Codling Moth (CM): Concern for internal worms, mostly codling moth, remains only for the latest varieties that ripen during October. Any grower with trap counts that exceed 5 moths per trap should still be treating for those latest varieties. Since we are either in or close to harvest, short PHI materials are important. CM effective materials with 7 (or less days PHI include: Altacor (5), Assail (7), Baythroid (7), Delegate (7), Exirel (3), Imidan (7), Leverage (7), Tombstone (7), and Madex (0, needs repeated applications).
Stink Bugs and Apples: BMSB populations continue to be more common, with a number of orchards showing trap counts above 10 bugs per trap per week and freshly damaged fruit. In northern counties BMSB counts average just over 9 bugs per trap with a high of over 40/trap. Continued protection is needed with effective materials that have short PHIs. If significant precipitation occurs after an application, then a reapplication is needed. This can be accomplished with toxicants, antifeedants and continued border spray strategies.
Border applications have been proven effective for a number of years. Since BMSB is a strong flyer and moves in (and out) of orchards especially late in the season, fresh toxicant materials applied to the border trees will kill BMSB when it first tries to enter the orchard. A border spray is defined as applying the insecticide in the last orchard row middle (both sides open), and along the outer border with the orchard side of the manifold on. See Figure 1 below (from Nielsen et al, 2018) Effective BMSB materials can either be toxicants or antifeedants. Our experience with border sprays has relied on the use of toxicants to kill the insects. Given the nature of BMSB and its movement, it is unlikely the antifeedants would work in border applications.
If the traps placed on an orchard border capture 10 or more bugs, or if BMSB feeding is present, then a broadcast application is required. Broadcast applications may be either toxicants or antifeedants. Antifeedants will not kill the insect, but will discourage and help prevent feeding and damage. Effective toxicants and antifeedants are listed below. Materials that can be used up to or within 7 days of harvest are highlighted in green. Venerate has a 2(ee) label for use within 7 days of harvest and during harvest.
| Material | Rate/A | Rating | PHI (days) | Toxicant vs Antifeedant |
| Actara | 5.5 oz | +++ | 35 | Toxicant |
| Admire Pro | 2.8 fl oz | +++ | 7 | Toxicant |
| Baythroid XL | 2.4 fl oz | +++ | 7 | Toxicant |
| Belay EC | 6-12 fl oz | ++++ | 7 | Toxicant |
| Besiege | 9-12 fl oz | +++ | 21 | Toxicant |
| Danitol | 16-21.3 fl oz | +++ | 14 | Toxicant |
| Declare (gamma cyhalothrin) | 1.02-2.05 fl oz | +++ | 21 | Toxicant |
| Endigo | 6 fl oz | ++++ | 35 | Toxicant |
| Lambda-Cy | 2.56-5.12 fl oz | +++ | 21 | Toxicant |
| Lannate LV or SP | 3 pt / 1 lb | +++ | 14 | Toxicant |
| Leverage 360 | 2.4-2.8 fl oz | +++ | 7 | Toxicant |
| Mustang Maxx | 4 fl oz | +++ | 14 | Toxicant |
| Proaxis (gamma cyhalothrin) | 2.56-5.12 fl oz | +++ | 14 | Toxicant |
| Tombstone (cyfluthrin) | 2.4-2.8 fl oz | +++ | 7 | Toxicant |
| Voliam Flexi | 7 oz | +++ | 35 | Toxicant |
| Warrior II | 1.28-2.56 fl oz | +++ | 21 | Toxicant |
| Closer SC | 5.75 fl oz | ++
+++ |
7
7 |
Toxicant
Antifeedant |
| Venerate XC | 4 qt | +++ | 0 | Antifeedant |
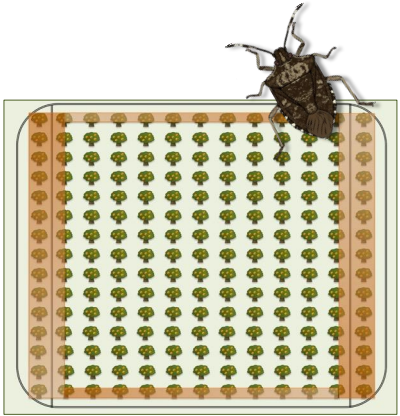
Figure 1. Diagram of the definition of a border spray.
Bitter Rot: Bitter rot infections have been occurring since June, but infected apples are becoming more visible. While the tendency might be to treat more intensively when you see the disease, this is not an optimal control strategy. That said, if the disease is still present on late varieties, then continued fungicide use is justified. Those materials that have a short preharvest interval and don’t leave an appreciable residue, that are effective for bitter rot include: Captan (0), Merivon (0), and Pristine (0).
