Sweet Corn
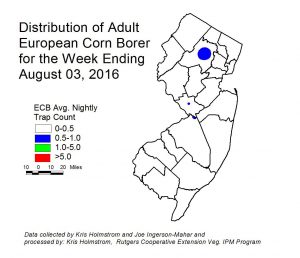 European corn borer (ECB) adult activity is stable at very low levels Areas of highest activity are in central Morris County (see ECB map). As always, consider treating when the number of infested plants in a 50 plant sample exceeds 12%. Any planting remaining at or above threshold as it proceeds to full tassel should be treated, as this is the last stage at which ECB larvae will be exposed and vulnerable to insecticidal sprays. See the 2016 Commercial Vegetable Recommendations Guide for insecticide choices.
European corn borer (ECB) adult activity is stable at very low levels Areas of highest activity are in central Morris County (see ECB map). As always, consider treating when the number of infested plants in a 50 plant sample exceeds 12%. Any planting remaining at or above threshold as it proceeds to full tassel should be treated, as this is the last stage at which ECB larvae will be exposed and vulnerable to insecticidal sprays. See the 2016 Commercial Vegetable Recommendations Guide for insecticide choices.




