Disease management continues to focus on downy and powdery mildew and also bunch rots (Figure 3).
Downy mildew has been particularly prevalent this season in vineyards throughout the state. Refer to the NJ Commercial Grape Production Guide for information on control.

Figure 4. Spotted lanternfly on grapevine.
Grape Berry Moth: The timing for the third generation is past. In some hot summers a fourth generation may occur, however no further treatments should be needed, especially where insecticides are being applied for Spotted lanternfly and Spotted-wing drosophila.
Spotted Lanternfly (SLF): SLF adults are now appearing in vineyards in low numbers mostly on vineyard edges (Figure 4). As we move into September adult migration will increase and at that point growers should apply materials with long residual efficacy. More information on biology and control can be found from Penn State.
Blueberry
As we look to postharvest management in blueberries, the focus is on sharp-nosed leafhopper, scales, black shadow, and fall weed management. Sharp-nosed leafhopper and scale crawler numbers remain low but will continue to be monitored into September.
For weekly reports on blueberry pests and recommendations read the Rutgers Blueberry Bulletin.