Trap Counts – Southern Counties
| Week ending | STLM | TABM-A | CM | BMSB | OFM-A | DWB | OFM-P | TABM-P | LPTB | PTB |
| 4/11 | 1 | 7 | 0 | |||||||
| 4/18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 36 | 2 | |||||
| 4/25 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 5/2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |||
| 5/9 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 26 | 2 | 1 | 12 | |||
| 5/16 | 7 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | ||
| 5/23 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 3 | ||
| 5/30 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 3 | ||
| 6/6 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 9 | 13 | ||
| 6/13 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 6 | 2 | 0 | |
| 6/20 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| 6/27 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | |
| 7/4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| 7/11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7/18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 7/25 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.8 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 8/1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 1 |
| 8/8 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0.6 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 37 | 4 |
| 8/15 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 0.6 | 6 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 26 | 9 |
| 8/22 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0.1 | 4 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24 |
| 8/29 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1.0 | 5 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 29 | 7 |
| 9/5 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 38 | 5 |
Tree Fruit Trap Counts – Northern Counties
| Weekending | STLM | TABM-A | CM | BMSB | OFM-A | DWB | OBLR | OFM-P | TABM-P | LPTB | PTB |
| 4/11 | 0 | 0.7 | |||||||||
| 4/18 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | |||||||
| 4/25 | 2 | 0 | 0.7 | 0.7 | |||||||
| 5/2 | 5 | 0 | 1.8 | 1.2 | |||||||
| 5/9 | 5 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 36.7 | 10.1 | 0 | |||||
| 5/16 | 17 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 19.2 | 0 | 2.7 | 1 | 1.8 | 0 | ||
| 5/23 | 18 | 5.7 | 2.1 | 36 | 1 | 6.3 | 10.3 | 1.5 | 0 | ||
| 5/30 | 5 | 7.2 | 1.9 | 57 | 1 | 2.6 | 6.7 | 9.1 | 0 | ||
| 6/6 | 4 | 15.8 | 4.1 | 25.8 | 0 | 4.6 | 18 | 13 | 0.3 | ||
| 6/13 | 15 | 17.4 | 4.3 | 8 | 1.3 | 9.5 | 3.4 | 20.6 | 21.8 | 0 | |
| 6/20 | 16 | 33.8 | 4.8 | 9.8 | 0 | 9 | 1.2 | 34.1 | 8.3 | 0 | |
| 6/27 | 20 | 10.9 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 9.8 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 12.7 | 5.8 | 0.3 |
| 7/4 | 18 | 5.8 | 0.7 | 2.5 | 9.4 | 0 | 0 | 1.5 | 9.3 | 3.8 | 2.5 |
| 7/11 | 14 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 1.9 | 14.3 | 0 | 0 | 2.4 | 4.3 | 5.1 | 1.5 |
| 7/18 | 11 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 3.4 | 0.5 | 1 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 3.8 |
| 7/25 | 32 | 1.3 | 3.5 | 3.4 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 0 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 2.6 | 0 |
| 8/1 | 23 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 3.3 | 5.6 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 0 |
| 8/8 | 15 | 2.2 | 2.8 | 1.8 | 4.3 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 1.9 | 0.6 | 1.0 | 5.8 |
| 8/15 | 13 | 1.0 | 2.6 | 4.4 | 2.7 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 3.5 | 1.5 | 5.0 | 3.8 |
| 8/22 | 7 | 2.5 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 7.3 | 0.6 | 0 | 4.8 | 1.3 | 2.1 | 0.5 |
| 8/29 | 7 | 3.2 | 2 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 0.4 | 0 | 2.5 | 3 | 6.4 | 1.5 |
| 9/5 | 6 | 6.3 | 0.8 | 9.1 | 5.3 | 0 | 0 | 1.5 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
Blueberry:
Sharpnosed Leafhopper (SNLH): The second generation of adult sharpnosed leafhoppers has started. Since it is the adult stage that has wings, this is the motile form that can readily move from bush to bush as it feeds and transmits blueberry stunt disease. See last week’s newsletter for more on SNLH biology. The most effective treatments include: Actara, Assail, Admire and other imidacloprids, Lannate, and malathion. Several newer insecticide materials are also registered in blueberries, but do not yet have enough efficacy data on SNLH to merit recommendations at this time.
| Blueberry Trap Counts | ||||||||||||
| Week Ending | SNLH – AC | SNLH-BC | BBM-AC | BBM-BC | Scale-AC | Scale-BC | ||||||
| Avg | Max | Avg | Max | Avg | Max | Avg | Max | Avg | Max | Avg | Max | |
| 6/27 | 0.14 | 3 | 0.8 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 7/4 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.8 | 5 | 0.009 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 7/11 | 0.12 | 1 | 1.82 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 7/18 | 0.11 | 2 | 1.16 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 7/25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 8/1 | 0.04 | 1 | 0.3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 8/8 | 0.152 | 3 | 0.14 | 2 | 0.03 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 9.25 | 57 | 0.5 | 1 |
| 8/15 | 0.37 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27 | 89 | 9 | 18 |
| 8/22 | 0.08 | 2 | 0.07 | 1 | . | . | . | . | 20.6 | 73 | 7 | 14 |
| 8/29 | 0.2 | 3 | 0.21 | 3 | . | . | . | . | 18.3 | 74 | 6.5 | 13 |
| 9/5 | 0.75 | 5 | 2 | 8 | . | . | . | . | 8.3 | 30 | 2.5 | 3 |
| Key: PC=plum curculio, Scale=Putnam scale, CBFW=cranberry fruitworm, SWD=spotted wing drosophila, OB=oriental beetle, SNLH-sharpnosed leafhopper, BBM=blueberry maggot, BC=Burlington County, AC=Atlantic County | ||||||||||||

